How to Perform System State Recovery with Wbadmin?
Pros and cons of system state recovery
A system state backup is really helpful when your system settings collapse because of mis-operation, virus attack, malware, etc. It can restore your system settings to the state when the backup was taken, so your system will function normally.
A system state recovery can be performed when your system is offline or online, so it is the most efficient way to recover your system after a disaster. However, a system state backup cannot be counted as a full backup of your computer for it only contains boot files, active directory, cluster database, the registry and other system files. If your computer is in serious status that refuse to boot, a system state backup becomes useless.
System state restore from Wbadmin command line
Disaster recovery is a critical process that ensures your system is restored to a previous state in case of a disaster. Windows Server Backup and the WBadmin utility provide a reliable way to perform disaster recovery. In this article, we'll explore how to use these tools to restore your system state.
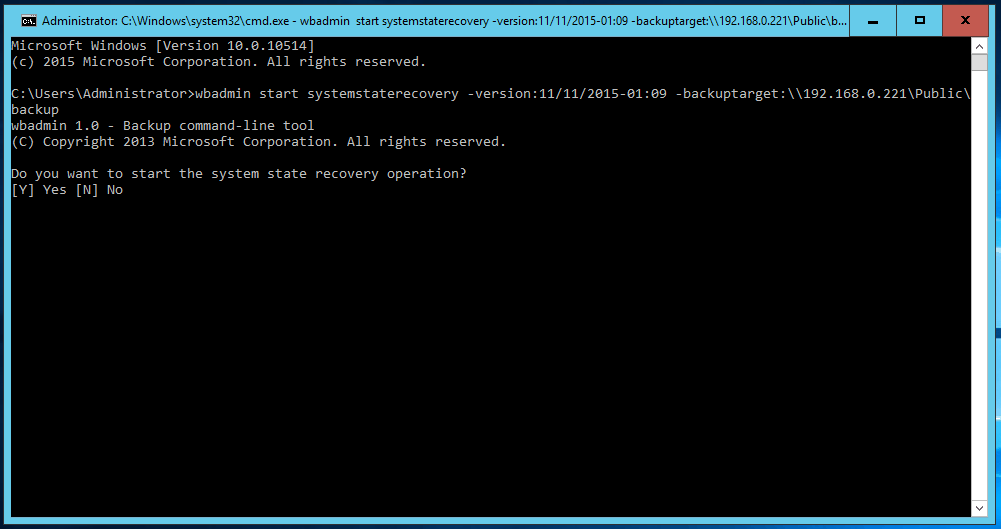
1. Open a command prompt with administrator privileges. Type "CMD" in the search box, right-click Command Prompt in the search results, and then click Run as administrator.
2. Type in a command based on the following syntax and press Enter to run a system state restore.
If you do not know the backup version, you can run the command "wbadmin get versions" to show the version identifier. The backup destination location can be a drive letter, a volume GUID-based path, or a remote shared folder path. If there are multiple computers backed up to a same location, you can use "-machine" switch to specify the server to be recovered. The "-quiet" switch means to run the backup without prompt.
To run a system state restore from the command line, follow these steps:
While the built-in `wbadmin` utility can be used to backup and restore system state data, it may not be sufficient to recover a server from a critical condition. In such cases, using a third-party software can provide a more comprehensive and efficient solution.
Restore system with Qiling Disk Master command line utility
Qiling Disk Master's Server edition is a powerful tool for Windows Server backup and restore. It can also work with Windows PCs, making it a versatile solution for system administrators. With its advanced technology, Qiling Disk Master can perform backup and restore operations quickly and efficiently, while also saving disk space.
1. Open a command prompt. If your Server fails to boot, you can boot it from a bootable rescue media created by Qiling Disk Master.
2. Input the following command to navigate to Qiling Backuper: cd [installation path of Qiling Disk Master] and press Enter. For example: cd C:\Program Files\Qiling\Disk Master.
3. Run the following command to Proceed:
If the backup is saved in remote share folder, you may need to enter user name and password in the form [/u "user name" /p "password"].
To restore a system backup using Qiling Disk Master, you can use the following command:
To restore a system backup saved in a network share to its original location, you can use the following command:
Besides system state recovery, Qiling Disk Master can also be used to transfer system to dissimilar hardware, migrate OS to SSD, synchronize files in two folder, and more.
Related Articles
- System State Backup and Recovery with Wbadmin Commands
For Windows OS, data protection becomes critical because computer failure may cause data loss. But how to backup and restore Windows easily? Wbadmin command lines will help you. - WBAdmin Start Systemstatebackup Command Create System Backup
You can easily protect your system with Wbadmin start systemstatebackup command as well as other 2 alternatives. Learn more below. - Wbadmin in Windows Server 2016 User Manual to Backup and Restore
This article will introduce you to 3 very classis examples of Windows Server 2016 wbadmin, which help you safely protect the system and data on it. For novices, try the easier way! - 5 Methods to Reimage Dell Computer in Windows 10/8/7
If you fail to repair Windows operating system, it may be the time to factory reset it. Read the 5 methods to reimage Dell computer and find the most suitable one for your situation.