Incremental and Differential Backup
Qiling Disk Master allows for different backup types, including full, incremental, and differential backups. A full backup is typically performed first to ensure complete data and system backup. Incremental and differential backups are then necessary to optimize the backup process and save storage space. This optimizes the backup process and saves storage space. Incremental and differential backups are essential to optimize the backup process and save storage space.
Backup efficiency: Full backups back up the entire data set, while incremental and differential backups only back up the changes since the last backup, making them faster and more efficient, especially for large data sets.
Storage space savings: Using incremental or differential backups instead of full backups can help conserve storage space, especially for large data sets, allowing the backup device to last longer.
Backup frequency and flexibility: Incremental and differential backups allow for more frequent backups to capture smaller changes in data, providing finer granularity in restoration to earlier time points. The frequency of these backups can be chosen based on the importance and rate of data changes.
Run full, incremental, or differential backups in Windows 10
Qiling Disk Master supports both incremental and differential backups, allowing users to select the most suitable method based on their specific needs, thereby optimizing the backup process in terms of efficiency and storage utilization.
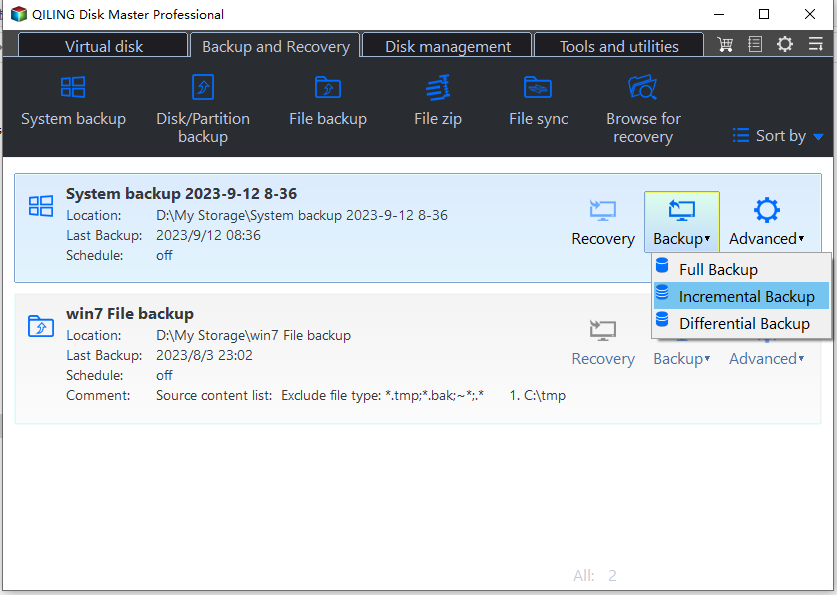
1. Manually run full, incremental, or differential backups
Once you have created a backup task, you can select the backup method from the Backup Management window. By hovering over the task and clicking the 3 lines icon, you can choose between Full Backup, Incremental Backup, and Differential Backup. A Full Backup creates a complete copy of your data, while an Incremental Backup only saves changes made since the last backup. A Differential Backup, on the other hand, saves all changes made since the last Full Backup, allowing you to restore your data to any point in time. This selection will help you determine which backup method is best suited for your needs.
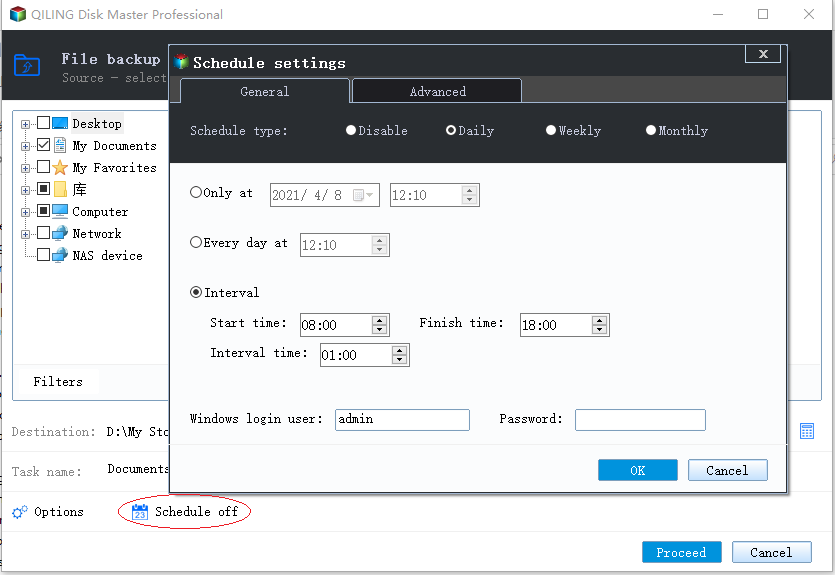
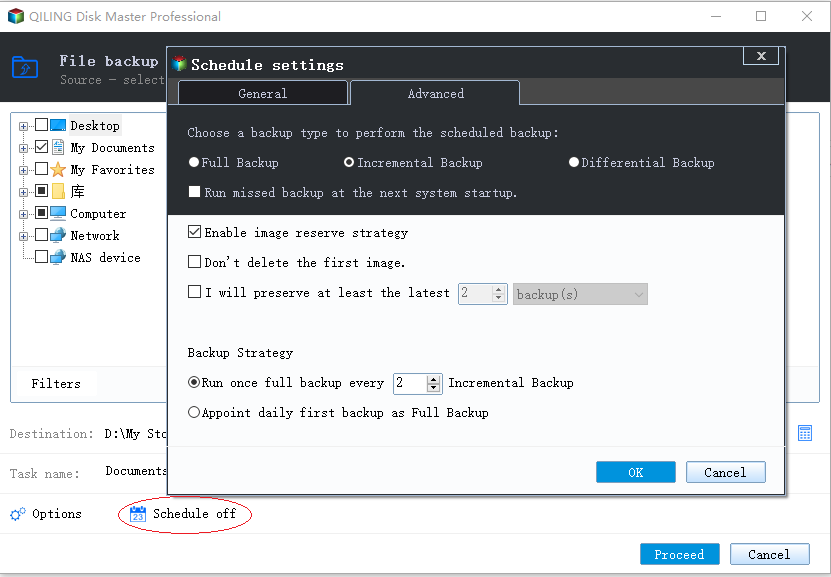
2. Create scheduled full, incremental, or differential backups
To create a scheduled full, differential, or incremental backup, follow the steps to create a scheduled backup.
The Backup Scheme tab in the Schedule window allows you to configure the backup method as full, differential, or incremental, which determines the type of backup the program will run according to the schedule.
Tips: For detailed backup steps, please refer to the article "How to Do Incremental and Differential Backup" for further information.
What is Full, Incremental and Differential Backup?
A full backup captures all data on selected folders, partitions, or hard disks at the time of backup and saves it as an image file, serving as the basis for incremental and differential backups, and can be used to restore all files and folders to their state at the time of image creation.
After performing a Full backup, you can create Incremental and Differential backups, which are significantly quicker and smaller in size compared to a Full backup of the same data.
An incremental backup captures only the changes made since the last backup, saving time and storage space by not duplicating unchanged data.
A full backup is required to start a series of incremental backups, which are taken in sequence over time. If any incremental backup is damaged or missing, the subsequent ones will be invalid, but the data can still be recovered to the state of the last complete backup.
A differential backup is related to its originating full backup and backs up all data added or changed since then, requiring less time and storage space than a full backup. If a differential backup image becomes damaged or lost, it won't affect others, and all data can be restored to the state when the differential backup was done.
Differential backups become progressively larger if many changes are made between backups, as each one contains more changes made since the last full backup. This approach costs more time and requires more disk space compared to incremental backups, but is more robust in terms of being able to restore when preceding differential backups are damaged or missing.
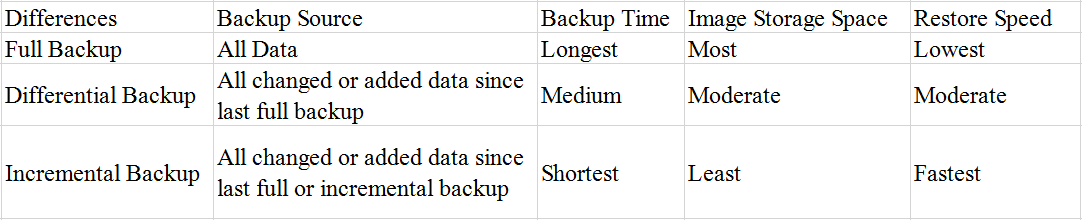
Differences among Full, Differential and Incremental Backup
The main differences between Google Drive and iCloud lie in their backup sources, backup times, image storage, and restore speeds. A table comparing these features is available.
How to restore an incremental or differential backup image
Before restoring an incremental or differential backup image, ensure that all image files, including full, incremental, and differential backups, are located in the same directory.
To restore an incremental or differential backup, simply select the corresponding backup version, which will restore the system to its state at the time of the incremental or differential backup creation, without needing to select the full backup or other incremental/differential backups. For example, restoring incremental backup 3 will restore the system to its state at the time of creating backup 3.
Tips: This also applies to the differential backup restore.
Which to choose, Full, Differential, or Incremental Backup?
With the descriptions above, you might have found out that the method of "Full Backup + Incremental Backup" or "Full Backup + Differential Backup" would be more convenient than a single full backup, allowing you to efficiently manage changed and newly added data and files.
The "Full Backup +Incremental Backup" method is more efficient for regular backups, as it only deals with changed files since the last full/incremental backup. It requires less time and storage space compared to the "Full Backup + Differential Backup" method, which is more resilient to the loss of a differential backup file but requires more resources.
Notes:
- If any one of the incremental image files in the sequence is damaged or missing, the subsequent image files will be invalid, rendering the entire sequence useless.
- A full backup must exist as the starting point for a series of incremental backups or differential backups.
- If you want to create an incremental or differential backup, you need to create a new backup task first, which will run as a full backup by default.
Conclusion
Using a combination of full, incremental, and differential backups can offer flexibility, time efficiency, and storage space efficiency. Full backups provide the most comprehensive data and system recovery, while incremental and differential backups can save time and storage space with each backup. By choosing the right backup strategy, you can balance backup speed, storage requirements, and data recovery needs to suit your needs and resource constraints.
FAQs:
Q: When you set to perform a differential backup, but it prompts: The volume configuration has changed, so now is executing a full backup.
A: Please run the backup task again to check if it will start to perform the differential backup. If you still get the same situation, please try to contact our Qiling Support Team and attach the log folder under the installation directory of Qiling Disk Master to further analyze this issue.
Q: When you run an incremental/differential backup, does it actually run a full backup?
A: If there is no full backup in the destination, or the full backup is damaged, a new full backup will need to be run.
Q: It shows Information code 4105/21: Not enough memory to process this command when you run an incremental backup.
A: To manage a large number of incremental backup versions, perform a full backup regularly and then continue with incremental backups based on the new full backup. This helps maintain a manageable backup history and ensures you can recover data effectively.
Related Articles
- Solve Acronis True Image for Crucial Clone Failed Easily(2 Ways)
The article provides 2 easy ways to fix Acronis True Image for Crucial clone failed. You can use Acronis to create bootable rescue media or use professional disk cloning software - Qiling Disk Master. - 4K Alignment: Align SSD after Clone in Windows 11, 10, 8, 7
You'll learn to align SSD after clone in this post with a secure and powerful tool. - Unspecified Error During System Restore 0x80070002 - Fixed!
This tutorial shows how to fix an unspecified error occurred during System Restore 0x80070002 and provides an easier way to perform system backup and restore in Windows. - Automatic USB Backup Portable for Windows 10
In need of best automatic USB backup portable for Windows to backup, restore, sync or clone? Read this article and get all you need to know.