RAID VS AHCI: Which Is Better? [Complete Guide]
RAID vs. AHCI, Which One Should I Choose?
I installed Windows 10 on my mechanical hard drive two days ago, but I accidentally set the SATA mode to RAID instead of AHCI. As a result, my boot speed is much slower than before. I was wondering if the performance of mechanical hard drives is affected in RAID mode compared to AHCI, and if someone could tell me which mode is better, RAID or AHCI.
Since RAID allows you to create a bootable RAID volume, when your motherboard is set to RAID and booted, it will temporarily transfer control to the RAID BIOS, which will find a bootable RAID volume, increasing start time by a few seconds, but not affecting performance.
The debate between RAID and AHCI often boils down to understanding their fundamental differences. RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a technology that combines multiple disks into a single unit, providing increased storage capacity and redundancy in case of disk failure.
What is RAID?
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) combines multiple physical disk drives into one or more logical units, offering advantages such as fast transmission rates, high security, and data protection, making it more suitable for mechanical hard drives than solid state drives.
RAID can be used as a SATA control mode and divided into Software RAID and Hardware RAID control modes, each supporting different RAID levels. Hardware RAID is generally more powerful than Software RAID, especially for high-level RAID configurations. I'll provide a detailed introduction to RAID levels next.
Differences in RAID Levels
Data is distributed on hard disks in various ways, and RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) levels can be categorized based on data redundancy and performance. Common levels include RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10, each using a parity check protection scheme to provide fault tolerance for a given data set. The main differences between these levels lie in their respective advantages and disadvantages, as well as their underlying working methods, making it essential to choose the optimal level based on individual needs. I'll introduce each level in more detail below.
RAID 0
This level allows you to write data to multiple hard drives, with multiple hard drives processing the data together, also known as disk striping, and supports a combination of software and hardware configuration.
- Main Advantage: It can effectively improve server performance and has better compatibility.
- Main Disadvantage: This level has no fault tolerance, so if one hard disk fails, the entire strip will be affected, resulting in the loss of all hard disk data, making it essential to make a backup in advance.
RAID 1
In a RAID array, each disk can serve as a copy, allowing data to be directly copied to another disk if one fails, making it also known as "disk mirroring".
- Main Advantage: This level of RAID provides a higher level of fault tolerance compared to RAID 0, offering better protection for data security.
- Main Disadvantage: RAID 1 is a configuration that stores data across multiple hard drives, but it has relatively slow writing speeds and insufficient overall performance. Additionally, due to data redundancy, the total usable capacity of the array is only about 50% of the total capacity of the hard disk.
RAID 5
This level is an upgrade of RAID 1, combining block-level striping with distributed parity, primarily used for enterprise NAS devices and business servers.
- Main Advantage: RAID 5 offers a balanced performance and fault tolerance, making it suitable for professional data storage. It reduces the performance loss caused by RAID 1, and supports the "hot swap" function, allowing for swapping hard disks into the array during system operation. This enables users to maintain high system uptime and reliability.
- Main Disadvantage: When multiple users access and write to a shared array on a large server simultaneously, the write performance suffers.
RAID 6
RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5, but with two independent parity check protection schemes, using block-level striping with dual distributed parity. This allows it to withstand two simultaneous hard disk failures, ensuring data remains unaffected.
RAID 10
This level is a combination of RAID 1 and RAID 0, implementing stripe set mirroring through parity to provide a high-security redundant backup array and improve performance with a read-write array of auxiliary data.
- Main Advantage: Combining RAID 1 and RAID 0 creates a system that balances performance and fault tolerance. By leveraging the strengths of both, it can provide improved performance while also ensuring higher reliability, making it an ideal solution for servers that require high data write capabilities.
- Main Disadvantage: This level requires at least 4 hard drives, is twice as expensive as other levels, and can only use half the capacity of all hard disks, making it less suitable for large data storage.
What is AHCI?
AHCI is a technology that allows computer hardware vendors to exchange data between host system memory and storage devices, adopting advanced functions of the SATA standard interface, such as NCQ and hot swap, which improve compatibility and performance. It is commonly used in newer computers.
AHCI The SATA/AHCI specification is beneficial for both hardware and software designers as it provides a standardized method for detecting, configuring, and programming SATA/AHCI adapters. However, if AHCI is not enabled on the motherboard and chipset, the SATA controller will default to IDE mode, limiting access to device functions that don't support the IDE standard.
Windows, Linux, Unix, and other operating systems support AHCI. It's essential to enable AHCI before installing Windows 10 on a solid-state drive, as failing to do so may result in a blue screen of death (BSOD) error even after a successful installation.
If you're still unsure about which is better, RAID or AHCI, don't worry - I'll cover the difference between the two next.
RAID vs. AHCI
The age-old debate between RAID and AHCI continues, with some still unsure which is better. To provide clarity, let's look at the historical development and performance differences between the two. Historically, RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) was developed first, allowing for data to be striped across multiple disks for increased performance and redundancy. AHCI (Advanced Host Controller Interface), on the other hand, was introduced later, focusing on improved communication between the host and storage devices, but not necessarily increasing performance.
| RAID | AHCI | |
| Full Name | Redundant Array of Independent Disks | Advanced Host Controller Interface |
| Birth Time | In 1970 | In 2000 |
| Advantages | The software provides data protection for multiple hard drives and improves performance by combining multiple hard drives. | This component supports SATA advanced functions like NCQ and hot swap, which enhances the performance of hard disks. |
| Disadvantages | The current technology is outdated and does not support the combination of mechanical hard drives and SSDs, making it unsuitable for modern use. | Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RST) is a software feature that allows for the management of multiple hard drives in a single system, but it has some limitations. Specifically, it only supports Intel chipsets and may not be compatible with other types of chipsets. |
| Developer | Multiple suppliers | Intel |
| Supported Operating System | Mac, Windows and some open source software, such as OpenVMS. | Windows, Linux, Unix and some open source software. |
| Risk of Being Replaced | Not yet. | Gradually replaced by NVMe. |
| Performance Difference | The performance of a RAID system can vary significantly depending on the specific hardware and software used, as well as the RAID level implemented. Different RAID configurations can result in varying degrees of performance, making it essential to choose the right setup for a particular application or use case. | There is no noticeable performance difference between SATA interface mechanical hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs) in terms of speed. |
| Purpose | Backup and store data. | The SATA technology standard allows for improved compatibility and performance of hard drives. |
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) technology combines multiple hard drives to enhance performance, while AHCI (Advanced Host Controller Interface) is an advanced SATA operation mode that improves device compatibility and performance.
History Development
AHCI AHCI was born in 2000 and has been gradually replacing the traditional IDE model since 2007. It has the latest specification version of 1.3.1. However, with the rapid development of interface technology, AHCI, although not old, is now being replaced by NVMe, which is a better substitute for current SSDs.
The history of RAID development is longer than that of ZFS, dating back to the 1970s when David Patterson proposed the concept of RAID. The technology was named Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks with the development of RAID 1, and IBM filed patents for RAID 4 and RAID 5 in 1977 and 1986, respectively. The name was later changed to Redundant Array of Independent Disks as the technology grew and evolved.
Performance Difference
For most users, the impact of AHCI and RAID modes is most noticeable on mechanical hard drives and solid state drives. While AHCI and RAID have effects on motherboards and storage devices, the key consideration is how they affect hard drives. Therefore, this discussion will focus on the performance of mechanical hard drives and solid state drives in AHCI and RAID modes.
AHCI Using a SATA interface mechanical hard drive or SSD? Consider setting it to AHCI mode, a suggestion made by many SSD manufacturers. However, user feedback suggests that AHCI mode has a negligible impact on SSD performance, but may affect its lifespan. Choose wisely.
RAID Hardware RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) allows you to combine multiple mechanical hard drives or SSDs into an array, which can boost data read and write speed and provide data protection. The choice between hardware RAID control mode and software RAID control mode can significantly impact performance, with hardware generally being faster. Additionally, different RAID levels, such as RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 5, will also affect performance, with some levels prioritizing data protection over speed and vice versa.
NoteThe RAID mode, which allows combining solid-state drives and mechanical hard drives, has limited performance benefits and can easily compromise the stability of the array. It's recommended to use the same type of hard drives in RAID mode for optimal performance and stability.
Is RAID Better than AHCI?
RAID is faster than AHCI when using multiple hard drives, as it combines them to form an array, providing faster read and write speeds and higher fault tolerance.
If you're using a single SSD with a SATA interface, AHCI is a better choice, as it's more suitable than RAID for a single drive, even if it doesn't greatly increase speed.
✡ It is recommended to choose AHCI mode when using an SSD with a SATA interface, as it provides better performance and compatibility compared to IDE mode.
✡ If you're using multiple hard drives with SATA interfaces, RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is highly recommended. This technology allows you to combine your drives into a single, larger storage unit, providing increased storage capacity, improved data protection, and enhanced performance.
✡ Your hard disk is already in RAID mode, so it's best to stick with RAID even if you add new hard disks.
RAID vs. AHCI FAQ
What is RAID and AHCI? RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a storage technology that combines multiple disks into a single unit, providing improved performance, capacity, and reliability.
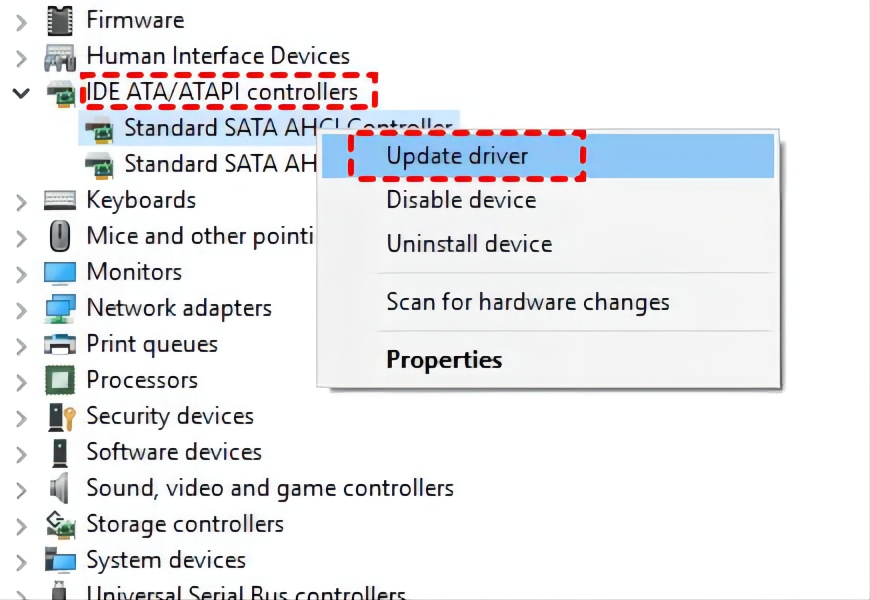
How to Update SATA AHCI
- Right-To access the Device Manager, click on the Windows logo in the bottom left corner of the screen, then select Device Manager from the expanded menu.
- To update the IDE ATA/ATAPI controllers, go to Device Manager, expand the IDE ATA/ATAPI controllers section, right-click the Standard SATA AHCI Controller, and select Update driver from the context menu.
- In the pop-1. Click on the Start menu and select the option Device Manager.
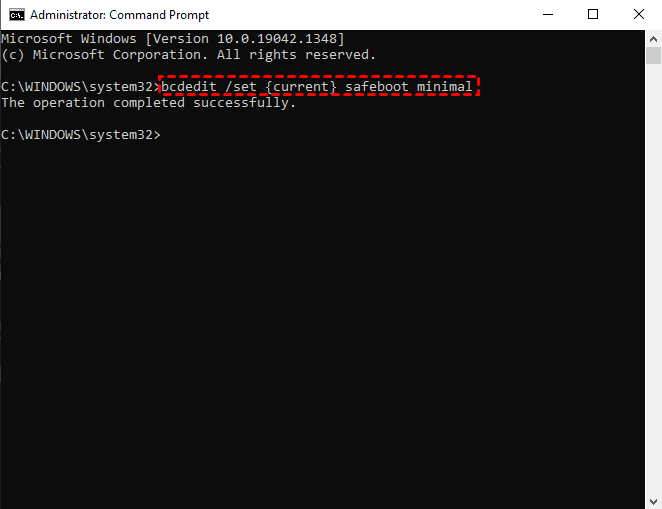
How to Switch from RAID to AHCI in Windows 10
- To open the Command Prompt as an administrator, type "cmd" in the taskbar search box, find and select "Run as administrator" in the right window.
- 1. net user /add
2.
▶ bcdedit /set {current} safeboot minimal
- Restart your computer, press the corresponding button to enter the BIOS, as the BIOS entry method for motherboards of different brands varies.
- To enter Safe Mode in Windows, change the SATA operating mode to AHCI in the BIOS settings, save and exit, and Windows will automatically enter Safe Mode.
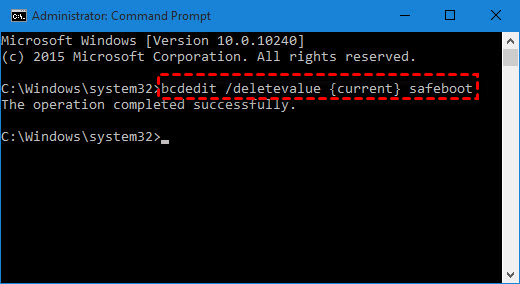
- Right-To access the Command Prompt as an administrator, click on the Windows logo and select "Command Prompt (Admin)" from the menu.
- To execute the command, enter the following in the command prompt window and press Enter: `wmic /namespace:\\root\default path Win32_OperatingSystem get LocalDateTime`
▶ bcdedit /deletevalue {current} safeboot
- Restart your computer again, at this time, your SATA operating mode will be changed to AHCI.
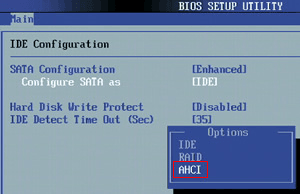
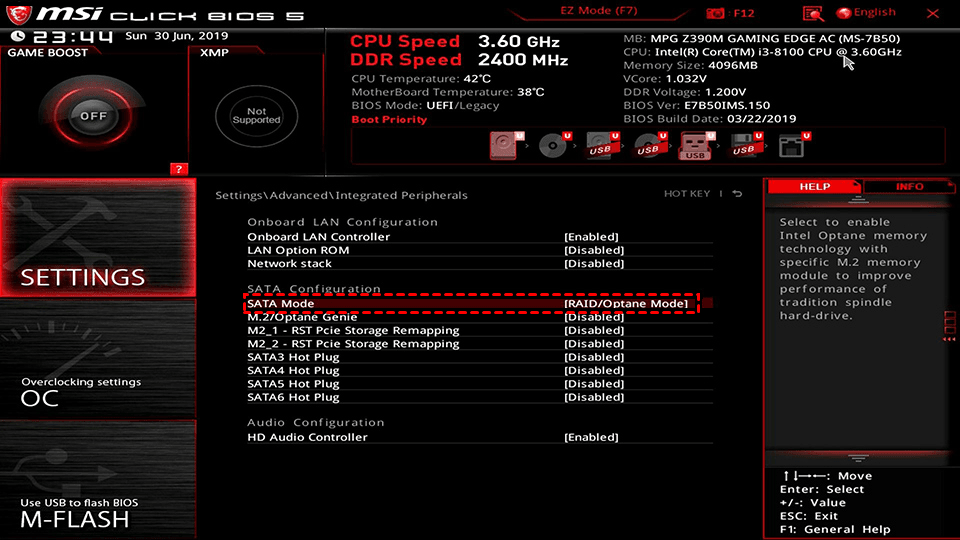
How to Set Up RAID
- Restart your computer and enter the BIOS by pressing the corresponding button, as the entry method varies by motherboard brand.
- To change the SATA mode to RAID, go to the SATA Configuration section and select the option next to SATA Mode to change it to RAID mode. Save the changes and exit, then wait for the computer to restart.
Summary
If you're unsure whether RAID or AHCI is better for your needs, I recommend reading the article in-depth to gain a thorough understanding of both concepts. By learning about their historical development and performance differences, you'll be able to make an informed decision based on the type and number of hard drives you're using.
When using a SATA interface SSD, it's recommended to choose AHCI mode, while multiple SATA hard drives are best configured in RAID mode. Mixing mechanical hard drives with solid state drives in RAID mode is not advised.
Related Articles
- Best Free RAID Array Clone Software
Get the best free RAID array clone software for data security - Qiling Disk Master Standard and Qiling Disk Master and then clone RAID 0/1 to a single drive safely. - How to Wipe a Hard Drive in Windows 7 Without CD (2 Ways)
This tutorial provides two ways to wipe a hard drive in Windows 7 without CD. Whether you want to reserve Windows 7 or remove everything, you can find the way from this page. - Move Windows Server 2008 (R2) to New Machine with Different Hardware
Moving Windows Server 2008 or 2008 R2 to new machine with dissimilar hardware can be as easy as pie if we find the best solution. Get a powerful server backup and restore tool to help you from this page. - Create Windows Server 2003 System Restore Point with Alternative Ways
Does Windows Server include restore point featue? How do I create system restore point in Windows Server 2003 (R2)? You could use built-in Backup Utility or Qiling Disk Master.