Recovery Partition After Upgrading to Windows 10 from Windows 7/8
What Is Recovery Partition?
A recovery partition is a small partition on your hard drive that can help you restore your Windows or troubleshoot system issues. There are two kinds of recovery partitions you may see in Windows, including the system image recovery partition and the system repair recovery partition. The system image recovery partition is used to restore your Windows to its original state by creating a system image, while the system repair recovery partition is used to troubleshoot system issues by running a system repair.
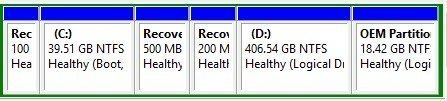
Windows recovery partition
When installing a Windows OS on a hard drive, Windows Setup creates a system reserved partition on MBR disks and a recovery partition and EFI system partition on GPT disks, without a drive letter. The size of the recovery partition varies by Windows version, with Windows 10 consuming 450MB, Windows 8/8.1 using 200MB, and Windows 7 using 100MB.
The Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) is stored on a recovery partition, but it can also be saved on a separate drive or in a folder on the system drive if Windows is installed on a hard drive with multiple partitions. Deleting the recovery partition will prevent the use of Windows Recovery options, but creating a Windows 10 recovery disk allows you to still access these options.
OEM recovery partition
There may be an additional recovery partition, created by the computer manufacturer, that consumes 7-20 GB, containing WinRE and factory installation files, aside from Windows' own recovery partition.
On some computers, the WinRE and factory installation are separately stored on two partitions, allowing you to boot into Recovery Environment by pressing a specified key. This OEM partition can be deleted if you have a Windows installation disc, freeing up disk space.
Why An Extra Recovery Partition Created During Upgrade?
When upgrading to Windows 10, the upgrade program creates a recovery partition if it detects insufficient space on the recovery partition (GPT disk) or system reserved partition (MBR disk). This can result in multiple recovery partitions over time. To prevent this, you can increase the size of the recovery partition or system reserved partition before upgrading to Windows 10.
Microsoft notes that the previous Windows version recovery partition will be nonfunctional after upgrading to Windows 10, allowing you to delete it to free up disk space. The recovery partition created by upgrading to Windows 10 can be identified by its position, as Windows can only shrink a partition from its right side. This means that the recovery partition created by the Windows 10 upgrade will be to the right of the previous one, allowing you to determine which one was created by the upgrade. For example, if you have a 100MB recovery partition from Windows 7, a 200MB recovery partition from Windows 8, and a 500MB recovery partition from the Windows 10 upgrade, you can delete the 100MB and 200MB partitions to free up space.
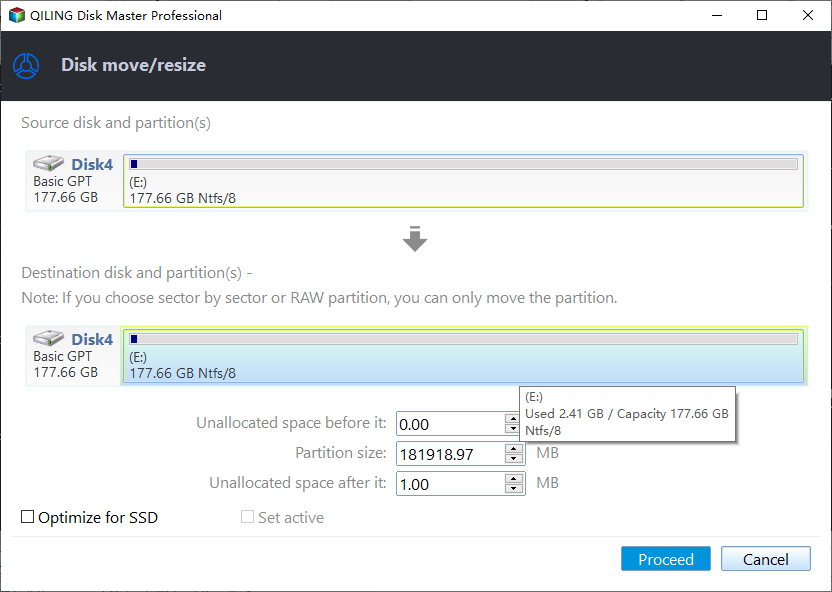
If you're trying to extend the system partition but the new Windows recovery partition is in the way, you can move the recovery partition without losing any data. This will clear the space needed to extend the system partition.
How to Delete Recovery Partition in Windows 10?
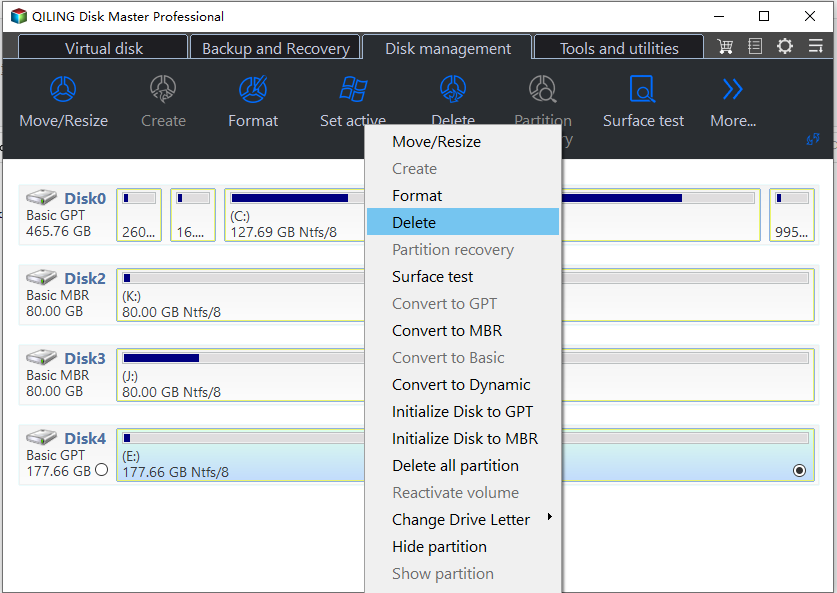
You can't delete a recovery partition using Windows 10 Disk Management, but you can use diskpart.exe to delete it. However, if the recovery partition is before the C: drive, you can't extend the C: drive with the new unallocated space using built-in tools, and you'll need a third-party partition software like Qiling Disk Master Standard to delete the recovery partition and extend the C: drive if there's unallocated space.
1. Download this free software. Install and launch it.
2. To delete a recovery partition, right-click on the recovery partition and select "Delete Partition". This will convert the partition into unallocated space.
3. To merge partitions, click on "Advanced" and then "Merge Partitions". In the resulting pop-out window, select the unallocated space and the partition you wish to extend.
4. Check the pending operations and click "Proceed" to save the changes.
This operation will complete under Qiling PreOS mode, so do not be panic when your computer reboot.
Related Articles
- How to Check If It's UEFI or BIOS on Your PC?
How to check if it's UEFI or BIOS that your PC is running on? Here, 2 ways will be provided to help find it out. - Upgrade BIOS to UEFI Before You Want to Convert MBR to GPT
How to upgrade BIOS to UEFI before converting MBR to GPT? In this post, detailed steps will be given to help get it done easily. - Cannot Convert Partition Between Primary and Logical
Situations that a partition cannot be converted to primary/logical. - Can not Merge Partitions
Solution for cannot merge partitions