What's the Difference Between GPT and MBR Partition Style?
- Preface
- Difference between MBR and GPT partition style
- You can check if your hard disk is MBR or GPT by using the command line. Type "diskpart" in the command prompt and then type "list disk" to see a list of all disks connected to your system. Select the disk you want to check by typing "select disk X" (where X is the number of the disk you want to check).
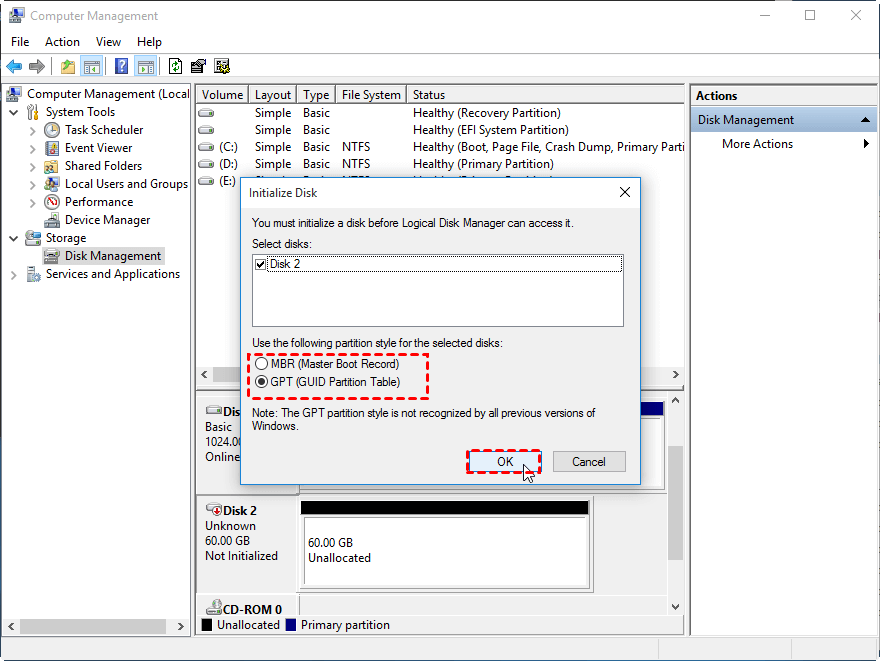
- Should I initialize the disk as MBR or GPT?
- To convert between MBR and GPT, you'll need to use a tool like GPT fdisk or parted. First, back up your data and ensure the system is shut down. Then, boot from a live Linux environment or a Windows installation media.
Preface
When initializing a new hard drive, you're presented with the choice between MBR and GPT disk. MBR (Master Boot Record) is an older partitioning scheme that's limited to 4 primary partitions, while GPT (GUID Partition Table) is a newer scheme that supports up to 128 partitions and is more flexible. GPT is also required for UEFI boot, which is the only boot mode supported by Windows 11. Choosing GPT over MBR provides more flexibility and is recommended for new installations, especially if you're planning to use UEFI boot. However, if you're upgrading from an older Windows version, you may need to choose MBR if your system is not UEFI-capable.
When installing a new hard drive, you'll be asked to initialize the disk and choose between MBR and GPT partition styles. Most people default to MBR, but it's worth considering the advantages and disadvantages of each. Typically, Windows initializes disks to MBR, but understanding the differences can help you make an informed decision.
Differences between MBR and GPT partition style
A disk's style is determined by its MBR (Master Boot Record) or GPT (GUID Partition Table) initialization. Once initialized, a disk can be referred to as an MBR disk or GPT disk, each with its own scheme for managing partitions. The structured information, including partition details, is recorded and stored in a specific segment of the disk, and updates are made as partition information changes, making it a partitioning scheme.
1. About MBR
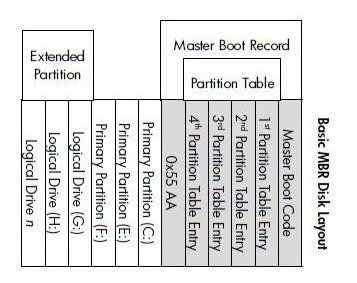
The Master Boot Record (MBR) is a traditional and widely used disk layout that has been around for a while.
The partition table in the MBR has limitations, allowing for a maximum storage space of 2 TB and only supporting up to 4 primary partitions or 3 primary and 1 extended partition combination.
If you want to create more partitions, you'll need to convert one of the primary partitions to an "extended partition" and then create more logical drives within it. This will prevent the disk from being converted to a dynamic disk, which can cause issues and prevent you from installing an OS on it.
2. About GPT
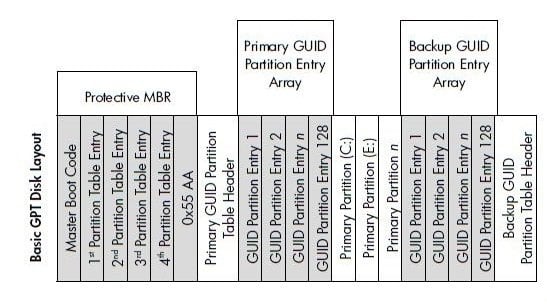
The GPT, or Globally Unique Identifier Partition Table, is a newer disk layout associated with UEFI, replacing the traditional MBR-based partitioning scheme in newer computers. This change is driven by the need for larger storage devices in the computer field, allowing for more efficient use of storage space in modern systems.
A partition table disk supports a maximum volume size of 2^64 blocks, which translates to approximately 9.44 zettabytes, and can have up to 128 primary partitions.
GPT (GUID Partition Table) is less compatible with operating systems compared to MBR (Master Boot Record), which is a more traditional and widely supported partitioning scheme. While GPT offers several advantages, including support for larger disk sizes and improved error handling, its compatibility issues with some operating systems and software can make it a less desirable choice for some users.
▶ 1. Windows XP 32-bit, Windows 2000, Windows NT 4, and Windows 95/98 are unable to read, write, and boot from GPT disks, instead they will only read the Protective MBR.
▶ 2. Windows XP x64 Edition can use GPT disks for data storage, but not for booting.
▶ 3. All versions of Windows, from 7 to Windows 11, can use GPT for data storage, but only the 64-bit versions on UEFI-based systems can use GPT as a system disk.
How to check if your hard disk is MBR or GPT?
You can determine whether your hard drive uses MBR (Master Boot Record) or GPT (GUID Partition Table) style by using either the built-in graphical Disk Management tool or the DiskPart command line. The Disk Management tool provides a graphical interface to view and manage disk partitions, while the DiskPart command line offers a more advanced and detailed way to interact with disk partitions. Both methods can help you identify the style of your hard drive.
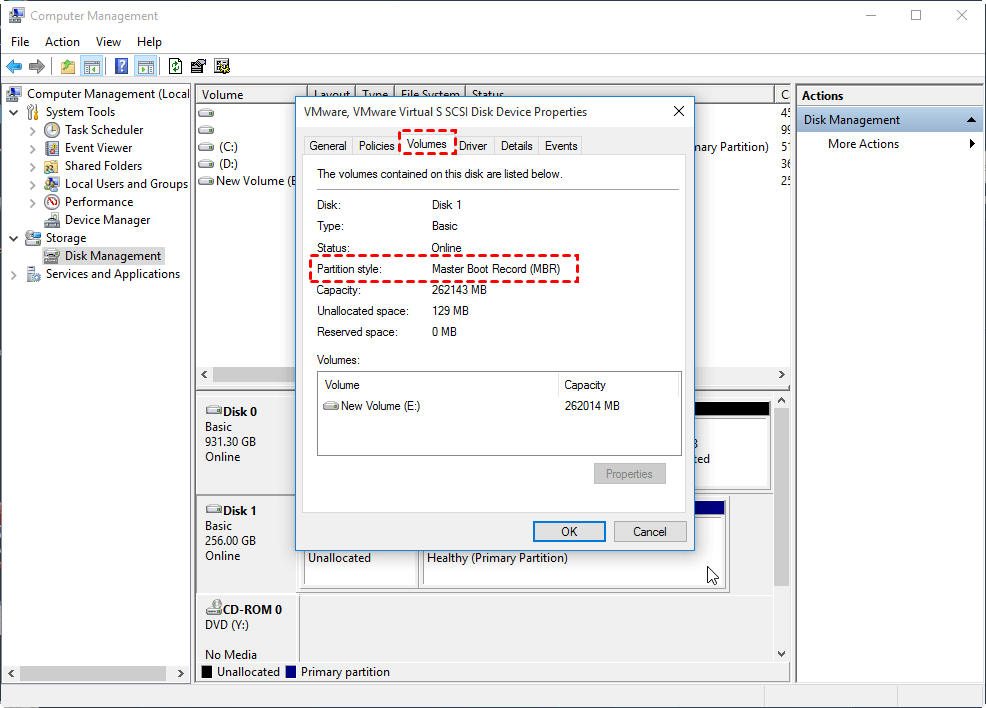
Method 1. Use Disk Management Tool
Step 1. To open Windows Disk Management, press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog, type "diskmgmt.msc" into the box, and click OK.
Step 2. Select the disk (here is Disk 0) you want to check. Right-click it and select "Properties".
Step 3. Select the "Volumes" tab. In the "Partition style" line, you'll know whether your disk is MBR or GPT.
You can also check the disk space using the DiskPart utility in a Command Prompt window, aside from the Disk Management tool.
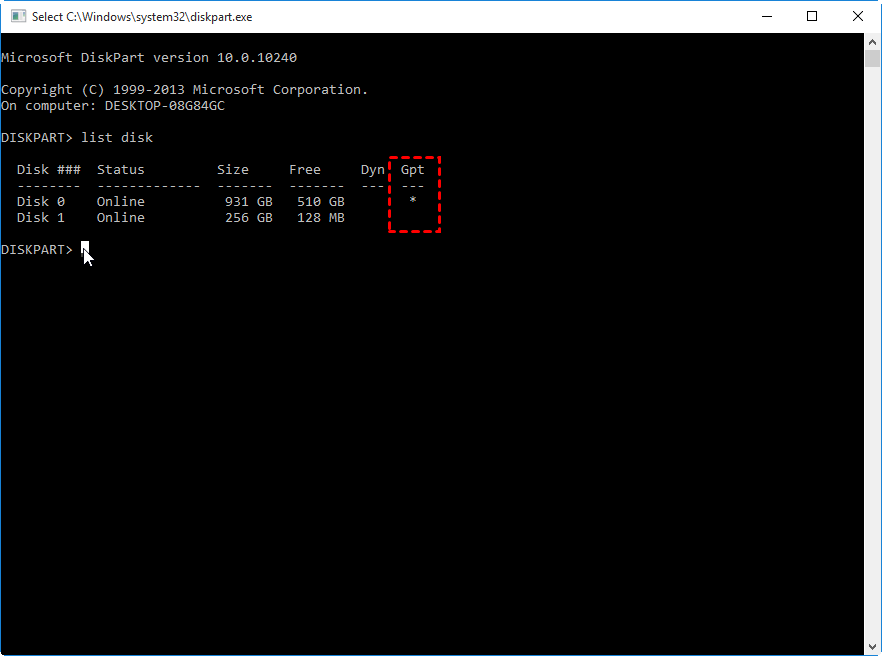
Method 2. Use DiskPart Command Line
Step 1. To launch the DiskPart utility, click the Start menu, type "diskpart" in the Search box, and right-click diskpart.exe to select "Run as administrator".
Step 2. To identify whether a disk is GPT or MBR, type the "list disk" command and hit Enter. This will display a table showing all connected disks, with an asterisk (*) under the "Gpt" column indicating a GPT disk and a blank space indicating an MBR disk. For example, Disk 0 might be a GPT disk, while Disk 1 is an MBR disk.
Should I initialize the disk as MBR or GPT?
When setting up a new hard drive, you can choose between GPT (GUID Partition Table) and MBR (Master Boot Record). GPT is a more modern and flexible partition table that allows for larger partition sizes and more partitions than MBR.
▶ If your hard drive is less than 2TB and you don't need more than 4 primary partitions, you can choose MBR.
▶If your hard drive is over 2TB and you want to create more than 4 primary partitions, or if your motherboard supports UEFI boot and the OS is 64-bit, it's recommended to choose GPT. Otherwise, choose MBR.
How to make a conversion between MBR and GPT when necessary?
The choice between GPT and MBR disk ultimately depends on your specific needs and current partition style. If you're starting from scratch, you can choose GPT for its larger partition size and bootability on UEFI systems, or MBR for its simplicity and compatibility with older systems. However, if you're converting from one to the other, you can use tools like fdisk or parted to convert the partition style from MBR to GPT or vice versa. This process typically involves backing up your data, re-partitioning the disk, and reformatting the file system to match the new partition style. It's essential to exercise caution and carefully follow the conversion process to avoid data loss or other issues.
To convert a disk to either MBR or GPT format, you can right-click the disk in Disk Management, choose "Convert to MBR Disk" or "Convert to GPT Disk", but this only works if the disk has no partitions, requiring deletion of all existing partitions which leads to data loss, and this method doesn't work for system disks.
In this situation, you can use the Qiling Disk Master Professional, a professional partition manager that can convert either a data disk or system disk without deleting partitions and data, and can complete the conversion in just 3 steps.
Step 1. To convert a disk to GPT using Qiling Disk Master Professional, follow these steps: Right-click the disk you want to convert, such as the OS disk, and select "Convert to GPT" from the context menu. Alternatively, click the disk and choose "Convert to GPT" from the right-hand column of the interface. This will initiate the conversion process.
Step 2. Waiting to proceed this operation.
When changing the partition style on the system disk, you need to switch the boot mode from Legacy BIOS to UEFI or from UEFI to Legacy BIOS accordingly.
Final lines
You can learn about the differences between GPT and MBR partition types in this post, and choose the most suitable one for your devices. Qiling Disk Master is a versatile tool for Windows users that can also perform tasks such as moving installed programs, cloning disks, converting file systems, and migrating OS, among others, making it easy to organize your disks and partitions according to your needs.
Related Articles
- 4 Easy Solutions to Fix 'Unable to Extend C Drive' in Windows 11
Are you Unable to Extend C Drive in Windows 11 and looking to fix your problem? Consider yourself lucky! Here, we have four excellent solutions that can help you do so. Read more. - Three Simple Ways to Format a Bootable SD Card (Useful Tips)
You are going to learn at least three ways to format a bootable SD card in Windows 11/10/8.1/8/7. Among these solutions, formatting an SD card with third-party software is my recommendation. Qiling Partition Master can not only format your SD card, SSD, and HDD with simple clicks but also manage your disk with excellent functions. - How to Decrypt and Format Encrypted SD Card [2022 Updated]
When your SD card gets encrypted, you cannot directly format encrypted SD card. You'll have to decrypt the SD card first and then format it. On this page, you'll learn the full process of decrypting SD card even without a password and format the encrypted SD card to a normal state again. - How to Format SSD with Windows on It? [Windows 11/10/8/7]
Do you know how to format SSD with Windows on it? If you are looking for a solution to format SSD with Windows OS on it, this passage will provide you with an efficient way with Qiling Partition Master.