MBR vs GPT: What's the Difference And Which Is Better?
✦ Content Navigation:
- Help! How to choose between MBR and GPT
- What's the difference between MBR and GPT?
- Should I upgrade from MBR to GPT?
- Step-by-step: Convert partition style between MBR and GPT
- Other FAQs about MBR vs GPT
- Conclusion
Help! How to choose between MBR and GPT
When initializing a disk for the first time in Windows, you may be faced with the decision of choosing between MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table) partition styles. While Windows doesn't provide additional information to help you make a decision, understanding the differences between the two can guide your choice. Understanding the differences between MBR and GPT can help you make a informed decision.
GPT (GUID Partition Table) is a standard for the layout of the partition table on a physical hard disk, using globally unique identifiers (GUID). It is more suitable for later systems compared to MBR (Master Boot Record), which is an older partition table that is more compatible with previous systems.
GPT disks offer advantages in terms of partition size, number of partitions, and resilience. With the shift towards UEFI, GPT has become the only supported system disk format, especially with Microsoft's announcement that Windows 11 will only support GPT and UEFI. As a result, GPT disks have become a crucial requirement for upgrading to Windows 11, and converting a MBR disk to GPT may be necessary for a smooth transition from Windows 10.
What's the difference between MBR and GPT?
A GPT disk, compared to an MBR disk, offers better performance in terms of disk space management, partitioning, and data recovery, making it a more efficient and reliable choice for modern storage needs.
▶ GPT supports disks larger than 2 TB in size while MBR cannot.
▶ The GPT disk partitioning style supports volumes up to 18 exabytes in size and up to 128 partitions per disk The MBR disk partitioning style supports volumes up to 2 terabytes in size and up to 4 primary partitions per disk, or three primary partitions, one extended partition, and unlimited logical drives.
▶ GPT disk provides greater reliability The partition table on a GPT disk is protected by replication and cyclical redundancy check (CRC) to prevent data loss. Unlike MBR partitioned disks, the data critical to platform operation is located in partitions, not in unpartitioned or hidden sectors.
▶ GPT partitioned disks have redundant primary and backup partition tables for improved partition data structure integrity.
The differences between MBR and GPT disks are primarily related to the partitioning and booting process. A GPT disk uses a GUID Partition Table (GPT) to store partition information, whereas an MBR disk uses the traditional Master Boot Record (MBR) method.
Typically, MBR and BIOS, and GPT and UEFI are paired together. This is required for some operating systems like Windows, but optional for others like Linux. To convert a system disk to GPT, ensure your computer's motherboard supports UEFI boot mode.
Should I upgrade from MBR to GPT?
If you have an MBI partition table on one of your drives, you might be wondering if it's a good idea to upgrade to the newer GPT standard. The short answer is yes, it's a good idea, but it's not entirely necessary.
In most cases, the answer is probably not. As the saying goes, there's no need to tinker with something that's working perfectly fine.
Modifying the Master Boot Record (MBR) sector can cause permanent damage to your drive, making it unbootable. To fix this, you can either create a recovery USB drive to repair the MBR, or completely wipe the drive and reinstall the operating system.
Dealing with the complications of transitioning from a Master Boot Record (MBR) to a GUID Partition Table (GPT) isn't worth the trouble for most users, but there are specific situations where it might be worth considering, such as upgrading to a drive larger than 2 terabytes or needing more than 26 partitions, provided the hardware supports both GPT and UEFI BIOS.
If you're confident about migrating to GPT, create a backup of your drive and all crucial data to ensure a smooth transition, allowing you to revert to your previous setup if needed.
Step-by-step: Convert partition style between MBR and GPT
After learning about MBR VS GPT, you might need to convert your current partition style, either from MBR to GPT or GPT to MBR. On Windows, you can achieve this using either built-in tools or third-party software.
① Convert to GPT/MBR disk via Windows built-in utilities (Data Loss)
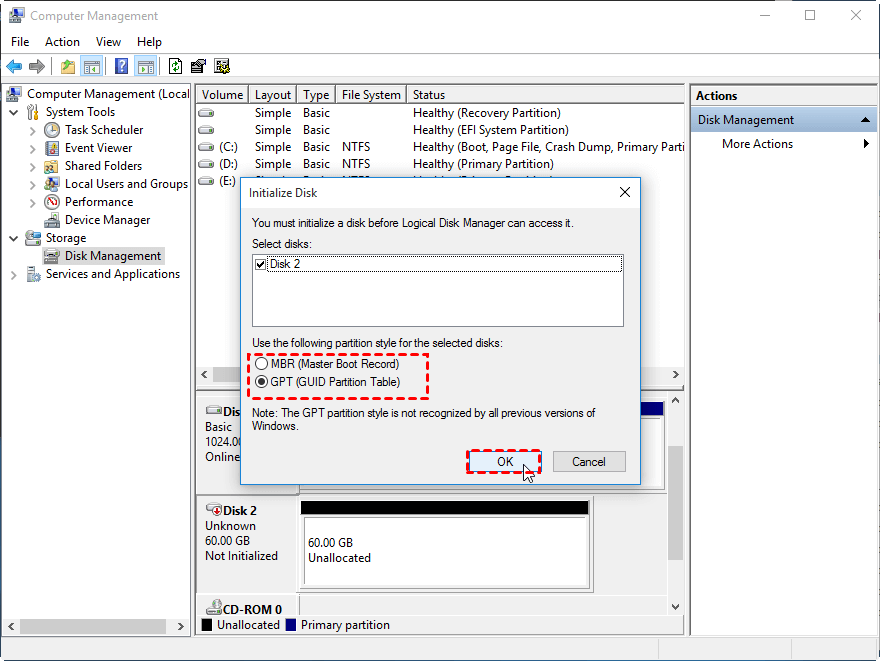
To convert an empty hard disk to MBR or GPT, you can use Windows Disk Management and Diskpart tools. First, delete all existing partitions on the disk, then back up important data to a safe place. After that, use Diskpart to convert the disk to the desired format, such as GPT. This process requires an empty disk, so make sure to remove all partitions before proceeding.
Step 1. To open the Diskpart utility, press the "Windows" key and the "R" key at the same time to bring up the Run dialog box. Then, type "diskpart" and press Enter to launch the Diskpart utility.
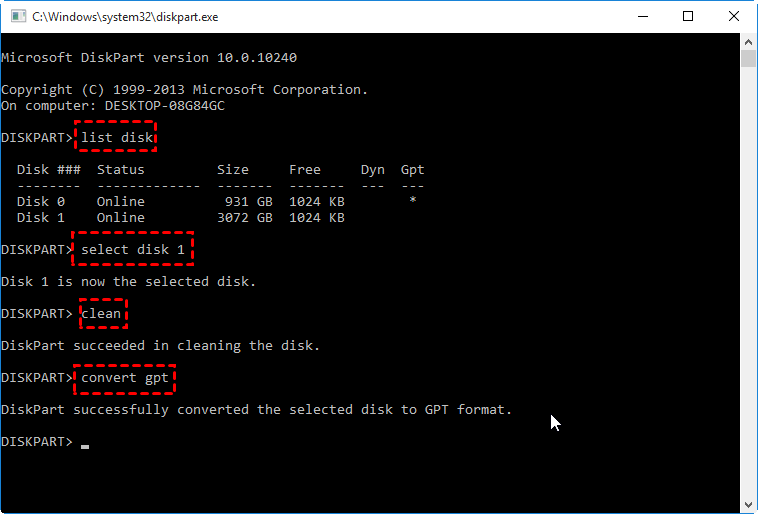
Step 2. 1. List all disks using the command "LIST DISK" and note the disk number of the drive you want to clean.
▪list disk
▪select disk n (where n is the disk number of target disk)
▪clean (this command will erase the entire disk)
▪convert gpt (or convert mbr)
▪exit
Note: To convert a system disk to GPT under Windows, you need to enter WinPE mode and perform the conversion, as the system partition cannot be deleted while Windows is running.
② Convert to GPT/MBR without data loss via professional software (System Disk data safe)
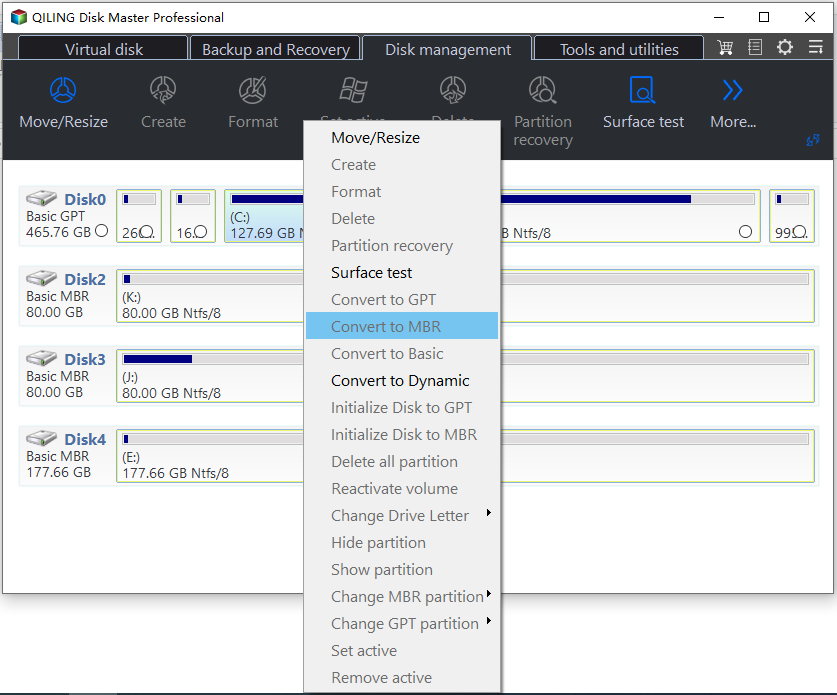
You can use the third-party software Qiling Disk Master Professional to convert MBR to GPT on both system and data disks without deleting partitions, making it a more ideal solution for users with lots of data on the target disk.
To convert MBR to GPT, you can download the Qiling Disk Master Professional Edition Demo, install and run it, and then take the conversion of MBR to GPT as an example.
Note: To prevent data loss due to human errors or unexpected events like power failures, it's a good idea to back up all the data you need.
Step 1. Right-click the MBR disk that you want to convert to GPT and choose Convert to GPT.
Step 2. Waiting for converting to GPT partition.
Notes:
1. A removable disk is also allowed to convert.
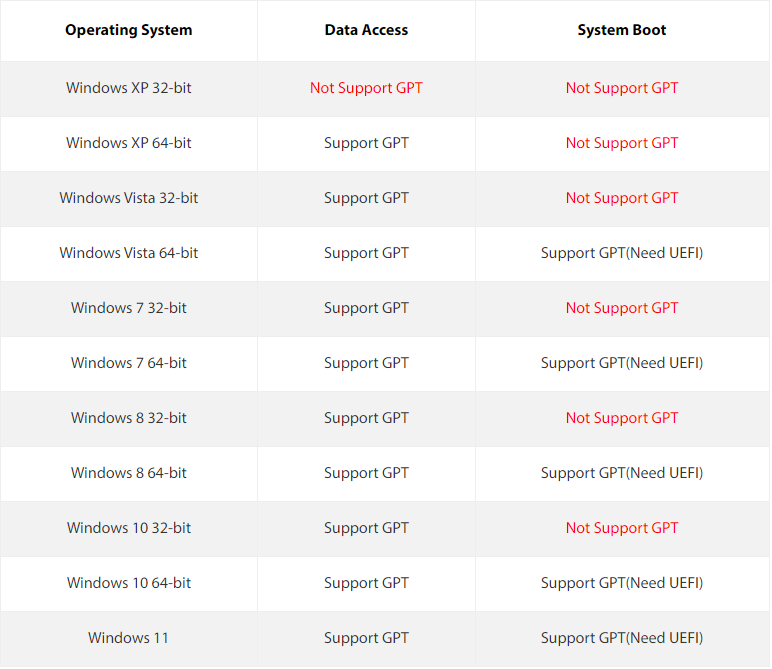
2. To convert a system disk to GPT partition style, you'll need a 64-bit operating system. However, it's worth noting that Windows XP 64-bit has a limitation and can only use GPT for data storage, not as the system disk itself.
3. After converting a system disk from MBR to GPT, or GPT to MBR, you need to switch the boot mode from UEFI to BIOS, or vice versa, for a seamless boot process.
Other FAQs about MBR vs GPT
▶ Is Windows 10 GPT or MBR?
If all other conditions are met, it is recommended to use the GPT partition style due to its reliability and CRC protection.
▶ Should my SSD be MBR or GPT?
SSDs are typically used for installing operating systems, and Windows operating systems can be installed on MBR disks, but some cannot be installed on GPT disks. However, Windows 8 and higher operating systems can be installed on GPT disks.
▶ Can UEFI boot MBR?
UEFI supports traditional MBR hard drive partition, but not Legacy boot GPT.
▶ When need to convert GPT to MBR disk?
When installing Windows, some situations require converting a GPT (GUID Partition Table) disk to MBR (Master Boot Record) format, such as when the selected disk is of the GPT partition style. Fortunately, users can convert GPT to MBR disk with the help of Qiling Disk Master Professional Edition.
Conclusion
With a basic understanding of MBR and GPT, you can now easily convert between the two via different methods, such as using software like Qiling Disk Master, which allows for safe and lossless conversions between MBR and GPT, as well as other partition types, including FAT32 and NTFS, primary and logical partitions, and even rebuilds a corrupted MBR to resolve boot failure issues.
Related Articles
- Fix CHKDSK Is Not Available For RAW Drives in Windows 10
Receive the error “CHKDSK is not available for RAW drives” in Windows 10 on USB flash drive, SD card and external hard drive? Find solutions here. - How to Convert FAT32 to NTFS Windows 10 without Data Loss?
Follow the steps to convert FAT32 to NTFS Windows 10 without losing data or formatting. Three methods are listed for changing FAT32 to NTFS. - Convert Primary Partition to Logical in Windows 7 with Ease
If you are in need of converting primary partition to logical in Windows 7, read this article patiently to get effortless methods. - Change File System between NTFS and FAT32 without Formatting
Want to change file system without formatting for external hard drive, USB drive, etc.? Here shows how to convert between NTFS and FAT32 without data loss.