How to Extend System Partition for Windows 10/8/7 and Windows Server?
To extend the system boot partition on basic disks with Windows partition manager, you can use a software like EaseUS Partition Master. This tool allows you to resize partitions, including the system boot partition, without losing any data. Simply download and install the software, then select the partition you want to extend and choose the size you want to add.
Why Need to Extend System Boot Partition?
As applications continue to be installed into the Windows system, one day you may find that the system and/or boot partition do not have enough free disk space. When the system starts, Windows will prompt that the disk is running out of space, resulting in a slow system and potential system crashes.
You are running out of disk space on SYSTEM (C:), To free space on this drive by deleting old or unnecessary files, click here…
To free up space and ensure normal Windows operations, deleting unwanted files is not the best solution. Instead, since the system disk has a large data partition (E:) with 834.84GB, the best approach is to allocate 100GB (or more) from E: to the system boot partition (C:) by extending the system partition using a Windows partition manager like Qiling Disk Master. This will permanently solve the problem and optimize the system disk layout.
Top 3 Solutions to Resize Partition without Losing Data
- Solution 1: Extend Partition Wizard Helps Expand System Boot Partition Safely and Easily
- Solution 2: Resize (Shrink/Extend) Partition via Qiling Disk Master Main Window
- Solution 3: How to Extend Volume with Windows Built-in Disk Management and Diskpart?
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Extend system partition by allocating free space of Qiling Disk Master.
Qiling Disk Master Pro Edition is a Windows partition manager that allows users to extend system boot partition and other partitions on a disk, utilizing free/unallocated space to meet needs. It automatically shrinks large partitions to release space and increases the size of appointed partitions, all without losing data or reformatting. The program also supports more advanced partition operations.
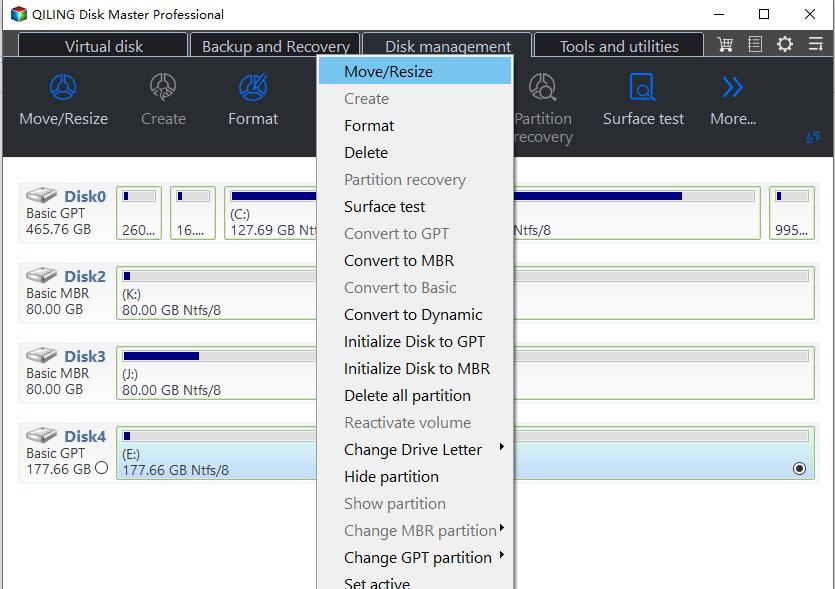
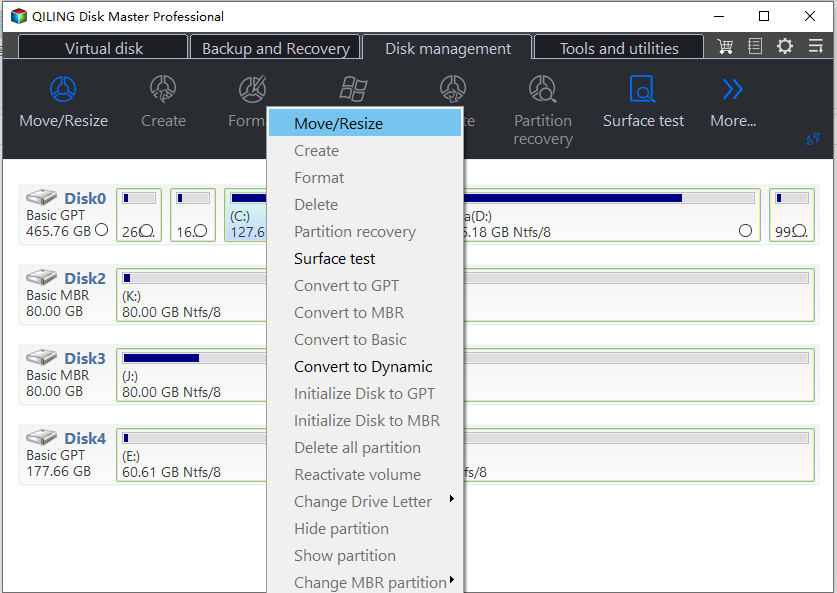
Step 1. Download Qiling Disk Master, run it, right-click the partition you want to allocate free space from, and select "Move/resize".
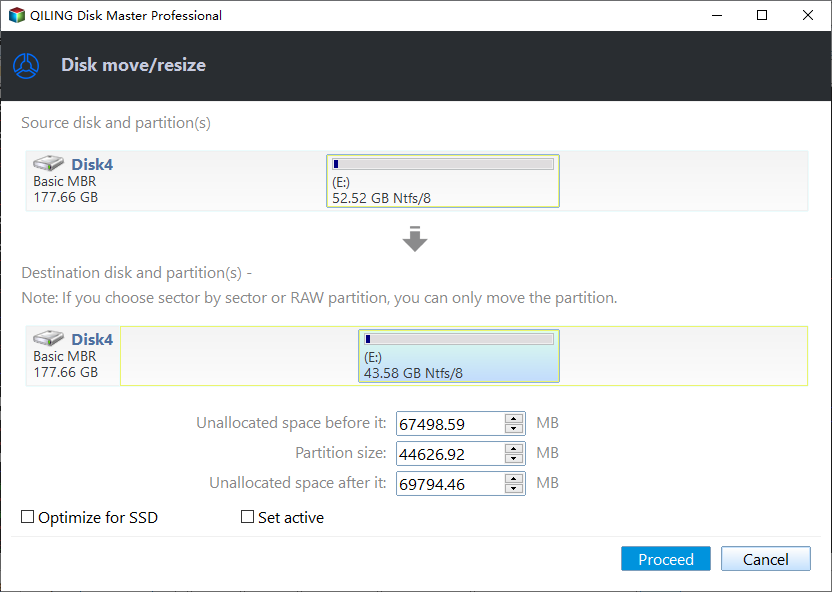
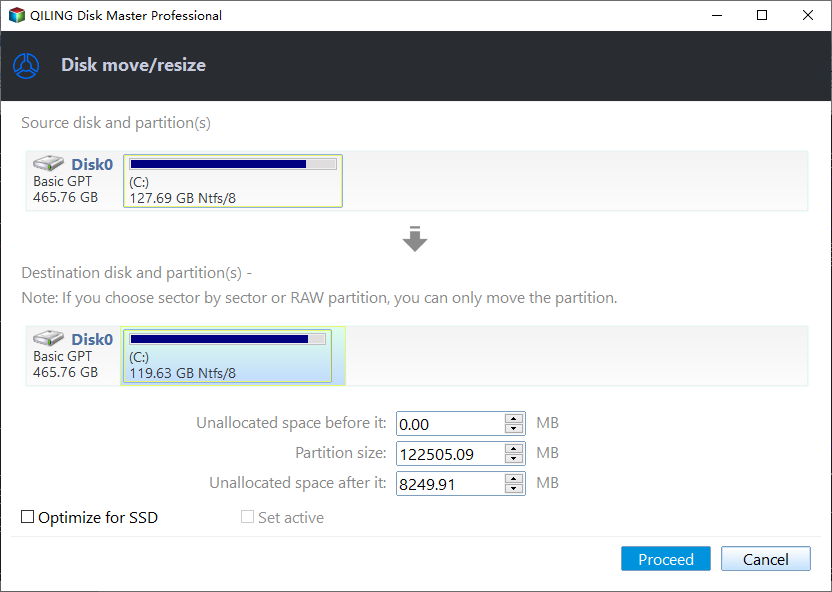
Step 2. As a result of step 1, a pop-up window will appear. In this window, enter the desired size of the free space to be cut from the D partition, and this free space will be directly added to the destination partition. For example, you can allocate 243.81 GB's free space from the D partition to the C partition.
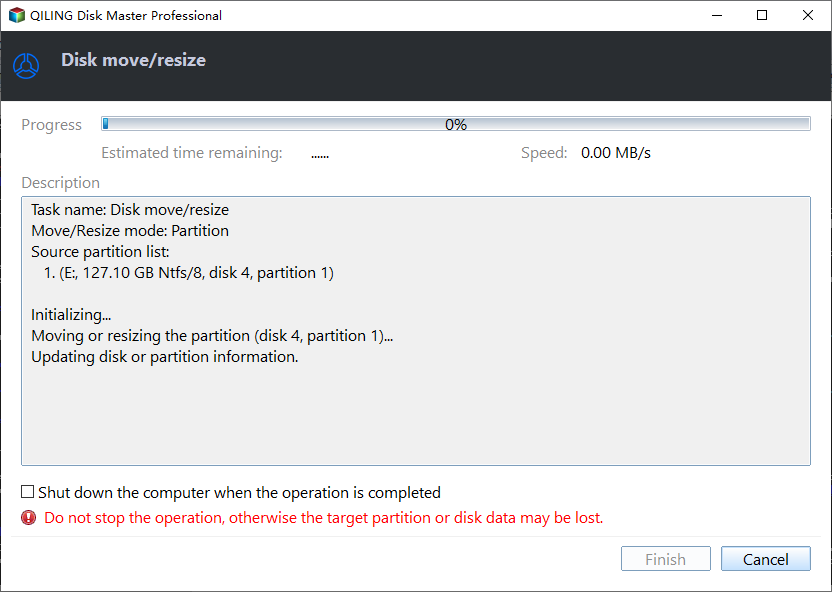
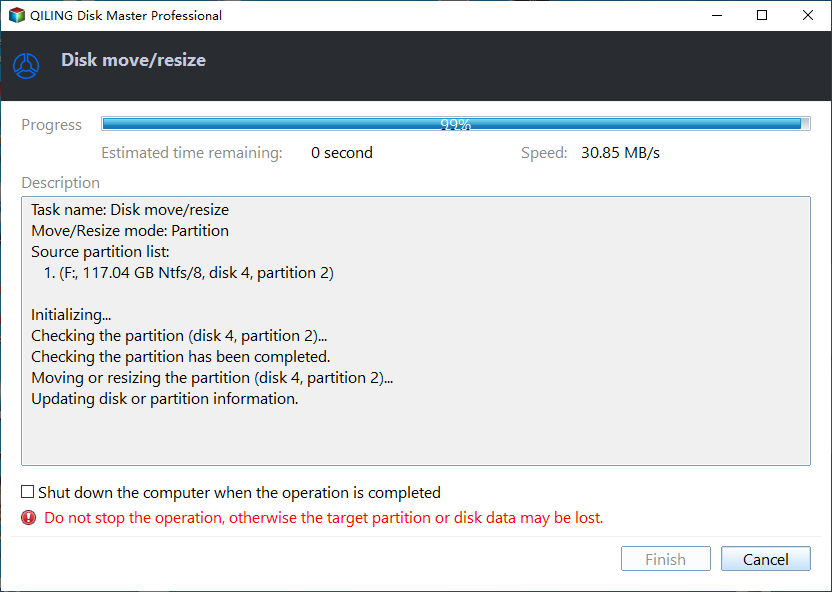
Step 3. The operation can be previewed before starting, and clicking "Proceed" will execute it. A pop-out window will display the estimated time required and the option to check partitions before execution, which is enabled by default.
Step 4. Then, extending system partition is complete successfully!
Qiling Disk Master is a top Windows partition manager that offers flexibility in choosing which partition to resize. With a graphical interface, you can easily operate functions such as extending, shrinking, moving, splitting, merging, copying partitions, and more. By right-clicking on the target partition, you can access a range of options, including resize, move, split, merge, allocate free space, copy, and advanced features like changing drive letters, hiding/unhiding partitions, setting active partitions, converting partition types, converting file systems, checking partitions, and wiping data.
Buy Qiling Disk Master Professional Edition (Only US $39)
Tips:
- For Windows Server users, Qiling Disk Master Server Edition is an ALL-IN-ONE Server partition manager software and reliable disk management utility.
- For all sizes of Enterprise, Qiling Disk Master Unlimited Edition supports all Windows operating systems and allows unlimited usage within one company, saving time and money.
- For IT service providers, Qiling Disk Master Technician Edition is the most cost-effective hard disk partition management toolkit, especially designed for IT consultants.
Resize Partition via Qiling Disk Master Main Window
Case Study - Resize Partition: To increase the system partition size when there is a partition next to it, follow these steps: First, back up your data to prevent any potential loss. Then, use a partition manager or disk management tool to shrink the adjacent partition to make space for the system partition.
Step 1. Install and launch Qiling Disk Master. In the main console, view the whole partition configuration, which in this demonstrator shows an unallocated space behind the C drive. To extend a partition, right-click the partition (in this case, the C drive) and select "Resize/Move Partition".
Step 2. To extend a partition, position the mouse pointer on the right border of the partition and drag the border rightwards in the pop-up window. If there's no unallocated space beside the partition, you won't be able to drag the border.
Step 3. To extend the partition, click the "Proceed" button after previewing the changes. This will commit the operation.
Tips:
- For Windows Server users, Qiling Disk Master Server Edition is an ALL-IN-ONE Server partition manager software and reliable disk management utility.
- For all sizes of Enterprise, Qiling Disk Master Unlimited Edition supports all Windows operating systems and allows unlimited usage within one company, saving time and money.
- IT service providers can use Qiling Disk Master Technician Edition as a cost-effective hard disk partition management toolkit, especially designed for IT consultants.
How to Extend Volume with Windows Built-in Disk Management?
In Windows 2000, XP, and 2003, extending the system boot partition and increasing its free space was a challenging task due to the limitations of the built-in Disk Management tool, which did not offer the ability to extend or shrink partitions. As a result, users had to rely on third-party software, such as Partition Magic, Disk Director, and others, to achieve this.
In Windows Vista and later versions, extending a volume is a straightforward process, thanks to the built-in Disk Management tool, which offers features like extending and shrinking volumes, as well as extending system partitions. This makes it easy to expand primary and logical partitions without relying on third-party partition utilities.
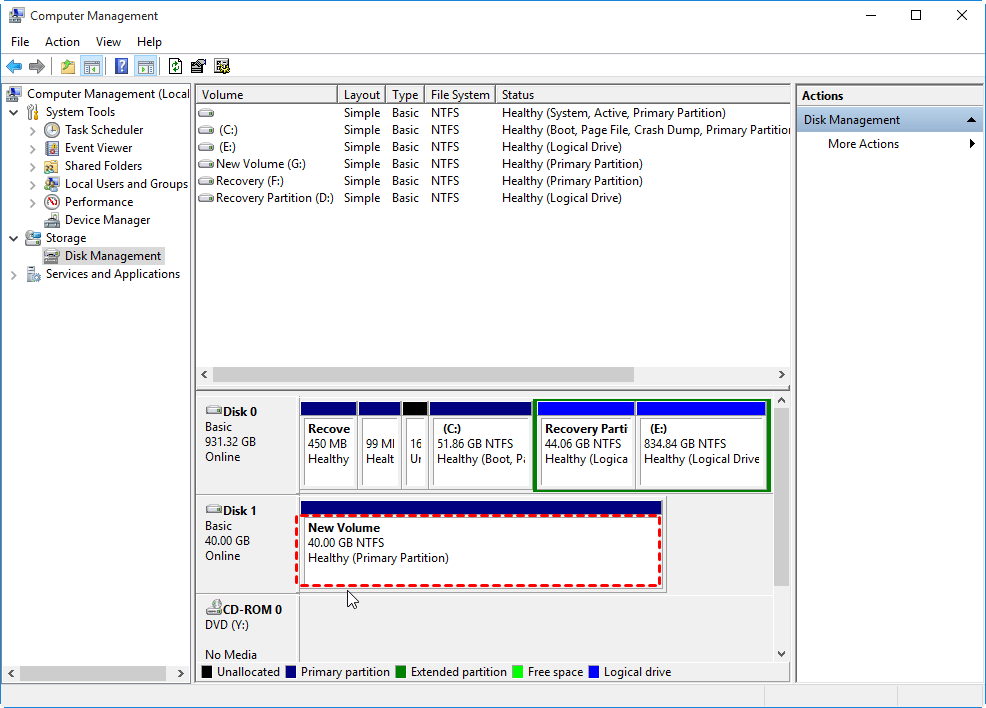
1. Launch Windows built-in Disk Management to extend C: drive
To access Disk Management, click Start Menu, then Control Panel, followed by System and Maintenance, then Administrative Tools, and finally double-click Computer Management. Alternatively, you can type "diskmgmt.msc" in the Start Menu's Run field.
2. Shrink Volume to generate unallocated space
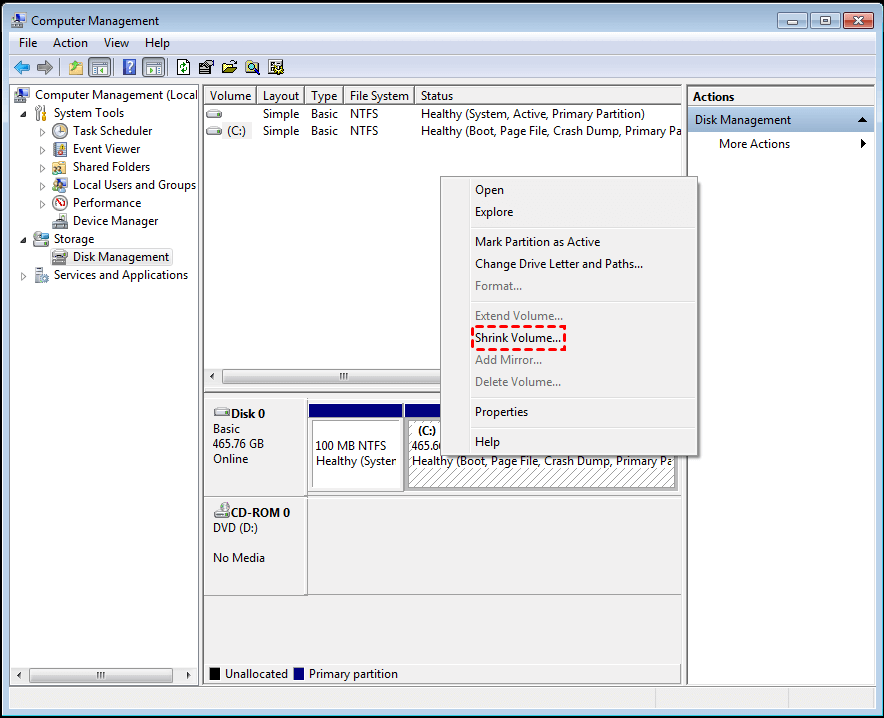
Step 1. The Disk Management tool should be launched, and the partition that needs to be shrunk should be right-clicked. Then, the option to "shrink volume" should be selected.
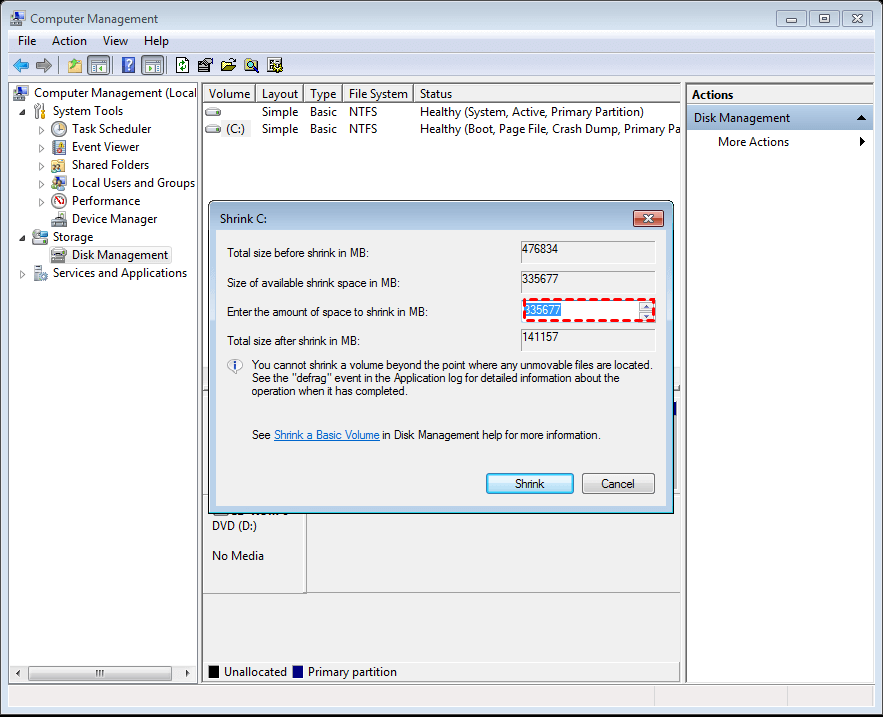
Step 2. In the pop-up window, you can shrink the size within the available shrinking space, then click the "shrink" button.
Step 3. The new unallocated space is behind the partition after the operation is finished, because the system partition is usually set to the front of the disk, and the new unallocated space is created at the end of the disk. This is a common behavior in many operating systems, including Windows and Linux.
3. What can we do when Extend Volume is greyed out in Disk Management?
Then right-To resolve the issue of the "Extend Volume" option being grayed out, you can try the following steps: Check if the disk is full, as the system will not allow you to extend the volume if it's already at maximum capacity. If the disk is not full, try deleting some files or uninstalling unused programs to free up space. If that doesn't work, you can try using the built-in disk management tool to extend the volume. To do this, open the Disk Management console, select the volume you want to extend, and then click on the "Extend Volume" button. If the button is still grayed out, you can try using a third-party partition manager tool to extend the volume. It's also possible that the issue is due to a corrupted system file, in which case you may need to run a System File Checker (SFC) scan to repair any corrupted files.
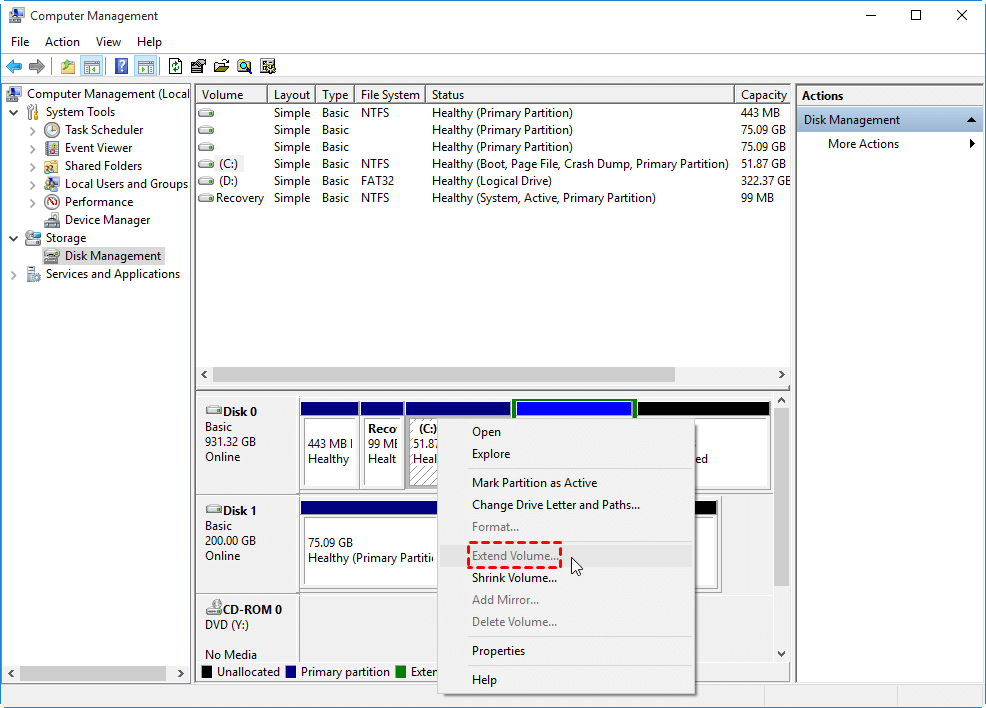
The "Extend Volume" option in Disk Management is only available if there is unallocated space adjacent to the partition you want to extend, making it impossible to extend the system partition (C:) as there is no such space available.
3. Generate a contiguous unallocated disk space to extend system partition
To enlarge the system partition, delete the partition between the system drive and unallocated space, copy all data from the D: partition to another partition or an external hard drive, and then delete the D: partition, allowing the system partition to expand into the next contiguous unallocated space.
Note: Try using Windows Partition manager, Qiling Disk Master, to extend your system partition if contiguous unallocated space can't be generated.
4. Extending system boot partition
After deleting the D: partition, you can extend the system partition. To do this, select the system partition (C:) and right-click on it, then choose "Extend Volume...".
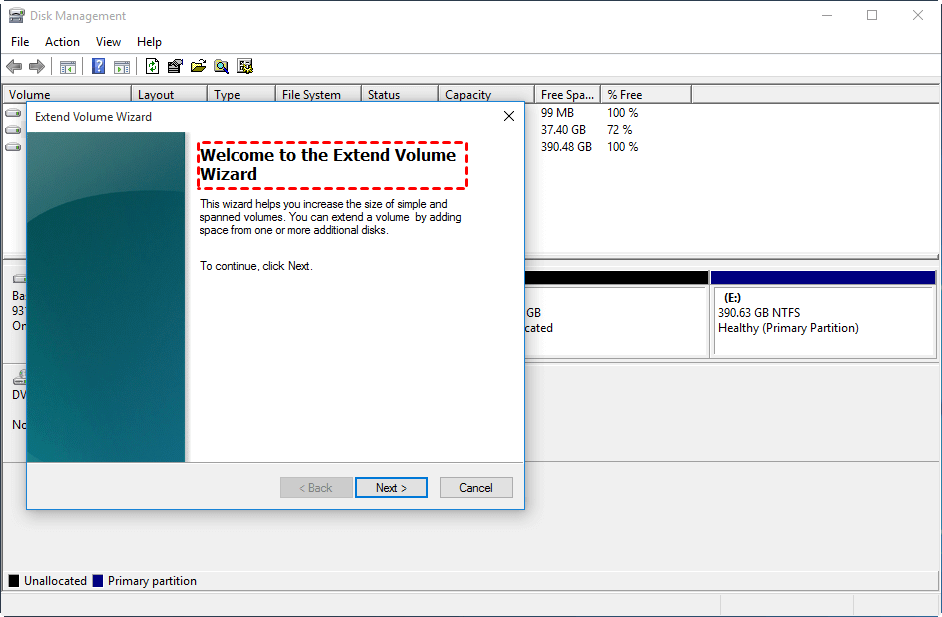
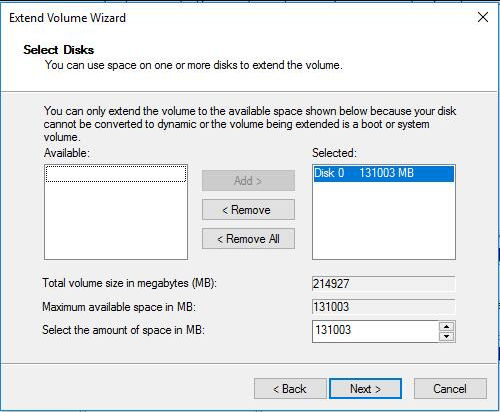
After clicking the "Extend Volume" option, the "Extend Volume Wizard" will pop up to guide you through the process.
Select the disk(s) from which to get free space, specify how much to add to the C drive, and click "Next".
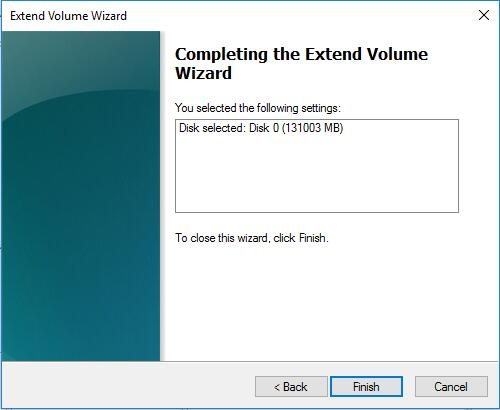
Check the setting. And click "Finish". When the process is completed, your C drive will be extended, and D will be deleted.
How to Extend Volume by using Diskpart Command Line?
To extend a partition or volume in Windows, you can use the DiskPart command-line utility. This process is compatible with Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, and Windows 8. To begin, open the Command Prompt as an administrator and type "DiskPart" to launch the utility. Then, list all the disks and select the one you want to extend by typing "list disk" and "select disk X," where X is the disk number. Next, list the partitions on the selected disk by typing "list partition" and select the partition you want to extend by typing "select partition Y," where Y is the partition number.
- Click Start and type CMD, then press Enter.
- In the command prompt type
DISKPART.exe
- Select the right hard disk and partition to work on. Typically this should be your system disk, usually /dev/sda1, but this may vary depending on your system configuration.disk 0 and partition 1.
SELECT disk 0SELECT partition 1
Note: You may want to execute a "LIST" To view existing disks and partitions, use the command `df -h` or `lsblk` followed by `fdisk -l` or `cfdisk` to see the current partition layout. This will give you an idea of the available space and whether you can extend the partition further. If you're unable to extend the partition, you'll be notified, and no harm will be done.LIST diskLIST partition - When the right disk and partition were selected, execute the command `sudo parted -a current -mskiptable resize 4 100%` to resize the partition to the full capacity of the disk. This command uses parted to resize the partition, specifying the current partition as the active one, skipping the table, and resizing the partition to 100% of the disk's capacity."EXTEND" The command will extend the partition by using all contiguous space available on that disk.
EXTENDThe command will enlarge the partition by using all of the contiguous space available on that disk.
EXTEND size=2048The command will enlarge the partition by 2048MB, increasing 2GB of free space to the selected partition.
Expanding system partition from my experience
To extend a partition using Windows' built-in Disk Management, there must be some contiguous unallocated disk space after the partition you want to extend. If no contiguous unallocated space exists, you can use a Windows partition manager to achieve the expansion.
2) When there is no contiguous unallocated space, there are two ways to release a contiguous space to extend the system boot partition.
- Copy all data and files from the D: drive to an external USB hard disk or other storage device. Then, right-click on the D: drive and select "Delete Volume" to free up a contiguous unallocated space.
- To resolve the issue, one troublesome way to consider is shrinking the D: drive partition to create a new partition (e.g. E: drive), then moving all the data and files from the D: drive to the E: drive, and finally applying the "Delete Volume…" option to the D: drive.
Windows Disk Management has limitations, one of which is its inability to move partitions from one location to another.
Windows 2000/XP/2003 Disk Management can only extend and shrink volumes on Vista and later operating systems, not on their own.
Related Articles
- How to Recover Deleted Files in Windows Server 2012/2008 R2?
How to recover deleted files in Windows Server 2012 R2? In fact, you can restore files from backup or previous versions and it works even for permanently deleted files. - How to Make Windows Server Backup Mapped Network Drive
Do you encounter Windows Server Backup cannot backup mapped network drive in Server 2008 (R2)/2012/2016? Find a workaround here to make Windows Server backup mapped drive. - Can I Transfer Game Saves to Another Computer? Yes, Sure!
Do you need to transfer your game saves to another computer? Follow our step-by-step guide and learn how to transfer your game saves to a new computer without reinstallation. - How to Unlock SD Card Without Switch [6 Methods]
Are you having trouble writing to a locked SD card? This post offers 6 ways to gain access to an SD card so you can use it without restrictions. Additionally, it describes how to retrieve data from an encrypted SD card. Deep Data Recovery is a one-stop software to recover different data types from a locked SD card.