Easily Manage Basic and Dynamic Disk via a Great Disk Manager
Basic disk VS dynamic disk
Basic disk and dynamic disk are two types of storage that support both GPT (GUID Partition Table) and MBR (Master Boot Record) disk formats, but they differ in various aspects.
- Basic and dynamic disks differ in how they track information. Basic disks rely on partition tables to store data, whereas dynamic disks use the Logical Disk Manager (LDM) or virtual disk service to manage disk space.
- A basic disk can hold primary, extended, and logical partitions, whereas a dynamic disk can contain simple, spanned, striped, mirrored, and RAID-5 volumes.
- Basic disks can be supported by all Windows OSes, from MS-DOS to Windows Server 2019, while dynamic disks are limited to Windows Server OSes, Windows 10/8.1/8/7, XP, and Windows 2000.
- You can own dual-A basic disk and a dynamic disk do not support a dual or multi-boot environment. In a basic disk, the operating system is installed on the same partition, whereas in a dynamic disk, the operating system is installed on a separate partition.
★ About different kinds of volume in dynamic disk
▪ Simple volume: It likes the primary partition in basic disk.
▪ Spanned volume: It allows you to combine multiple unallocated spaces across different physical disks.
▪ Striped volume: The use of a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) can improve read-write performance by distributing I/O requests among disks, leading to faster data access and retrieval times.
▪ Mirrored volume: It creates a copy of data in a mirrored volume to protect data.
▪ RAID-5 volume: RAID 5 is a type of disk array that combines disk striping with parity information to provide redundancy and protect against data loss in case of a disk failure.
After deciding between basic and dynamic disk, let's dive into how to manage each type. To manage basic disks, you can use the built-in Disk Management tool in Windows, which allows you to create, delete, and format partitions.
Employ a professional basic and dynamic disk manager
A user-friendly disk manager software, Qiling Disk Master Professional, is available for Windows 10, 8.1, 8, 7, XP, and Vista, allowing for flexible and convenient management of basic and dynamic disks.
Note: You can download the demo version of Qiling Disk Master Professional to try it out.
✔ To manage basic disk:
To extend a basic disk partition by allocating free space directly from another partition, you can use software that allows you to resize, split, move, and opy partitions. This process can be performed when there is no unallocated space behind the partition you want to extend.copy partitions. This process can be performed when there is no unallocated space behind the partition you want to extend.
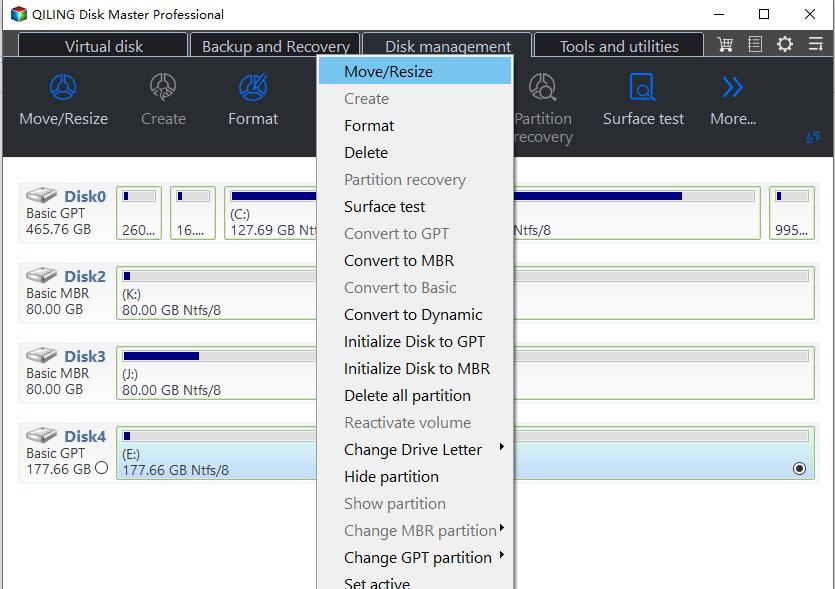
Step 1. Install and run the software, then right-click the partition with enough free space (e.g. partition D:) and choose "Move/resize".
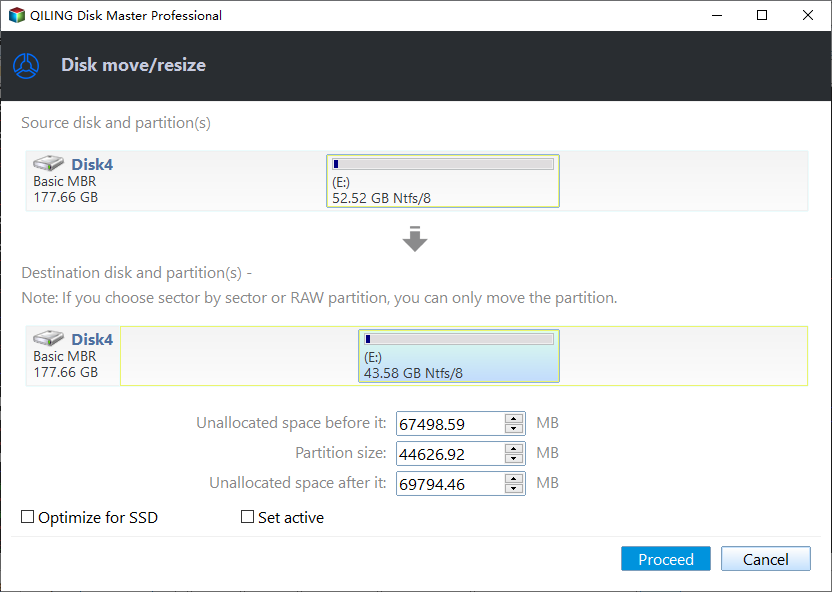
Step 2. You will be asked to input the size of free space you want to add to the destination partition, which in this case is partition C:. This is a step in the resizing process to ensure the destination partition has enough space for the migration.
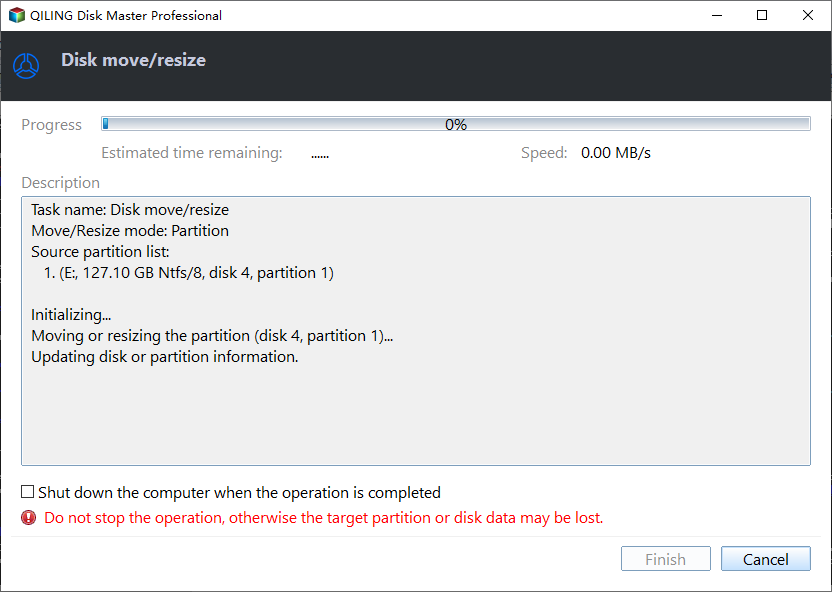
Step 3. You'll be taken back to the main interface. Click Proceed to confirm the operation.
Notes:
- This function is helpful in fixing Low Disk Space warning.
- If there is unallocated space on the same basic disk but not contiguously behind the partition that you want to extend, you can add the unallocated space to the partition via Merge Partition function.
✔ To manage dynamic disk
To manage dynamic disks, the basic and dynamic disk manager software can resize dynamic volumes, move volume slices, delete dynamic partitions, add drives to RAID 5 directly, and remove drives from RAID 5, among other tasks. To complete these tasks, run Qiling Disk Master Professional and click on the "Disk management" tab page.
Make conversion between basic and dynamic disk without data loss
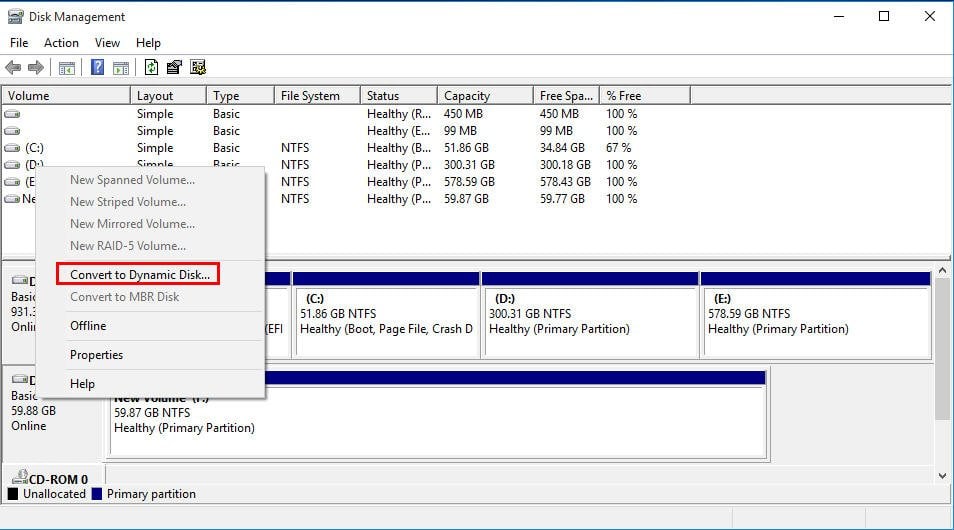
1. Open Disk Management by pressing Win+R, typing “diskmgmt.msc,” and pressing Enter.
Step 1. Press Windows + R, input "diskmgmt.msc" and press OK to open Disk Management.
Step 2. To convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk, right-click on the basic disk you want to convert and select the option to convert it to a dynamic disk. This action will change the disk's structure and allow it to be managed and used by the operating system in a different way.
Step 3. Check if you need to convert the disk. If so, click "OK" to proceed.
Step 4. Click Convert and you'll receive a message that tells what happens after the disk is converted to dynamic. Click Yes button.
If you're using a dynamic disk but encounter issues like an invalid dynamic disk, you may want to convert it back to a basic disk. However, when you right-click on it in Disk Management, the "Convert to Basic" option is greyed out. In this case, it's recommended to use a software like Qiling Disk Master Professional to convert the dynamic disk to a basic disk without deleting any partitions.
Step 1. Run Qiling Disk Master Professional and navigate to the "Disk management" tab page. Right-click the dynamic disk in the list and select the option to "Convert to Basic" to complete the conversion.
Step 2. Wait for a moment untill finish to the conversion operation.
☞ Note: If you're using Windows Server 2019, 2016, 2012 (R2), 2008 (R2), or 2003, you can utilize the Server edition of the software to manage basic and dynamic disks.
Related Articles
- Partition Manager Tutorials
You can find all you needed solutions to manage hard drive space in Windows. Qiling Partition Master is reliable partition manager that help you to resize and manage disk space. - Internal Drive vs External Hard Drive. Which is better?
Both external and internal hard drive have their importance. Depending on if you have a PC or Laptop, you need to backup or need one for playing games. You need to select one of them. It also depends on your budget, which can be estimated on the amount of storage you can get for the money. Find out which one you should select. - MBR or GPT for SSD, Which Is Better and How to Choose?
Should I choose MBR or GPT for SSD? If you are confused about selecting partition type for a second or larger SSD, there are a few tips to decide gpt or MBR for SSD. - MBR2GPT Conversion Failed? What if MBR2GPT Validation Failed?
MBR2GPT allows you to convert a disk from MBR (Master Boot Record) to GPT (GUID Partition Table) without deleting any data. But What if mbr2gpt conversion failed? Learn how to fix the mbr2gpt conversion error while successfully converting a disk from MBR to GPT.