Top 2 Ways to Create Incremental Backup in Windows Server 2008 (R2)
Contents of this article:
- Is Windows Server Backup Incremental?
- What Is Incremental Backup?
- Create Windows Server 2008 (R2) Incremental Backup with Windows Server Backup
- Simple Way to Create Windows Server 2008 Incremental Backup
- Further Reading: Windows Server 2008 (R2) End of Support
- Conclusion
Is Windows Server Backup Incremental?
"I understand your concern. Windows Server Backup is a full backup tool, not incremental. This means it will back up all data every time you run it, which can be time-consuming and disk-intensive, especially with large amounts of data. To mitigate the issue, you can try using the 'Backup Once' feature, which will create a full backup of your system, including all data, and then you can schedule periodic backups of only the changed data using the 'Backup Once' feature. Alternatively, you can use a third-party backup software that supports incremental backups, such as Acronis or Symantec, to save time and disk space. I recommend you to check the system requirements and compatibility before using any third-party software."
Windows Server Backup allows you to create an incremental backup, which will automatically delete old backups, only occupying space needed for incremental backup.
An incremental backup is a type of backup that only saves changes made since the last backup, reducing storage space and backup time. To create an incremental backup with Windows Server Backup, you can follow these steps: Open Server Manager, click on "Add roles and features", select "Windows Server Backup" and follow the wizard to install it. Once installed, open the Windows Server Backup console, select the drive you want to back up, and choose "Custom" as the backup type. Then, select the "Incremental" option and choose the location where you want to save the backup.
What Is Incremental Backup?
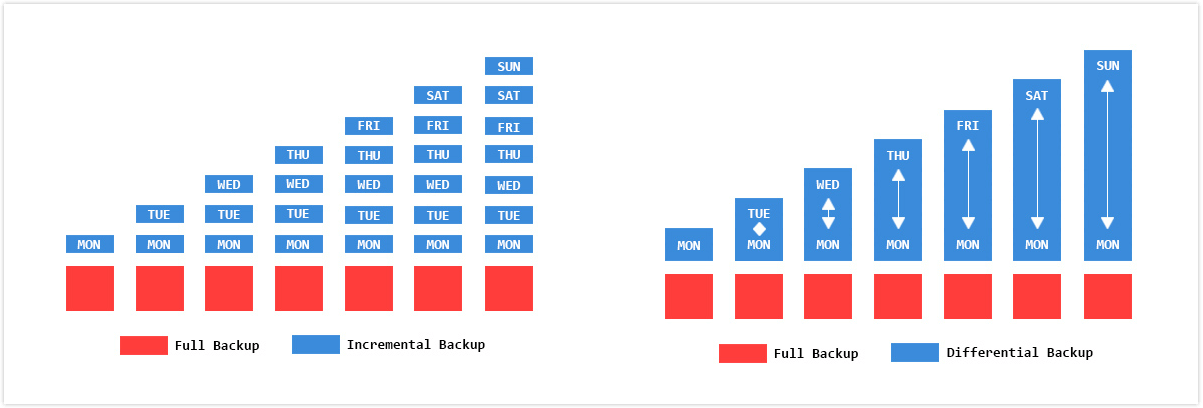
There are three types of backups: Full, Incremental, and Differential. A Full backup includes all data, while Incremental and Differential backups only store changes made since the last Full or Differential backup, respectively. The first backup is always a Full backup, and subsequent backups are either Incremental or Differential based on the type of backup taken after the Full backup.
Incremental backup: The backup system creates a new backup based on the last one, either full or incremental, which then depends on the previous image files, making them mutually dependent, and if one is deleted, all subsequent ones become invalid.
Differential backup: The backup system is designed to capture all changes since the last full backup, making it relatively independent and allowing for quick recovery with just one full backup and the latest differential backup. This ensures data integrity by using the most recent differential backup.
Incremental backups are a more efficient option, taking less time and disk space compared to full backups. They're a good choice if you want to maximize your backup method with minimal storage usage, but make sure the backup drive is secure. Alternatively, differential backups are also a viable option, offering ease of management and added safety, eliminating the risk of damaged backup images. For more information on the differences between incremental and differential backups, click here.
Create Windows Server 2008 (R2) Incremental Backup with Windows Server Backup
In Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2, Windows Server Backup can be used to create incremental backups with minimal disk space usage, but it requires manual installation through Server Manager.
To install the Windows Server Backup feature, open the Server Manager in Administrative Tools and click Features. Then click Add Features > Select Features and choose Windows Server Backup Features and click Install.
I'm happy to help! However, I need a bit more information to provide a concise answer. Could you please provide the context or details about what you are trying to accomplish with the incremental backup?
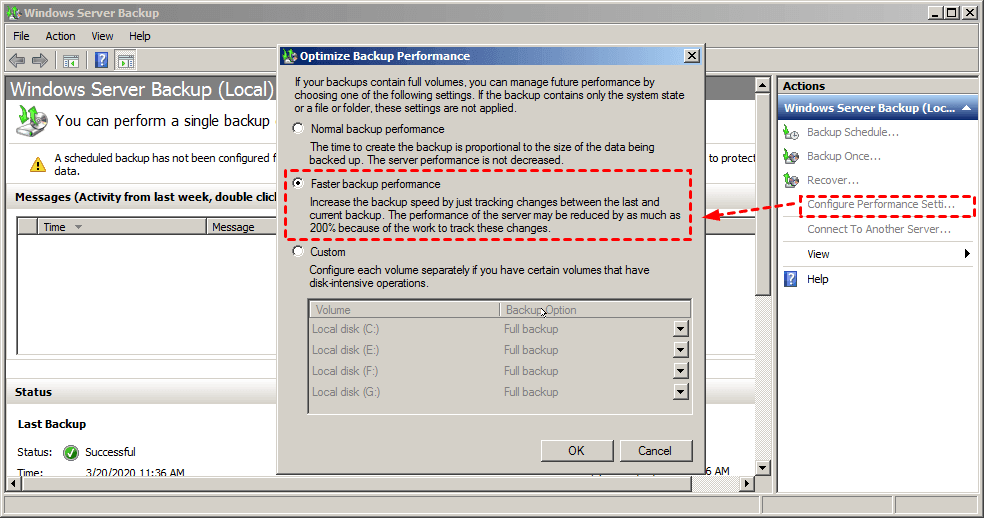
1. To open Windows Server Backup, click Start, then select Administrative Tools, followed by Windows Server Backup. From there, select Configure Performance Settings in the Actions column.
2. Tick Faster backup performance, and press OK.
Notes:
- Normal Backup Performance: It is what we call a full backup, which takes longer. (Note: I assume you meant to say "It is what we call a full backup, which takes longer to complete.
- Faster backup performance: An incremental backup is a type of backup that only saves the changes made since the last backup, rather than backing up the entire system or data set again. This approach helps reduce storage space and backup time, making it a more efficient and cost-effective option for data protection.
- Custom: This feature enables users to customize backup settings for individual volumes, allowing for specific backup types like full or incremental backups to be set for different partitions, such as data or system partitions.
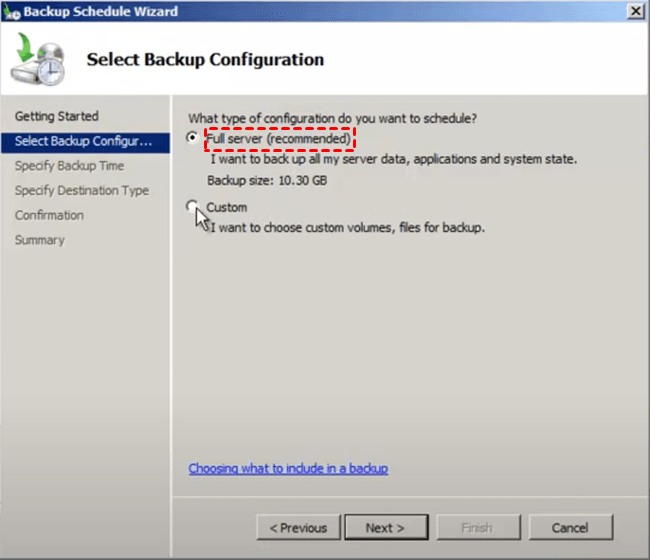
3. Press the "Backup Schedule..." button in the "Actions" column, then click "Next >".
4. Tick Full Server (Recommended), and press Next >.
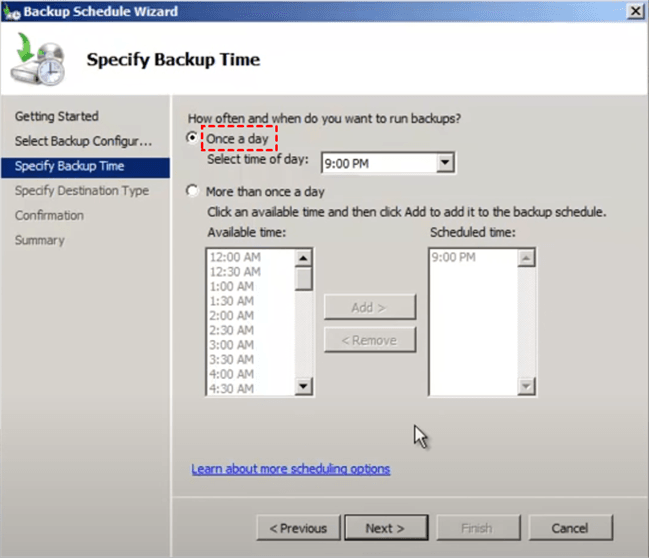
5. Select the desired frequency of backup, which can be "Once a day" or "More than Once a day", and specify the preferred time for the backup to take place, then proceed to the next step.
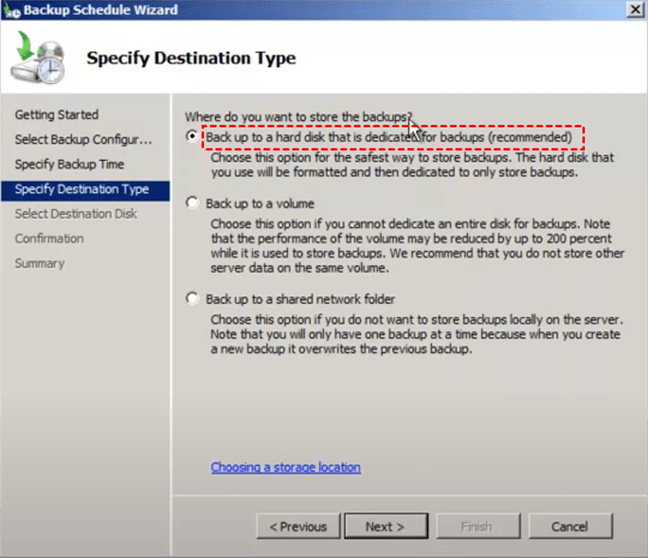
6. Select Back up to a hard disk that is dedicated for backups (recommended), and press Next.
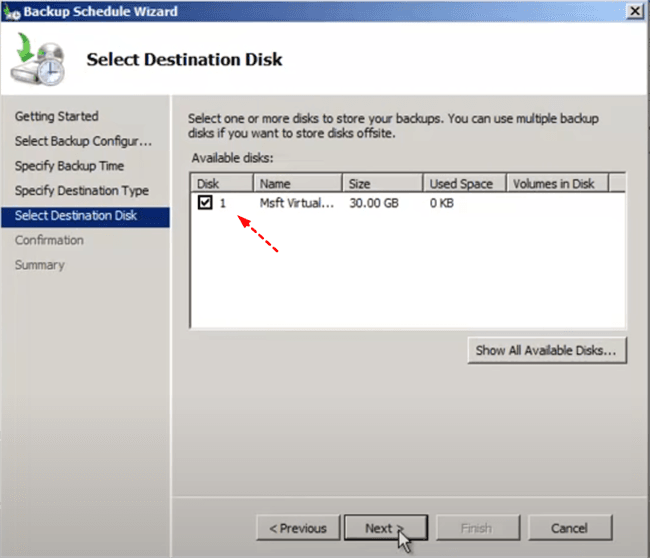
7. To add a disk to the system, select the disk from the list of available disks, click "OK" to add it, and then select it again before clicking "Next >".
8. Confirm the Windows Server 2008 (R2) incremental backup task and press Finish to create it.
In Windows Server 2008, you can create an incremental backup. This means that only changes made since the last backup will be backed up, rather than the entire system. You can use the built-in Windows Backup tool, wbadmin, to perform this type of backup.
However, there are some limitations of Windows Server Backup:
- You can schedule a backup to run once a day, or more frequently than once a day, such as every few hours or every minute.
- Windows Server Backup in Windows Server 2008 (R2) and Windows Server 2003 (R2) had a limitation that it could not backup volumes larger than 2 TB.
- Removable storage media not supported, like Tape, CD, USB flash drive, etc.
- Windows Server 2008 does not support backing up to a network share. Windows Server 2008 R2 and newer systems support, but it will only keep the latest network shared backup.
- Windows Server Backup does not support differential backup.
If you encounter issues or find the steps too complicated, you can create a Windows Server 2008 (R2) incremental backup using third-party software. This allows you to complete the backup task in simple steps and set up scheduled backups and incremental backups with a backup retention policy.
Simple Way to Create Windows Server 2008 Incremental Backup
Qiling Disk Master Server is a reliable and professional server backup software that creates incremental backups in Windows Server 2008, offering flexibility and ease of use. Its advantages and features include:
- All-in-one backup solutions: The five types of backups are system backup, disk backup, partition backup, file backup, and cloud backup. A system backup captures the entire operating system, including installed programs and settings. A disk backup saves the contents of an entire disk, including all files, folders, and operating systems.
- Flexible backup settings: It supports 5 schedule backup options, enabling one allows incremental backup without configuration, and you can also switch to differential backup and set automatic backup cleanup methods.
- Rich backup storage: You can store backups on various mediums, such as local disk, external hard drive, USB flash drive, CD/DVD, Network share or NAS, and even the cloud, and maintain multiple backups across all of them.
Please download Qiling Disk Master Server to have a try!
For a company with multiple computers or locations, the Qiling Disk Master TechPlus edition is a suitable option for creating an incremental backup. This edition supports an unlimited number of PCs and servers, allowing you to run the software from a flash drive without reinstalling it. This makes it a convenient and efficient solution for backing up data across different locations.
Step 1. Launch Qiling Disk Master Server, click Backup, and choose Disk Backup, System Backup, Partition Backup, File Backup, or Cloud Backup.
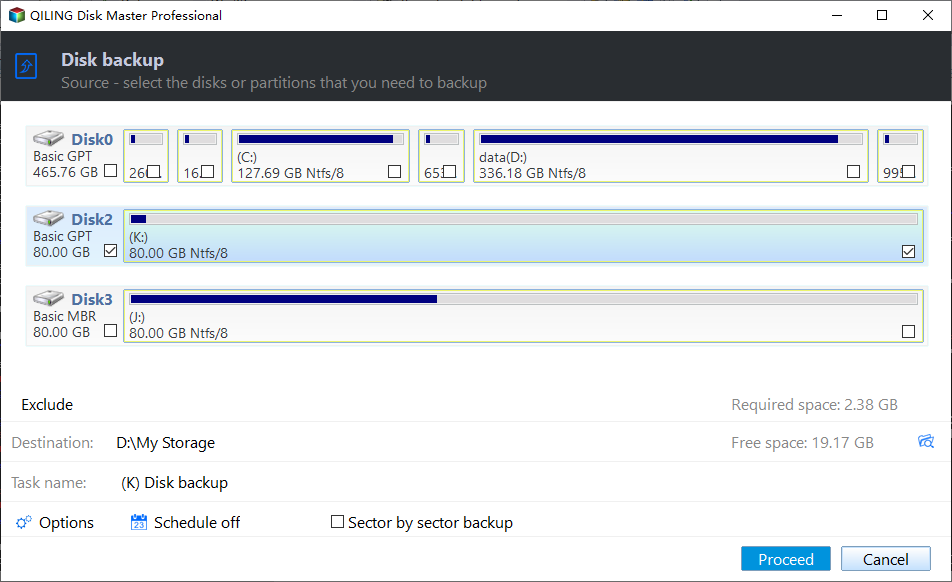
Step 2. Click Disks to choose Windows Server 2008 or 2008 R2 hard disk. Rename the Task Name if required.
Note: You can backup multiple hard drives simultaneously, but restore them individually. To do this, click on "Disks" to select the disks you want to backup, but when restoring, select each disk separately.
Step 3. To store backup images, press the inverted triangle icon and select a local path or add a share or NAS device, ensuring it's connected and accessible with proper permissions.
Step 4. To schedule a backup, click Schedule Backup and select a backup frequency, such as daily, weekly, or monthly, and optionally enable event triggers or USB plug in, with incremental backup enabled by default.
Besides, you still enjoy other useful features:
- Options: Windows Server 2008 R2's backup feature allows for incremental backups, as well as the option to split, compress, or encrypt the backup image. It also enables email or SMS notifications, utilizes Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS), and more.
- Schedule Backup: You can still set the computer to wake up to run a scheduled task and choose an action to take after the task is complete, such as shutting down, restarting, sleeping, or hibernating.
- Backup Scheme: To free up space, you can use different backup methods and automatic cleanup to delete old backup images. This can be done through incremental backup, or by setting up a hierarchical deletion method, such as daily, weekly, or monthly backups, which automatically delete older images.
Step 5. The Windows Server 2008 R2 incremental Backup task will automatically create a full backup initially, followed by incremental backups whenever changes occur, which can be triggered by clicking the "Proceed >>" button.
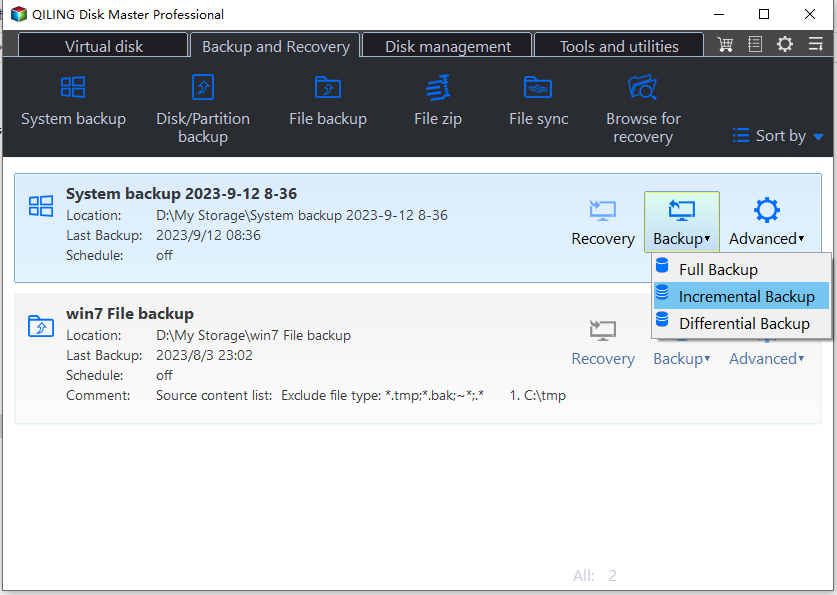
✎ How to set incremental backup manually:
To perform an incremental backup, go to Home > Find the backup task, and click the more options icon > Backup > Incremental Backup. This can also be done by selecting full backup or differential backup.
Further Reading: Windows Server 2008 (R2) End of Support
Microsoft has ended support for Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2, which means no more security updates, drivers, or patches, leaving these systems vulnerable to attacks and potential crashes.
You should decide based on the severity of the potential security breach, the likelihood of it occurring, and the cost of the upgrade. If the potential breach is severe and likely, and the cost of the upgrade is low, it would be wise to upgrade. On the other hand, if the potential breach is minor and unlikely, and the cost of the upgrade is high, it might not be worth it.
- If you want to keep your Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2 safe, the best thing to do is upgrade to a newer version like Windows Server 2012, 2016, 2019, or 2022, which will give you free security updates to protect your data. You can either do an in-place upgrade or a clean install.
- If you're running Windows Server 2008 or 2008 R2, it's recommended to schedule a weekly backup of the entire server. For individual files or folders, daily backups may be necessary.
Data protection is crucial, even for systems that are still supported, as they can be vulnerable to viruses like ransomware and other issues.
Conclusion
You can create incremental backups in Windows Server 2008 or 2008 R2 using the methods described above. However, if Windows Server Backup is not functioning as expected, consider using Qiling Disk Master Server, which supports various backup solutions, including system backup, disk backup, incremental backup, and differential backup, offering more flexible backup settings.
If you want to back up all files and folders from a Windows Server 2008 (R2), you can use file backup or File Sync to keep data and changes synced to a destination, allowing for easy modification and addition of new files without needing to restore an image file first.
Related Articles
- Step-by-step to Create Incremental Backup with WBADMIN Tool
If you don't clearly know Wbadmin incremental backup, keep reading this article, it helps you save much time and disk space, especially in a scheduled task. - Windows Server Backup Not Doing Incremental Backup? Solved Now!
Windows Server Backup incremental not working? This guide explains why Windows Server Backup not doing incremental backup but always perform full backups even when the settings are right. - How to Let Windows Server Backup Overwrite Old Backups
You can perform Windows Server backup overwrite old backups manually with 3 methods in simple steps, to make it flexible and automatic, try professional backup and restore software. - How to Use Windows Server Backup for Active Directory Backup
Backing up Active Directory is important for Windows Server users. Learn how to backup Active Directory 2008/2012/2016 efficiently in this article. - Windows Server Backup Restore Step by Step Guide
How to restore Windows Server backup? This article will detail every step of Windows Server Backup restore. It applies to Server 2022, 2019, 2016, 2012, 2008, etc.