Restore or Reset NTFS Permissions in Windows 10 Effectively (5 Ways)
- How do I reset NTFS permissions?
- What does NTFS permission in Windows do?
- Why restore NTFS permission?
- How to reset NTFS permissions in Windows 10
- Way 1: Reset NTFS security permissions with ICACLS command line
- Way 2: Backup and restore NTFS permissions with ICACLS command line
- Way 3: Backup and restore NTFS permission with Windows registry
- Way 4: Reset NTFS permission with the Windows registry
- Way 5: Restore NTFS permissions from backup with third-party software
- Summary
How do I reset NTFS permissions?
To reset NTFS file permissions on a Windows 7 system, you can try the following: Right-click on the affected folder or volume, select "Properties," then click on the "Security" tab. Click on "Edit" and then "Add" to add the original permissions back. You can also use the built-in "icacls" command in Command Prompt to reset permissions. If you're not comfortable with these steps, it might be easier to seek help from a IT professional or a Windows expert.
You're looking for a GUI tool that can automate the backup of vital data, such as NTFS permissions, so you can restore them easily. You're considering scheduling daily backups to keep the data up to date. I'd be happy to help you explore options. Would you like me to suggest some GUI tools that can help with this?"
Many users have doubts about NTFS permission, and if you're one of them, you're in luck. Below, you'll learn about NTFS permission and how to reset it, which will be clarified through 5 effective ways.
What does NTFS permission in Windows do?
In Windows networks, sharing permissions for drives and folders can be set, and NTFS permissions, specific to NTFS-formatted drives, also apply to local users and network users alike. This means that users can only access files or folders with assigned permissions, regardless of whether they're connecting from the same machine or over the network.
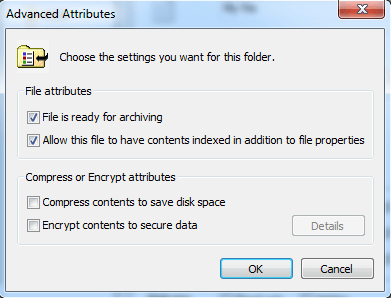
In NTFS drives, files have a Security attribute, unlike FAT32 drives. To access this, open a file, right-click, select Properties, then General and Advanced. There, you'll see two options: File attributes and Compress or Encrypt attributes.
Why restore NTFS permission?
System files, folders, and registry keys are typically owned by the "RrustedInstaller" user account, and other users only have read permission. When accessing these files or folders, the system checks permissions, and if you don't have the required permission, you won't be able to access them. To gain access, you need to restore NTFS permissions.
If you lose access to specific files or folders, you may need to restore NTFS permissions to regain access. This can occur when permission is lost, and other options like taking ownership or using the "Take ownership" option may not work. Restoring NTFS permissions can help resolve the issue and allow you to access the affected files or folders again.
How to reset NTFS permissions in Windows 10
To reset NTFS permissions, you can use the ICACLS command line, which is a replacement for cacls and allows you to define user access to filesystem objects. Additionally, you can backup and restore NTFS permissions, and reset them to default or inherit from parent folders if needed. This can help resolve permission issues and restore order to your NTFS permissions.
To back up your Windows system, you can use the built-in feature called System Restore, or the File History feature. You can also use the Windows registry and third-party backup software to help you out. Please read them carefully and select one.
Way 1: Reset NTFS security permissions with ICACLS command line
1. Open Command Prompt as administrator, navigate to the folder tree that needs fixing, and proceed with the necessary actions.
2. `icacls C:\path\to\folder /takeown /c /q` and press Enter.
takeown /R /F *.
3. Click "Yes" if you are prompted to replace the directory permissions with permissions granting you full control.
4. icacls C:\Path\To\Folder /reset /t /c /l
ICACLS * /T /Q /C /RESET
Tips:
- The /T switch is to get subfolder permissions too.
- The /C switch is to suppress success messages.
- The /C switch tells the command to continue running even if errors are encountered.
You can reset NTFS permission for specific folders and grant the current user full access permission by typing the command `icacls C:\path\to\folder /reset /grant *S-1-5-21-1234567890-1234567890-1234567890-1234567890-1000:F` in the Command Prompt, replacing `C:\path\to\folder` with the actual path to the folder and `*S-1-5-21-1234567890-1234567890-1234567890-1234567890-1000` with the actual SID of the current user. This will reset the NTFS permissions for the specified folder to their default values and grant the current user full access permission.
ICACLS * /t /grant: F
Tips:
- The F switch is to grant full access permission.
- To view the ICACLS switches, you can use the following command: `icacels /?` or `icacels /help`.
Way 2: Backup and restore NTFS permissions with ICACLS command line
You can also backup and restore NTFS permissions using this command line.
1. Open Command Prompt and run as administrator.
2. To backup NTFS permissions, use the following command.
icacls d:data /save ntfsperms.txt /t /c
3. To restore NTFS permissions, use the following command.
icacls d: /restore ntfsperms.txt
Note: The target path to save NTFS permissions may differ from the path to restore them, but it will still be recognized.
Way 3: Backup and restore NTFS permission with Windows registry
1. To backup NTFS share permissions, navigate to the Registry and go to the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanManServer\Parameters. In this key, look for the permissions stored in the values "Allow" and "Deny" under the key "Security". You can then export these values to a file for backup purposes.
HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesLanmanServerShares
2. Right-click the Share registry key, select Export, and set a unique name for the exported file, such as ntfsperms.reg.
3. To restore NTFS share permissions, you can import the ntfsperms.reg file into the registry, which will reset the permissions to their original state.
Way 4: Reset NTFS permission with the Windows registry
1. Open command prompt and run as administrator.
2. To backup the registry key - ntfsperms.reg, type the command: regedit /e ntfsperms.reg "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem\NtfsPermissions" .
reg export HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesLanmanServerShares ntfsperms.reg
3. You can restore the registry key by typing the command "regedit /s ntfsperms.reg" in the command prompt.
reg import ntfsperms.reg
Way 5: Restore NTFS permissions from backup with third-party software
You can use third-party backup and restore software to help with permissions issues, such as Qiling Disk Master Professional, which can backup files and their NTFS permissions together. This way, if you lose permissions or something goes wrong, you can restore the NTFS permissions from the backup on the computer where you saved it.
Before proceeding, you need to download and install the software, and have an external storage device or other devices ready to receive the backup image.
This version only works on Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, XP, and Vista. For server users, you can choose to use its Server edition instead.
1. To backup files with NTFS permissions, run Qiling Disk Master Professional on your Windows machine and go to the Backup tab. Select File Backup and click on Files or Folders to choose the data you want to backup. Then, select a destination path and click Proceed to start the backup process, which will preserve NTFS permissions.
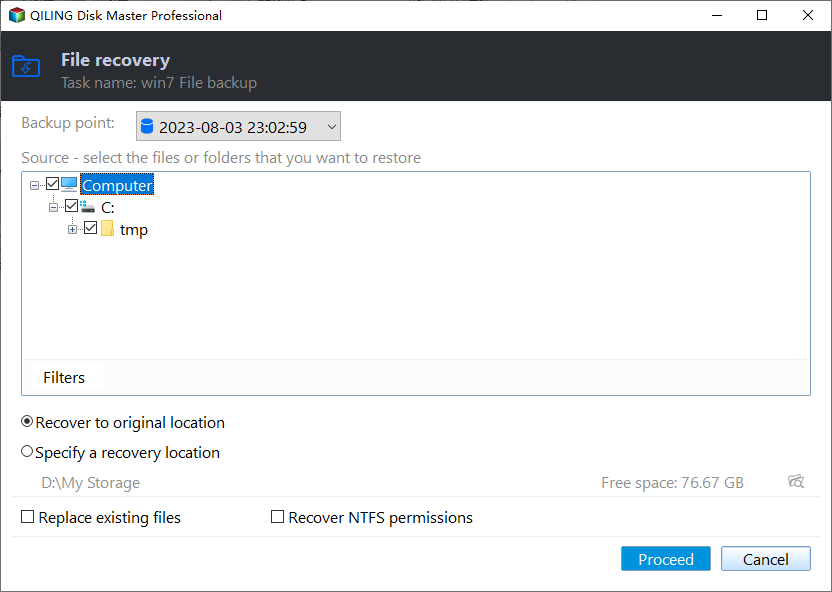
2. To restore NTFS permissions, go to the Restore tab, select Select Task, and choose the file backup from the list. If it's not listed, browse manually by selecting Select Image File.
Tip: To restore NTFS permissions on the external drive, connect it to your machine beforehand.
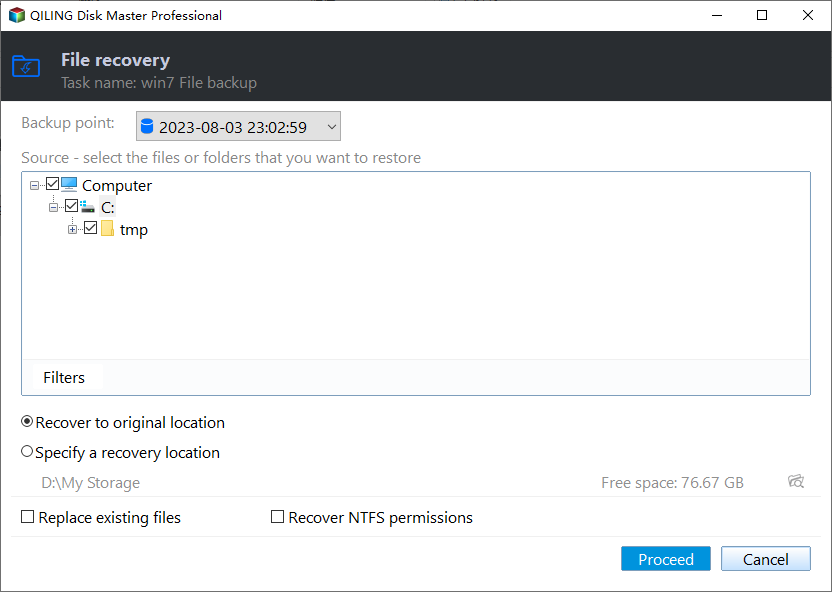
3. To restore files or folders with NTFS permissions, select them and click "Next" after that.
4. Choose where you want to restore your files or folders, either the original location or a new location.
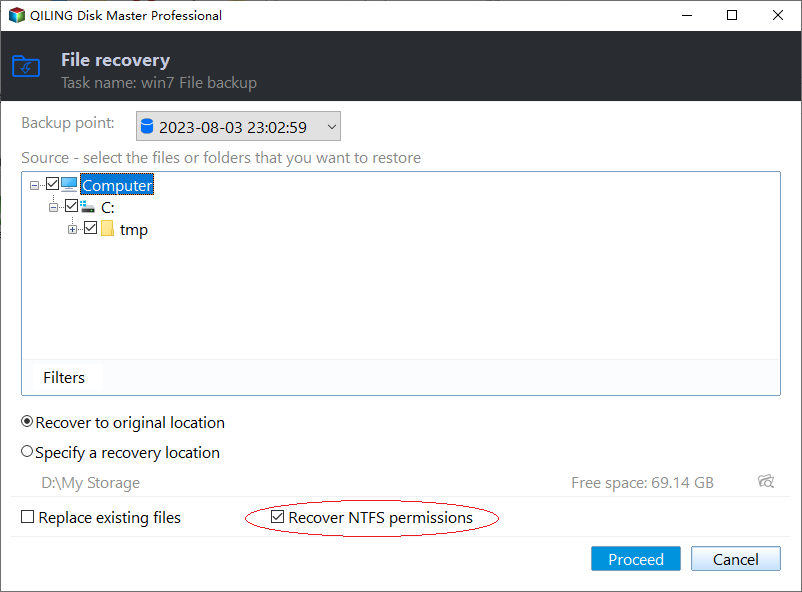
5. To restore NTFS permissions on a Windows system, click the "Setting" icon at the lower left corner, select "Restore NTFS Permissions", and then click "OK". Finally, go back to the main page and click "Proceed" to restore files with NTFS permissions.
Tip: NTFS permissions can only be restored from a backup on the same NTFS formatted drive on the computer where the backup was created.
Summary
If your files with NTFS permission get messed up, you can try resetting NTFS permissions to default. To ensure your files are always safe, it's recommended to keep Qiling Disk Master Standard and regularly back up files to an external hard drive. This way, even if you lose permission or it's damaged, you can easily recover it.
To protect unlimited PCs & servers within one company, the Technician Plus edition of this software can be used to backup files, allowing for the creation of a portable version that can backup files without requiring a re-installation.
Related Articles
- Why Does My Computer Keep Blue Screen | 100% Solved
Do you have the issue of the computer keeping a blue screen? If yes, you are in the right place. This article gives a complete tutorial on what a blue screen means, why it appears, how to troubleshoot it, and some practical tips to prevent the computer blue screen of death. Keep reading and find your solution. - Why Is My Windows 10 Backup Taking So Long? (Here's the Answer)
Why is my Windows 10 backup taking so long? Do you want to know why? If yes, you are coming to the right page. This article will explain the reasons for the slow backup of Windows 10 and offer an alternative to Windows 10 backup. - A Quick Answer to: Will Updating My BIOS Delete Anything?
Updating BIOS is something you might have heard about. But have you ever been stuck on a question like, 'Will updating my BIOS delete anything?' This article will describe whether updating BIOS will delete anything on your PC and offer a tool called Qiling Disk Master to protect your data. - Windows 10 Backup Error Code (0x807800C5) – Why & How to Fix
Are you experiencing the Windows 10 backup error code (0x807800C5)? This guide will show you why the error occurs and how to fix it. Moreover, we'll provide an alternative to Backup and Restore, which can help you create a system image with ease.