How to Restore SQL Database from Bak File (3 Methods)
- How to restore SQL database from .bak file
- Method 1. Restore SQL database from .bak file in SSMS
- Method 2. Restore SQL database from .bak file using T-SQL statement
- How to restore database from a differential backup
- Issue: The tail of the log for the database has not been backed up
- Method 3. Restore SQL database from bak file via command line
- Easier alternative to restore SQL database from backup
- Conclusion
How to restore SQL database from .bak file
After successfully backing up SQL Server, you will get a `.bak` file that can be used to restore the database from backup via various methods such as SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), Transact-SQL, or the command line.
I'll be introducing common recovery approaches and a simple alternative to easily restore a SQL database from a backup. Read on to learn more and choose the method that suits you best.
📢Note: The methods below only support restoring a database from a lower version to the same or higher version, such as from SQL Server 2012 to 2016. If you want to migrate a database to a lower version, you should refer to a different guide.
Method 1. Restore SQL database from .bak file in SSMS
To restore a database using the SSMS restore wizard, connect to the instance you want to restore the database to, and then follow the wizard's intuitive steps to complete the restore process.
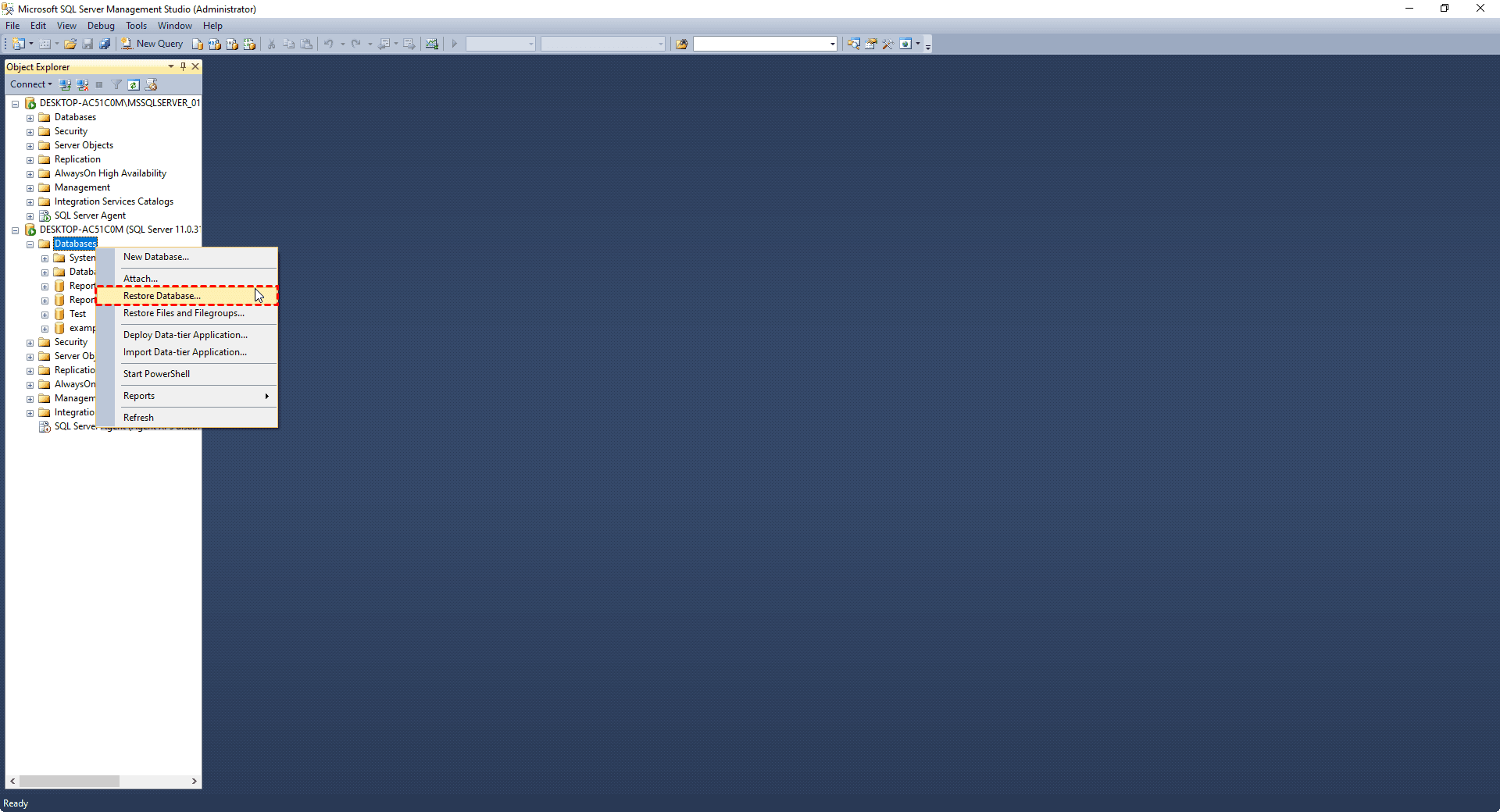
1. Right-click Databases and choose Restore Database… in the menu.
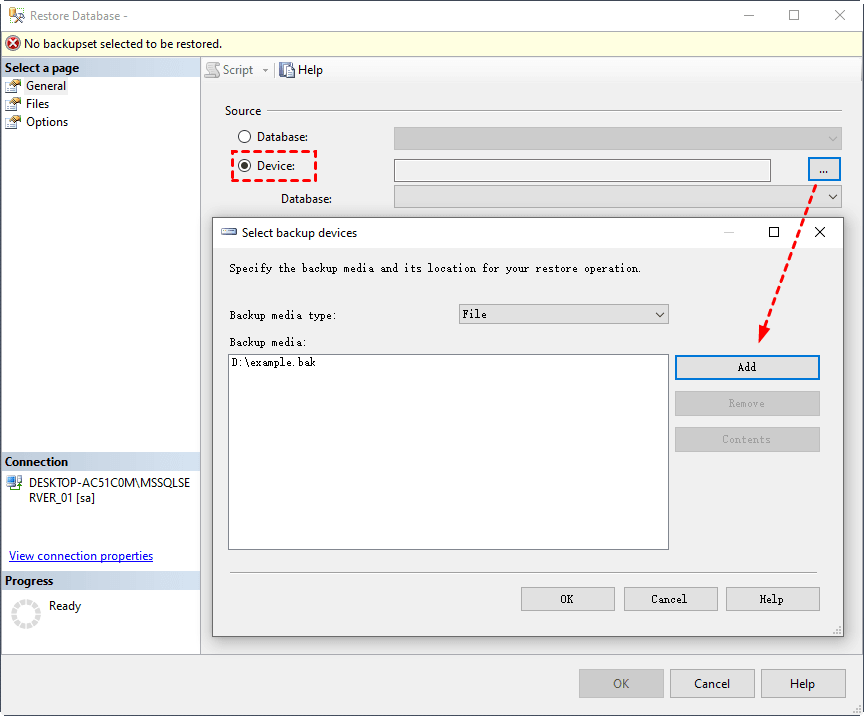
2. To add a bak file, go to the popping out window and select "Source" as "Device". Click the three dots to add the bak file. If you can't find it, look for its save path and enter its full name, including the .bak extension.
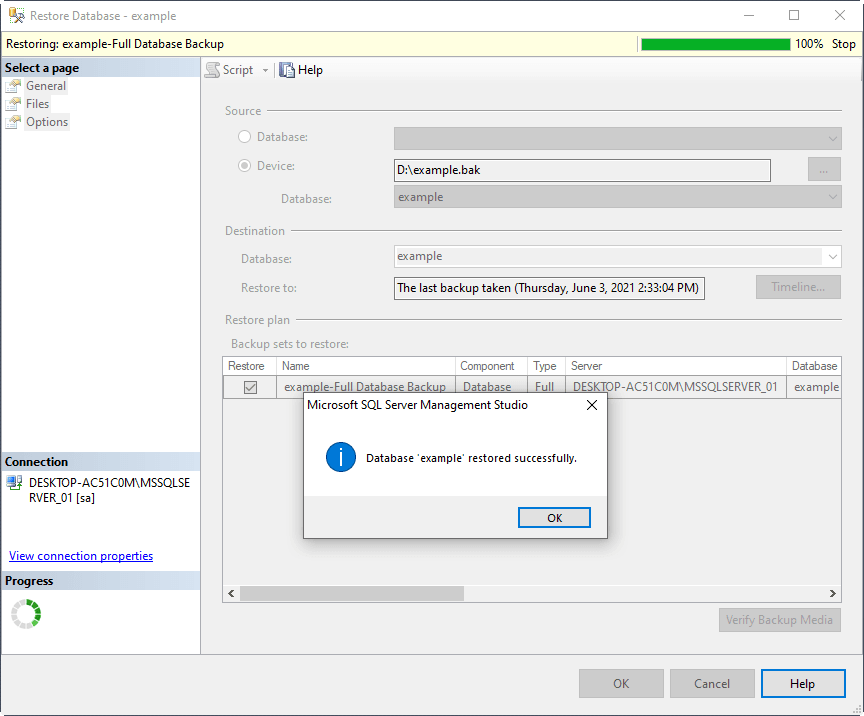
3. If the backup information shows up in the Restore Database window without any issues, you can click OK to proceed with restoring the SQL database from the .bak file.
- Notes:✎...
- If the restoration failed due to an "Access is denied" error, try switching to the "Files" tab, checking the "Relocate all files to folder" option, and then attempting the restoration again.
- If your SQL database is stuck in a restoring state, it could be due to various reasons such as not stopping the restore process correctly, insufficient disk space, or others using the database. However, the most common reason is often using the No Recovery option incorrectly during the restore process. This can cause the database to remain in a restoring state, preventing you from accessing or using it as intended.
- If you're restoring a database from a backup file, make sure the target database doesn't already exist with the same name, as this can cause an error. Instead, let the system create a new database with the same name to receive the restored data. Don't create an empty database with the same name as the target, as this will result in error 3154.
Method 2. Restore SQL database from .bak file using T-SQL statement
You can also restore a SQL Server database using a T-SQL query, which is a more straightforward approach if you're familiar with the statements. This method allows you to restore the database without needing to follow the wizard.
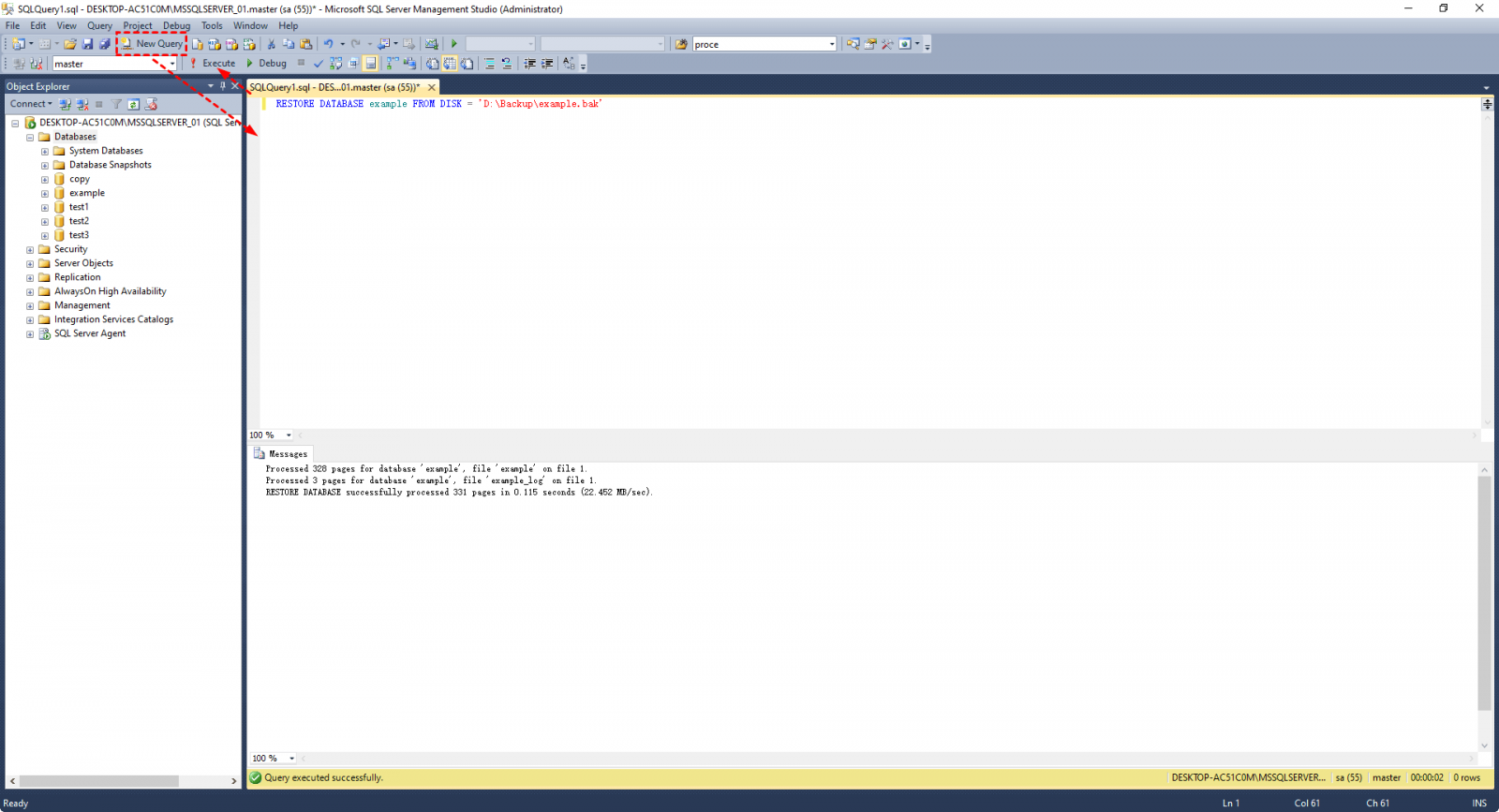
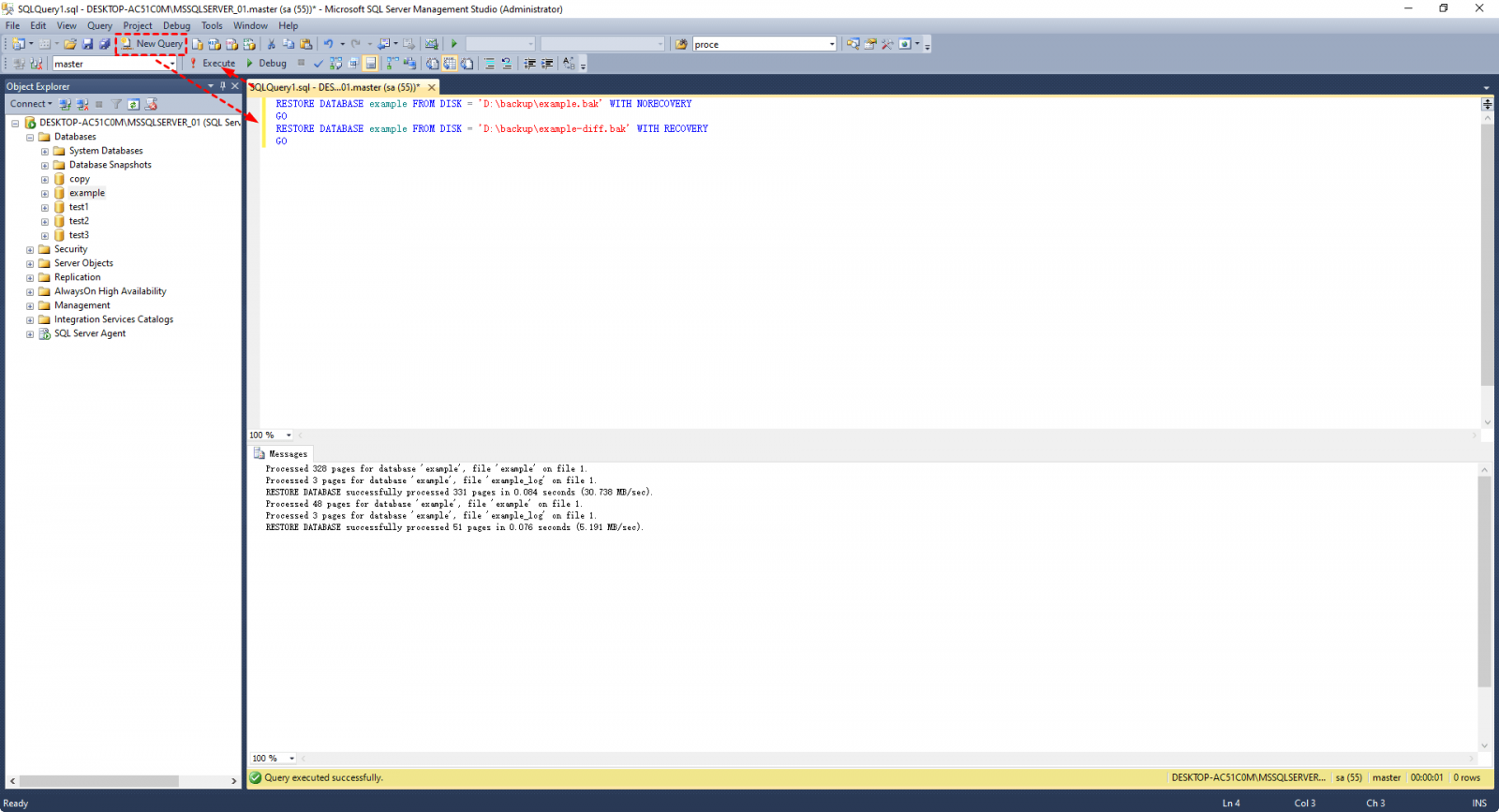
1. To restore a SQL Server database, click on the "New Query" button to open a SQL Query window. Then, type the restore command in it, such as `RESTORE DATABASE [database_name] FROM DISK = 'path_to_backup_file'` and press Enter to execute the command. This will restore the database from the specified backup file to the current server.
The command to restore a SQL database from a full backup is: `RESTORE DATABASE example FROM DISK='D:\Backup\example.bak' WITH MOVE 'example' TO 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\example.
2. To run the backup command, click the Execute button. The backup status will be displayed in the Messages section below.
How to restore database from a differential backup
To restore a differential backup, you need to restore the last full backup with the NORECOVERY option first, followed by the differential backup. For example, the command would be: `RESTORE DATABASE DatabaseName FROM DISK='C:\Path\To\FullBackup.
GO
RESTORE DATABASE databasename FROM DISK = 'filepath\filename.bak' WITH RECOVERY
GO
Note: The first bak file should be the full backup file, containing all data, and the second one should be the differential backup file, which contains only the changes made since the last full backup.
Issue: The tail of the log for the database has not been backed up
During the restoration, you may receive an error saying "The tail of the log for the database has not been backed up. Use BACKUP LOG WITH NORECOVERY to backup the log if it contains work you do not want to lose. Use the WITH REPLACE or WITH STOPAT clause of the RESTORE statement to just overwrite the contents of the log."
To resolve the issue where the backup file you're trying to restore is older than the target database, you can follow the tips mentioned in the message, which likely suggest updating the target database to a version that matches the backup file's age or using a different backup file that's more recent.
1. To resolve the issue, backup the transaction log with the option "WITH NORECOVERY" before attempting to restore the .bak file again.
2. To restore a database using the WITH REPLACE or WITH STOPAT clause, you can use the `RESTORE DATABASE` command with the specified option. The `WITH REPLACE` clause allows you to replace an existing database with a new one, while the `WITH STOPAT` clause enables you to stop the backup at a specific point in time.
Method 3. Restore SQL database from bak file via command line
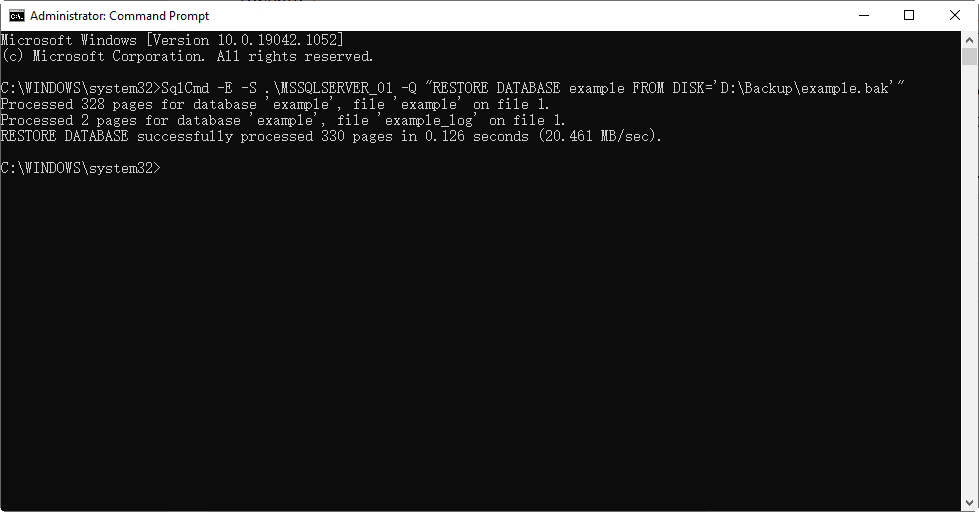
To restore a SQL database from a backup without launching SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), you can use the SQLCMD command-line tool, which is included with SQL Server 2014 and earlier versions. If you're running a higher version, you can download SQLCMD from here.
In a previous article, I explained how to backup a SQL Server database using the command line, and now I'll be focusing on restoring a bak file. You can refer to the previous article for more details on the backup process. To restore a bak file, you can use the SQL command line or a tool like SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), where you can right-click on the database and select "Tasks" > "Restore" to initiate the restoration process.
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box, type "cmd" in the input box, and click "OK" to open Command Prompt.
2. To get the list of all the files in a specific directory on your server, you can use the following command in your terminal or command prompt: `ls -l /path/to/your/directory`. Replace `/path/to/your/directory` with the actual path to the directory on your server where you want to list the files.
In my case, it should be:
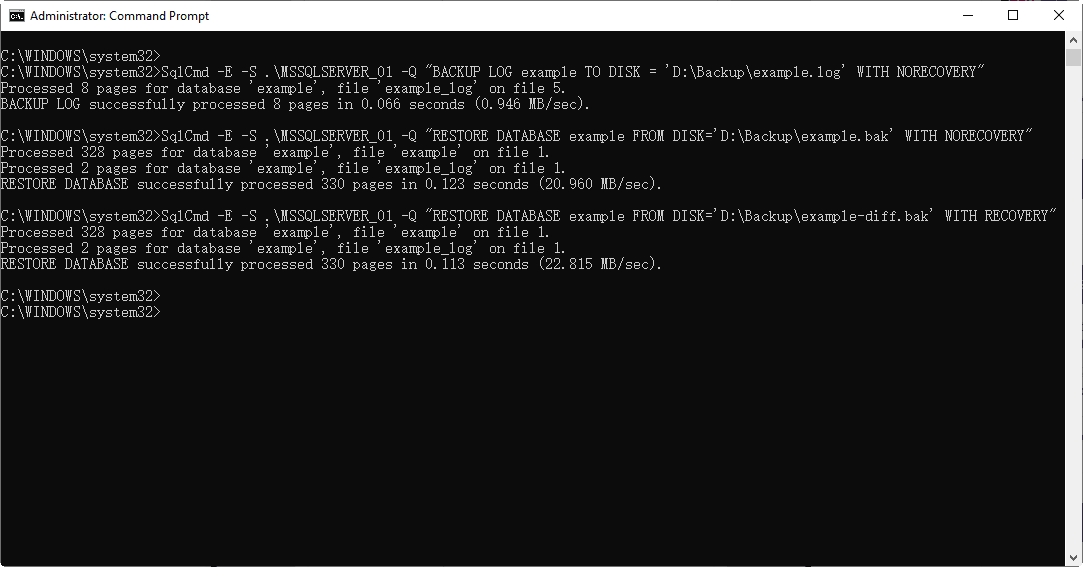
To restore a differential backup using the command line, you can first restore the full backup with the option "WITH NORECOVERY" to prevent the database from being brought online, and then restore the differential backup with the "WITH RECOVERY" option to allow the database to be brought online and made accessible.
SqlCmd -To restore a SQL Server database, use the command `RESTORE DATABASE databasename FROM DISK='filepath\filename.bak' WITH RECOVERY` on the server `MSSQLSERVER_01` using the query `-Q`. This command restores the database from a backup file located at the specified path and makes the database available for use.
Note: The first bak file should be the full backup file, and the second one should be the differential backup file. This is because the full backup file contains all the data, while the differential backup file only contains the changes made since the last full backup.
If you encounter the error "The tail of the log for the database has not been backed up" and you need to run BACKUP LOG WITH NORECOVERY in advance, you can do so to resolve the issue.
Or restore the database WITH REPLACE or WITH STOPAT:
That's it, the recovery issue should be resolved.
Easier alternative to restore SQL database from backup
Restoring a SQL database from a .bak file can be done in various ways, but the methods can be cumbersome or require T-SQL knowledge. However, there's a simpler solution: Qiling Backup, which allows for central backup and restoration of SQL Server databases across all network-connected Windows PCs or servers, making it a convenient option for managing database backups and restorations.
This software supports all Windows OS versions above Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, and its SQL Server Backup feature is compatible with SQL Server 2005 to 2022, allowing for simultaneous backup and restore of multiple databases with just a few clicks, no expertise required.
Here's a 30-day free trial:
✍Backup Cleanup This feature automatically deletes history backup versions based on a set rule, helping to free up storage space.
✍Email Notification This feature allows you to receive email notifications when a task is completed abnormally or successfully.
✍Archvie Cloud backup archives your backup files to a Cloud storage like Amazon S3 object storage, allowing you to store and manage your data securely and access it from anywhere.
✍Notes:
- To avoid confusion, the "Restore to original location" option should only be available if the original location actually exists. If the original location does not exist, the user should only be able to select "Restore to new location".
- If the original database has important data, it's recommended to choose "Restore to new location" to avoid overwriting or deleting the original database data.
Conclusion
This article provides three methods to restore a SQL database from a .bak file, but also suggests using a third-party software, Qiling Backup, for more intuitive SQL Server backup and restore management.
Related Articles
- Backup SQL Server Database and Restore to Another Server | Guide
Here's a simple guide to backup SQL Server databases and restore to another server. In addition, you can also migrate databases via Copy Database Wizard, or try a centralized backup solution. Keep reading to learn the details. - How to Use PowerShell Script to Backup Multiple SQL Databases
Have multiple SQL databases that need to be backed up? Go through this article to learn two effective backup solutions – PowerShell script and Qiling Centralized Disk Master. - How to Use Batch Script to Backup SQL Server Databases
Compared to other methods, a batch script is especially useful when you want to back up batches of databases regularly. This post shares batch scripts for backing up SQL Server databases, and an alternative with equal functionality. - 4 Methods to Automatically Backup SQL Server Databases
If you don't want to set up backup task every time, you can try the following 4 methods to auto backup SQL Server databases with schedule. In addition to SSMS tools and batch file, auto backup software is also a considerable solution.