Could Not Be Performed Because of an I/O Device Error, What to Do?
The Scenario
When backing up to an external hard drive on Windows Server 2003/2008/2012 (R2)/SBS 2003/2008/2011 or Windows 10/8.1/8/7/XP/Vista, you may encounter error messages during the backup process. These errors can occur due to various reasons such as disk space issues, file system corruption, or problems with the external hard drive itself.
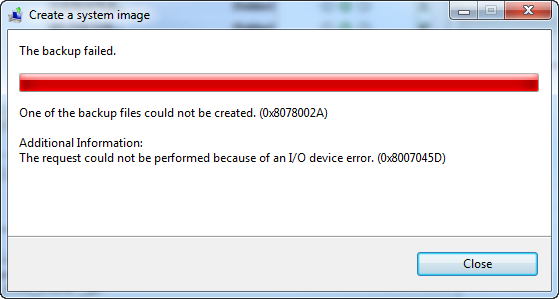
- One of the backup files could not be created. (0x8078002A)
- The request could not be performed because of an I/O device error (0x8007045D) or (2147943517)
- Both error codes 2147943517, in decimal, and 0x8007045D, in hexadecimal, represent the same I/O device error.
Possible Causes for I/O Device Error
- If the backup process has been ongoing for an extended period, it's likely that there are bad sectors on either the source disk or the destination disk. This can cause the backup process to stall or fail.
- If the backup is almost complete and an error occurs, it's possible that the last cluster on the volume has become corrupted. This can prevent the backup from finishing successfully.
- If you back up to a large drive with a 4K sector size, instead of the 512-byte sector size commonly used in smaller HDDs, you may encounter an I/O error 0x8007045d when using the backup and restore tool on older Windows versions, which rely on the standard file format that assumes 512-byte sectors.
Resolutions to Hard Drive I/O Device Error
To fix the hard drive I/O device error, you can try one or more of the following steps. First, restart your computer to see if the issue resolves itself.
Close other software
To troubleshoot an I/O device error when running a backup utility, you can try closing all non-system processes, disabling antivirus software temporarily, or booting your computer into safe mode to minimize the impact of third-party applications. This may resolve the issue and allow the backup to complete successfully.
Check and fix bad sector
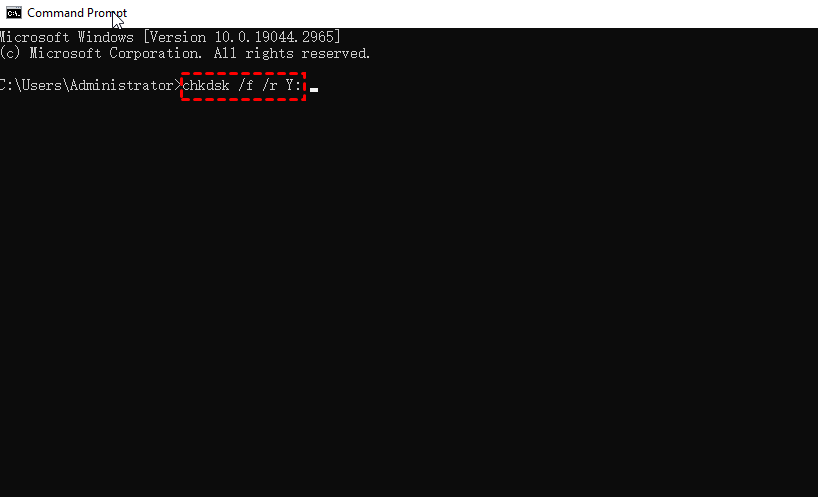
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box, type "cmd" in the box, and press Enter. Run it as an administrator.
2. To run a disk check on a specific drive, open the Command Prompt, type "chkdsk X: /f /r" (where "X" is the drive letter you want to check), and press Enter. This command will check the drive for errors, fix them, locate bad sectors, and attempt to recover readable information.
3. After the process is finished, reboot the system and retry the backup task.
Resize the partition
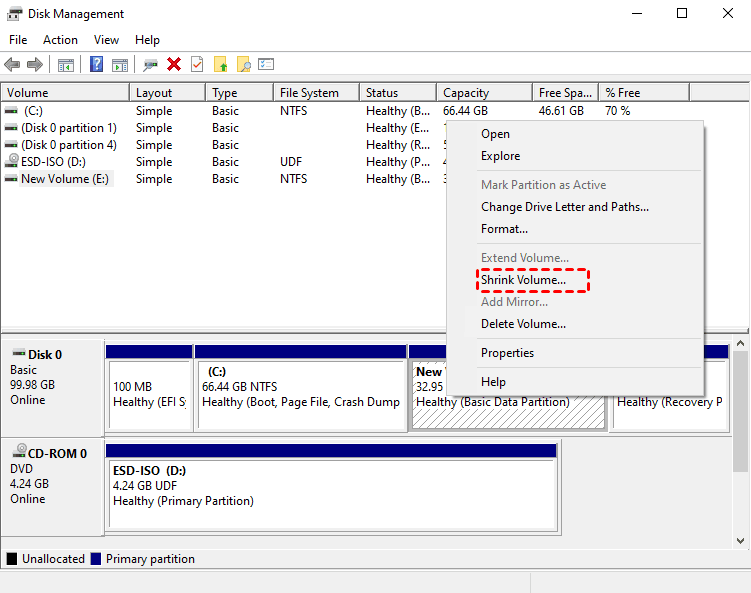
To resolve the issue with the last cluster of the partition not being allocated, you can try shrinking or extending the partition to move the last cluster to a new location. This can be done through the Disk Management tool in Windows, where you right-click the partition you want to adjust and select "Shrink Volume". Alternatively, you can use third-party software to resize the partition without losing any data. After making these adjustments, running the "chkdsk" command again may help resolve the issue.
Format to factory default
Format your hard disk drive to Factory Default with WD Quick Formatter tool and retry. Note that formatting will wipe out all data and make it unrecognizable in Windows XP, so backup your hard drive if it contains valuable data.
Check physical sectorsize
If the issue persists after trying the previous steps, it's likely that your hard drive is an advanced format (4K) disk. In this case, you may need to consider replacing the hard drive with a new one or upgrading your Windows operating system to resolve the problem caused by an I/O device error.
4K disks come in two types: 512-byte emulation (512e), which reports 512-byte sectors but has 4KB physical sectors, and 4 KB native, which has both 4KB logical and physical sectors.
Advanced format (4K) disk with 512-byte emulation is supported on Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, Windows 7 with MS KB 982018, Windows 7 SP1, Windows Server 2008 R2 with MS KB 982018, Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1, Windows Vista with MS KB 2553708, and Windows Server 2008 with MS KB 2553708.
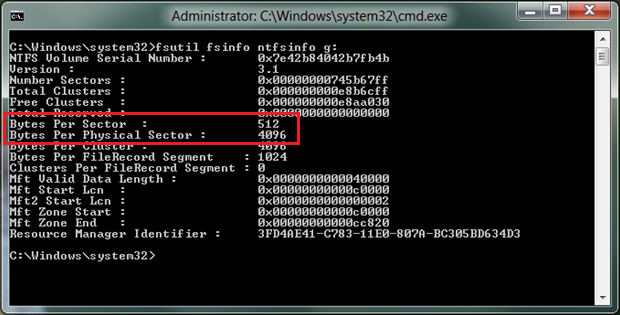
To get the physical and logical sector size, run "fsutil fsinfo ntfsinfo" in an elevated command prompt, which will show whether the disk is a 4K disk with 512-byte emulation, a 4 KB native disk, or if the driver doesn't support IOCTL_STORAGE_QUERY_PROPERTY.
If you're still getting the error "the request could not be performed because of an I/O device error", you can try using third-party free backup software or upgrade your system. This issue is supported on Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows Server 2012 (R2) and Windows 2016.
Related Articles
- What Is I/O Device Error and How to Fix It on Windows
On this page, you will get to know what is I/O error and how to fix I/O device error on your Windows computer. Continue reading for further information about it. - Windows 10 Backup 0 Bytes? Get Clear Ideas Here!
Are you confused with Windows 10 backup 0 bytes problem? Get clear ideas from this article. - (Fixed) 4 Solutions to Acer eRecovery Management Restore Failed
This essay will gather several common situations with acer erecovery management restore failed problem and give some solutions. - Can I Use a USB Flash Drive to Backup My Computer? [Answered with Details]
Can I use a USB flash drive to back up my computer? Have you ever been stuck on this question? This article will describe whether you can back up your computer to a USB drive and offer a backup tool named Qiling Disk Master to help you.