SSD Reports Wrong Size in Windows? Why and How to Fix it Easily!
- Why does SSD reports wrong size?
- How to fix "SSD reporting wrong size" in Windows?
- ▌Solution 1. Make conversion between vendor and OS capacity calculating method
- ▌Solution 2. Reset the Virtual Memory paging file
- ▌Solution 3. Convert MBR SSD to GPT
- Further reading: SSD reports the wrong size after cloning
- Summary
- FAQs about 'SSD reports wrong size'
Why does SSD reports wrong size?
Users who have transferred their operating system to a solid-state drive (SSD) may experience their new SSD showing the wrong capacity, despite optimal reading and writing performance and low latency. This can be frustrating for tech-savvy individuals who value quick boot times. The discrepancy in capacity may be puzzling, but it can be resolved.
SSD not showing full capacity can be attributed to several reasons. The drive's firmware may not be reporting the correct capacity, or the operating system may not be able to recognize the full size of the SSD. Additionally, the SSD may be configured in a way that limits its visible capacity, such as being formatted with a smaller partition size.
▶ The Virtual Memory paging file is located on the SSD/HDD.
▶ The SSD drive is larger than 2TB but initialized to be MBR.
How to fix "SSD reporting wrong size" in Windows?
After identifying possible reasons for the SSD drive showing the wrong size, it's time to delve deeper into each reason and explore the corresponding solutions. This will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the issue and help determine the best course of action to resolve it.
- Solution 1. Make a conversion between vendor and OS capacity calculating method
- Solution 2. Reset the Virtual Memory paging file
- Solution 3. Convert MBR SSD to GPT
▌Solution 1. Make conversion between vendor and OS capacity calculating method
Computers operate in binary, using only 0 and 1, so operating system capacities are calculated in increments of 1024, with 1024MB being 1GB and 1024GB being 1TB.
The hard disk manufacturers calculate storage capacity in a way that leads to a "reduction" in SSD capacity. Specifically, they round down to the nearest thousand, so every 1000MB is considered 1GB, and every 1000GB is considered 1TB.
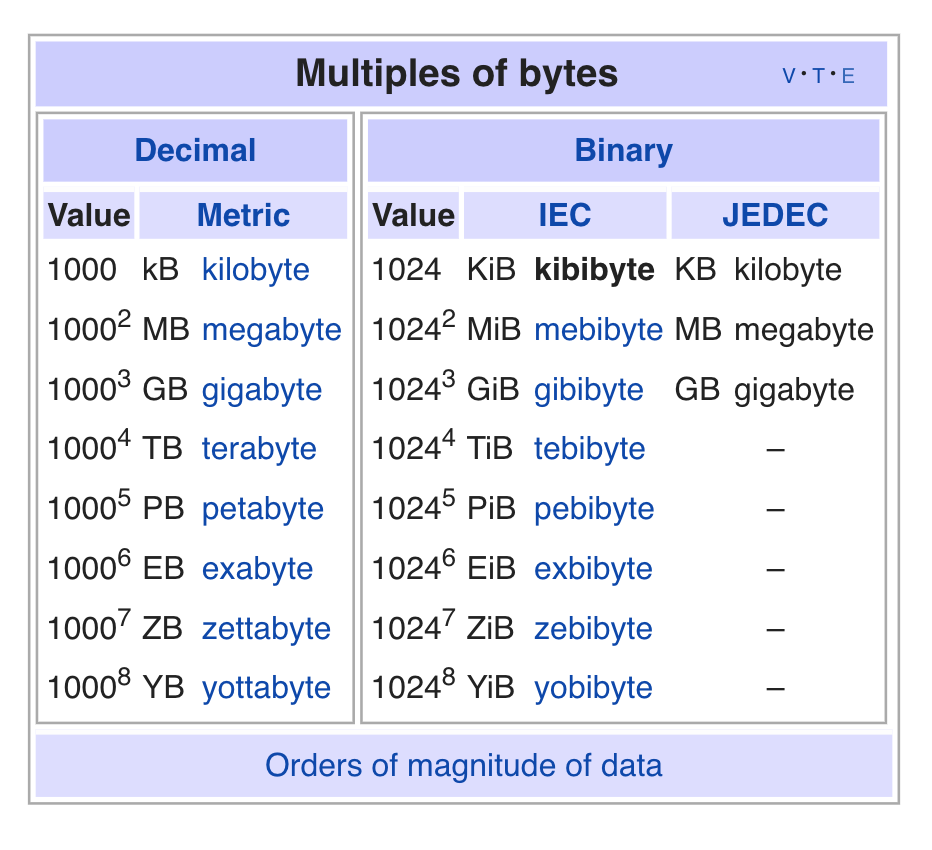
When buying an SSD, you might notice that the actual available capacity is less than the advertised size, such as a 120GB SSD showing only 112GB available for use in your computer's operating system. This discrepancy can be resolved by converting the capacity using a simple calculation method, allowing you to accurately determine the usable storage space.
NOTE:
Actual capacity= byte/(1024*1024*1024 *1024)
Take 120GB as an example:
In manufacturer capacity calculating: 120GB=120,000MB=120,000,000KB=120,000,000,000 bytes
Actual capacity (in computer operating system)=120,000,000,000/(1024*1024*1024)≈111.8GB
The actual capacity of an SSD labeled as 120GB is just about 112GB.
▌Solution 2. Reset the Virtual Memory paging file
Storage and memory are crucial for computers, as all running programs need to be executed in memory. This means that if programs are too large or multiple programs are running simultaneously, memory can quickly become depleted.
Windows uses a technology called "Virtual Memory" to supplement its RAM by taking up some disk space, creating a large range of contiguous addresses to support running programs. This virtual memory exists on the hard disk as PAGEFILE.SYS.
The size of the Virtual Memory in the computer is exactly how much space it takes up in the hard disk. So if you find the actual size of SSD is different from the described one, you can check and reset the size of the virtual storage in the computer taking the steps below.
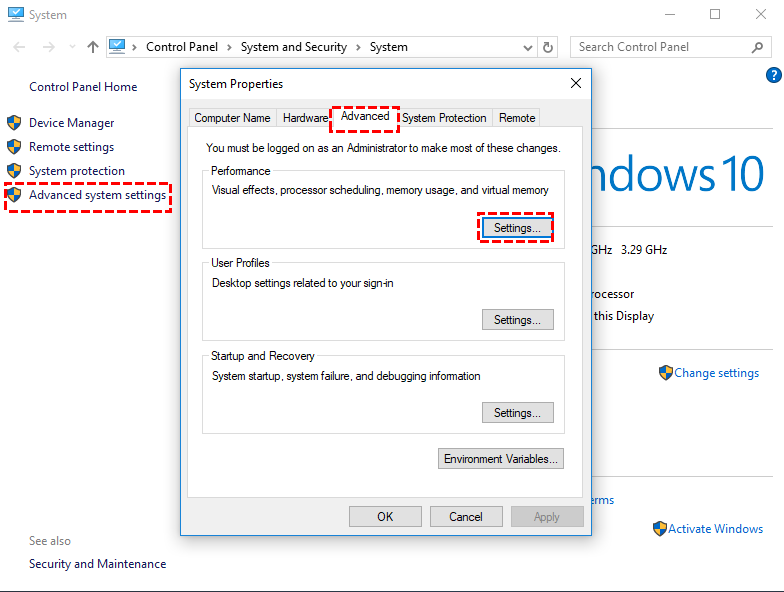
Step 1. Right-click "My Computer/This PC" and choose "Properties".
Step 2. To access the performance settings, click on "Advanced system settings" in the left panel, then select "Advanced" from the next mini window, and finally choose "Settings" under the "Performance" tab.
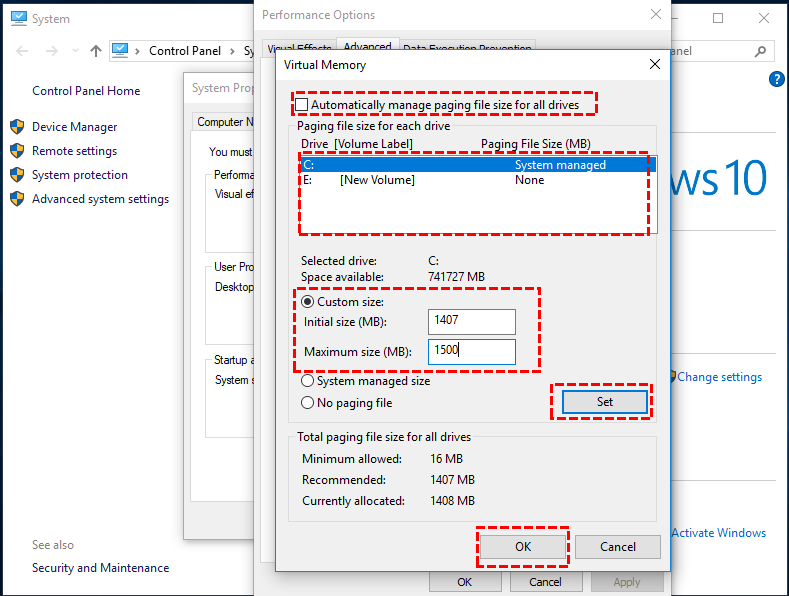
Step 3. In the "Performance Options" windows, locate "Advanced" and click "Change".
Step 4. To manage the SSD's drive letter, you need to locate it, then deselect the "Automatically manage paging file size for all drive" option, select "Custom size", and enter the initial and maximum sizes, before clicking "Set" and "OK".
Step 5. Finally, reboot your computer.
To ensure the smooth operation of your system, it is recommended to allocate a suitable size of virtual memory based on your computer's specifications, rather than cancelling it directly. This will help prevent potential issues and maintain system performance.
▌Solution 3. Convert MBR SSD to GPT
If your SSD drive is over 2TB but initialized to be MBR, it's likely that the drive reports the wrong size. This is because MBR partition style only works with disks up to 2TB and cannot recognize the surpassing space, showing it as unallocated space in Disk Management and invisible in Windows File Explorer. Converting the SSD to GPT, which supports disks beyond 2TB, can resolve this issue, and there are two methods to achieve this conversion.
Method 1. Using Diskpart (data loss)
To convert an SSD reporting the wrong capacity to GPT, you can use DiskPart, but be aware that it can only convert an empty disk to GPT or MBR, requiring you to delete all existing partitions, which means you'll lose everything on the drive. Therefore, it's essential to back up files that are important beforehand.
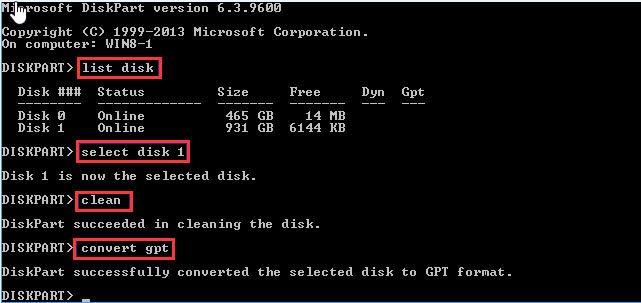
To run diskpart and wipe a hard drive, follow these steps: After making a backup, press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog, type "diskpart" and press Enter. Then, type the following commands in the diskpart window: list disk, select disk [number], clean, and exit. Replace [number] with the number of the disk you want to wipe.
• list disk
• select disk 1 (replace "1" with the disk number of your SSD)
• clean (delete all partitions on the chosen SSD drive.)
• convert gpt
The MBR SSD has been successfully converted to GPT, allowing the remaining space over 2TB to be recognized.
Method 2. Apply a free partition manager (without data loss)
To convert an MBR disk to GPT using Diskpart, you'll need to delete all partitions first, then convert it. If you don't want to clear the disk beforehand, you can use a free partition manager like Qiling Disk Master Standard, which can convert any data disk from MBR to GPT or GPT to MBR without deleting partitions.
▶ Important:
✔ To prevent data loss due to factors like sudden power failures, it's a good idea to make backups at any time.
✔If you need to convert boot disk, you can upgrade to Qiling Disk Master Professional.
✔ If your SSD loses data unfortunately on the rest space that doesn't show, you need to perform data recover before you convert it to GPT.
Step 1. Download the freeware, install and run it, then right-click the SSD and select "Convert to GPT" to convert the SSD to GPT.
Step 3. I apologize, but I don't see a conversation history. This conversation just started.
Further reading: SSD reports the wrong size after cloning
Upgrading to a larger SSD by cloning the old hard disk can result in the new SSD showing the same disk space as the old one, with the rest of the capacity appearing as unallocated and unusable. This is because the cloned partition size of the original disk is retained on the new SSD. As a result, the additional capacity beyond the original disk's size is not utilized for data storage.
You can create a new partition from the unallocated space using Disk Management or merge the unallocated space into another existing partition, such as the C drive, using Qiling Disk Master.
Step 1. Launch this software. Right-click the C drive, select "Move/resize Partitions".
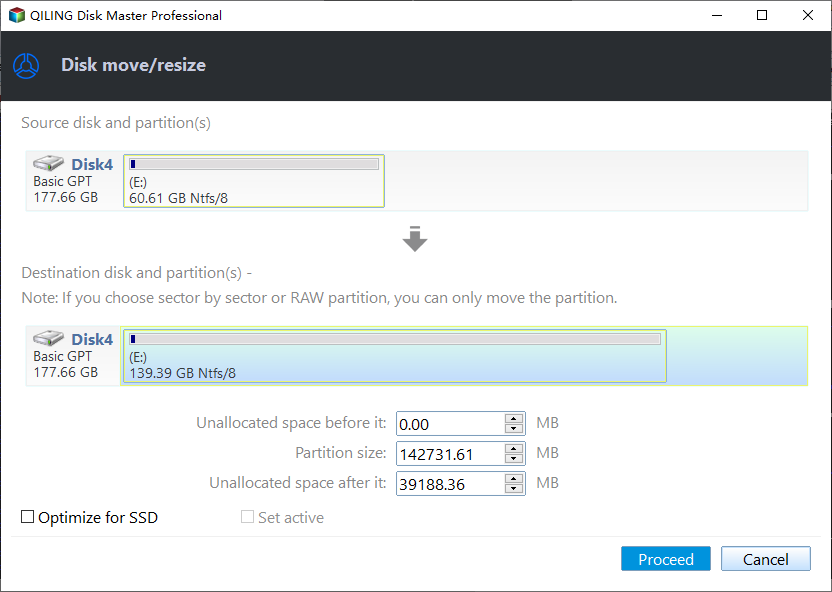
Step 2. Drag it to the unallocated space.
Step 3. Hit on "Proceed" to commit the pending operation.
Summary
Now that you know how to handle SSD size discrepancies, you can use the Qiling Disk Master Professional software to tackle various SSD-related tasks, including aligning SSD partitions, securely erasing SSD drives, transferring OS to SSD drives, cloning SSD to SSD/HDD, and more. If you're a Windows Server user, you can switch to the Server partition manager, which is compatible with both Server and Windows PC.
FAQs about 'SSD reports wrong size'
1. How do I know if my SSD size discrepancy is normal or a problem?
A small difference in storage capacity between an SSD's advertised size and the reported size in your operating system is usually normal, but a significant discrepancy may indicate a problem. To verify, compare the SSD's advertised capacity to the reported size in your operating system, and if the difference is substantial, further investigation is needed.
2. What are the consequences of an SSD reporting the wrong size?
If your SSD reports the wrong size, you may experience issues with installing operating systems or applications, or you may run out of storage space unexpectedly, which can lead to data loss or corruption.
3. Is an SSD that reports the wrong size still usable?
Using an SSD with a reported incorrect size can lead to data loss, corruption, and system instability, making it not recommended to continue using it until the issue is resolved.
4. How can I prevent SSD size discrepancies in the future?
To minimize the risks of discrepancies, you can't eliminate the possibility entirely, but you can take steps to reduce them. By being thorough and accurate in your data collection and analysis, you can minimize the likelihood of errors or inconsistencies that might lead to discrepancies.
- Purchasing SSDs from reputable brands: Established manufacturers are less likely to have significant discrepancies in reported storage, as they have more resources and expertise to accurately track and record their inventory.
- Checking reviews and specifications: Before purchasing a solid-state drive (SSD), it's essential to research and compare the actual reported capacity of the drive, as reported by users, with the advertised size. This will help you make an informed decision and avoid any potential issues related to storage capacity.
- Keeping your system and SSD firmware updated: Updates often include fixes for storage reporting issues.
Related Articles
- Easily Fixed: Hard Drive Only Showing Half Capacity in Windows
If you found your hard drive only shows half capacity in Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, read this article and you will know why it occurs. Besides, you can learn how to fix the hard drive showing wrong capacity issue. - Fixed: 64GB Flash Drive/SD Card/Memory Stick Only Showing 32GB in Windows 7/8/10
On this page, we will tell why your 64GB flash drive only shows 32GB as well as how to restore the USB flash drive back to full capacity without losing data. - Fixed: Unallocated Space on 4TB Hard Drive that Shows up Only 2TB
If you find your 4TB hard drive only shows 2TB space and the rest storage shows unallocated space in your Windows 11/10/8/7, don't worry since here we will explain why the unallocated space appears on 4TB drive and how to deal with it safely. - Windows Needs More Space to Update – How Do I Do?
Get an error saying that Windows needs more space for the upgrade? You can free up system partition or increase system partition size to solve the problem.