Cold Clone V.S. Hot Clone-Differences between Hot and Cold Cloning
Cold clone V.S. hot clone
When buying a new disk, users can clone their current disk or perform an OS migration to avoid reinstalling the system, making the transition smoother and more efficient.
But, do you know there are different types of cloning?
There are two types of cloning: cold cloning and hot cloning. A brief introduction to these methods and their differences is in order. Both types involve creating a copy of a machine, but they differ in the approach taken.
▶ About cold cloning
Cold clone, also known as cold migration, is the process of migrating a computer to another node while it is shut down, requiring a restart to complete the migration.
With cold migration, you can optionally move associated disks from one data device to another, requiring a reboot to work.
▶ About hot cloning
Hot cloning, also known as live migration, is a process that creates a clone of a system or virtual machine without interrupting the workload or stopping running programs, allowing for seamless cloning and disk duplication.
Using a virtual machine snapshot can be very helpful in diagnosing issues without taking the machine offline. You can take a snapshot, diagnose, analyze, and solve the problem without disrupting the system. However, the snapshot only duplicates the transaction at the start, so any new files or changes made during the copying process will not be included.
So, for users, the biggest difference between clod clone and hot clone might be rebooting the PC or not during the cloning progress.
How to do a hot clone in Windows
If you opt for a cold clone, your computer and data will be inaccessible until the operation is finished. However, a hot clone allows you to work on the system without interrupting the cloning process, making it a more desirable choice, especially considering the lost productive hours for employees and management.
If you only want to move your operating system, we suggest using Qiling Disk Master Professional. This tool's "Migrate OS to SSD" feature uses a hot migration approach to help you migrate your operating system from the current drive to the destination disk, allowing you to use your programs and computer as usual while the migration takes place.
What operation are you referring to? I want to help you with it.
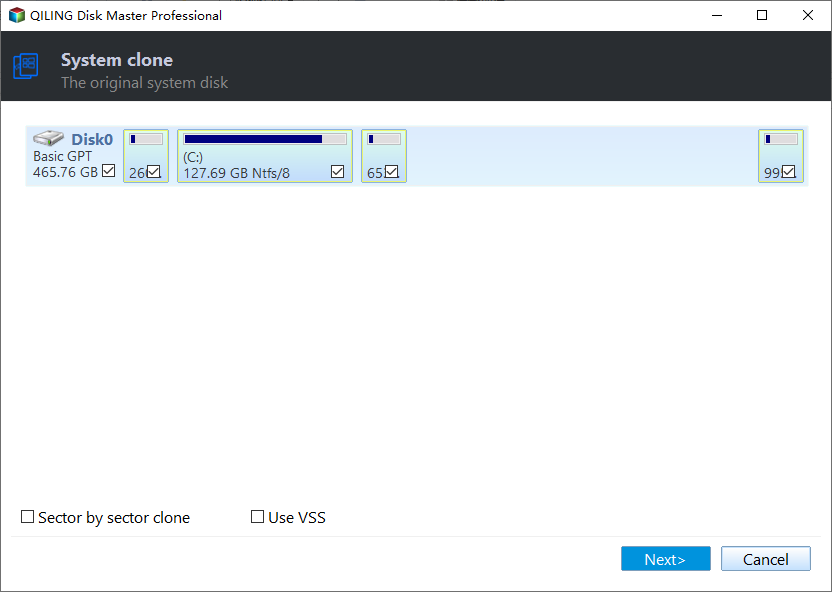
Step 1. Connect the target disk to your computer, ensure it can be detected, install and launch Qiling Disk Master, click "Clone" > "Migrate OS" and proceed with "Next" to continue.
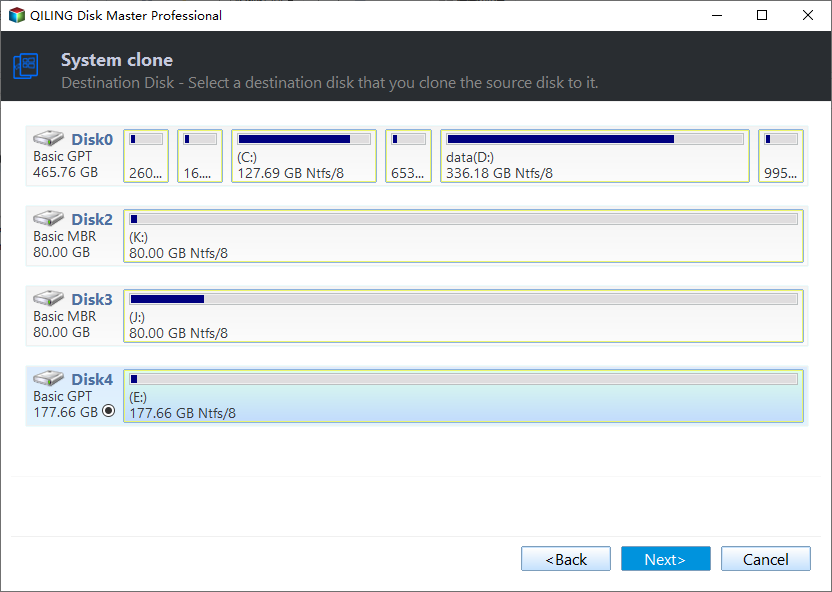
Step 2. To select the target disk, choose an unallocated space on the target disk as the location. If there is no unallocated space, you can check the option to delete all partitions on the target disk to migrate the system. Then click "Next".
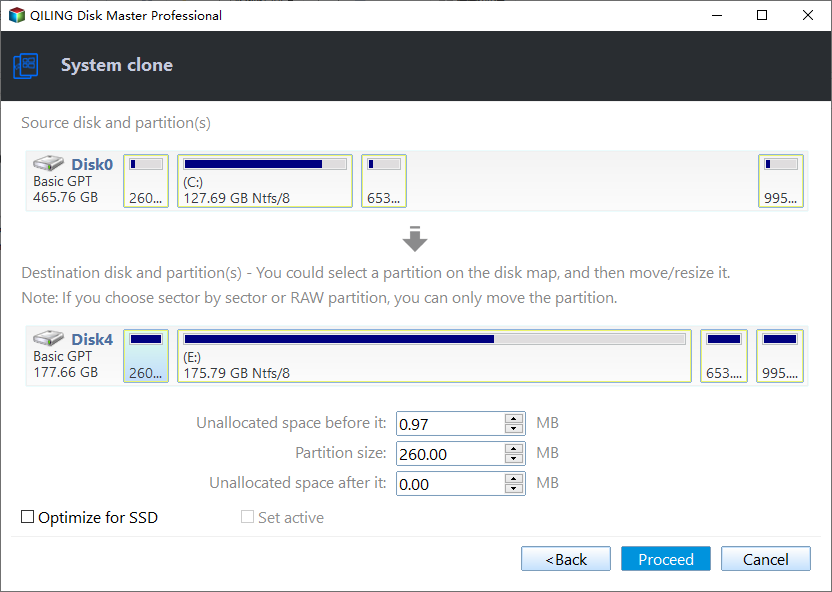
Step 3. In this window, you can resize the partition, change its location, and modify other settings, such as the drive letter, on the new disk. You can also keep the default settings.
Step 4. You'll back to the main interface where you can preview the result of the operation. To commit it, click "Proceed".
Step 5. I don't see any user message. It seems like this is a conversation between a program and itself.
After replacing the old system disk with a new one, the new disk will become the system disk, taking over the role of storing the operating system and all other system files.
Final words
The choice between cold cloning and hot cloning depends on your specific needs. If you're willing to temporarily stop your PC's working to migrate the OS and then reboot to finish the job, cold cloning is a suitable option. However, if you're running programs that can't be interrupted, a hot clone is a better choice, allowing you to clone the OS without stopping the PC.
Qiling Disk Master is a Windows disk and partition manager that allows users to migrate OS, clone disk, convert file systems without formatting, move installed programs or folders, and convert to GPT/MBR without data loss. It also has a Server Edition for Server device users and an Unlimited Edition for business users to manage multiple computers efficiently.
Related Articles
- Two Ways to Create New Partition on Hard Drive
There're 2 ways to create new partition. 1 of them uses Partition Assistant providing the creating partition feature that Disk Management can't do. - How to Backup D Drive in Windows 7/10 (Free and Easy)
Want to backup D drive for data restoring or security? This article shows how to backup D drive full in Windows 7/10 safely and easily with the best free backup software. - The Windows RE Image Was Not Found - Fix It Right Now!
You will learn how to fix the Windows RE image was not found error effortlessly and how to reimage your computer. Scroll down to learn more and find the solutions working for you. - Windows Unable to Repair Drive-Fix It Right Now!
Here are 5 quick solutions to fix “Windows unable to repair drive” easily? Get them right now!