(Fixed)Windows Server Backup Keep Only One Copy
How does Windows Server Backup work?
Before diving into the world of deep learning, it's essential to gain a solid understanding of Windows Server Backup and how it operates during the backup process.
Windows Server Backup (WSB) is a feature that offers robust backup and recovery capabilities for Windows server environments. Administrators can utilize it to back up the entire server, system state, specific storage volumes, or individual files and folders, as long as the data volume does not exceed 2 terabytes. But how does it actually work?
When you run a backup, especially a Windows Server Backup to a network share incremental backup, it creates a VHD file for the source volume. The process also generates a shadow copy of the target backup drive, where the image backup is stored. The backup time, shadow copy identifier (Shadow Copy ID), and version identifier are then recorded in the backup catalog. This allows you to restore your server using the shadow copies. However, if you continue to run scheduled backups, a large number of shadow copies will be accumulated.
Does Windows Server Backup keep only one copy?
One might assume that Windows Server Backup automatically deletes old backups to conserve storage space. However, this is not the case. Windows Server Backup does not have a built-in mechanism to automatically delete old backups, which means that it will continue to store all previous backups, resulting in a large accumulation of backup data over time.
In fact, when you configure a disk for scheduled backups in Windows Server, it automatically enables backup version and space management within Windows Server Backup. This feature allows old backups to be deleted and the resulting space to be reused for creating new backups. As a result, you will not encounter issues with running out of space when creating scheduled backups.
Before reusing the space, Windows Server Backup will first check if shrinking the storage space allocated for snapshots (the 'diff area') will provide enough space for the new backup. If so, it will proceed to shrink the diff area. However, it will not shrink it to less than 1/8 of the target volume size.
Causes and solutions to Windows Server Backup keep only one copy
Encountering the error 'Windows Server Backup keeps only one copy' can be frustrating. So, what are the main reasons behind this issue, and how can you resolve it? Below, we'll explore the primary causes and provide corresponding solutions to get you back on track.
- Firstly, it's possible that the backup mode was automatically switched from incremental to full backup. To troubleshoot this, check the current backup mode and reset it to normal full backup if necessary.
- Secondly, it's possible that the disk is corrupted. To verify this, run a disk check on the current disk. If the disk is indeed corrupted, you'll need to set up a scheduled backup using a new hard drive within Windows Server Backup.
- Thirdly, you can adjust the disk space used by VSS by running the command 'vssadmin resize shadowstorage'. In this scenario, you may need to recreate multiple schedules within Windows Server Backup. Alternatively, if you need to adjust the space, you can do so directly within the Shadow Copies.
Note: Windows Server Backup does not have a feature to limit the number of copies to keep or the number of copies to be stored. However, it's essential to ensure that Windows Server Backup does not overwrite older backups to make room for new ones, effectively shrinking the space occupied by old backups.
Easier way to keep multiple backup copies
According to the article, if you want to keep multiple copies with Windows Server Backup, you can try to fix the issue and then recreate the backup. However, the article also warns that the provided solutions may not work in all cases, leaving you with limited options to achieve your goal of keeping multiple backups.
For a straightforward solution, consider using a reliable backup software like Qiling Disk Master Server. This tool is compatible with various Windows Server versions, including 2003, 2008, 2012, 2016, 2019, and 2022, as well as Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10, and 11.
By utilizing Qiling Disk Master Server, you can efficiently create and manage multiple backup copies. You can specify the desired number of backup copies to keep and automatically delete old backup images when the maximum number is exceeded. Here are some features you can leverage to make it work:
- Daily/weekly/monthly schedule backup: "Qiling Disk Master Server enables you to schedule regular backups of any desired items. You can also set specific backup times or intervals, allowing for a flexible and automated backup process.
- Wake the computer to run scheduled tasks: "Once enabled, Qiling Disk Master Server will automatically wake your computer 2 minutes prior to the scheduled backup time and execute the task. This feature is particularly useful for setting backups during off-peak hours.
- Incremental or differential backup: "This option is set to back up only changed files, ensuring that the latest updates, newly installed applications, and modified files are included in the backup.
- Backup scheme: "It enables you to set the number of backup copies you wish to retain and automatically delete old backup images when the specified number is exceeded. A total of 5 options are available.
Now, let's begin creating multiple scheduled backups using Qiling Disk Master Server:
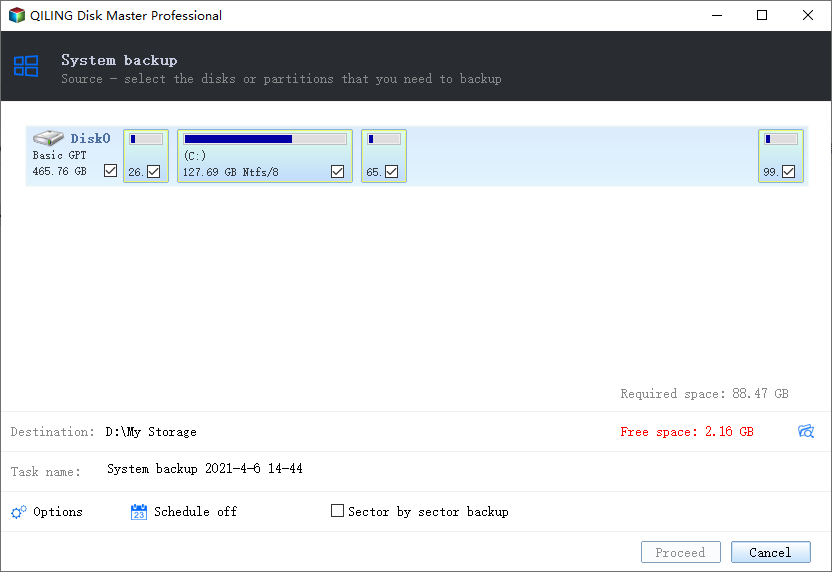
1. First, download, install, and launch Qiling Disk Master Server. Next, navigate to the main page and click on 'System Backup' under the Backup tab.
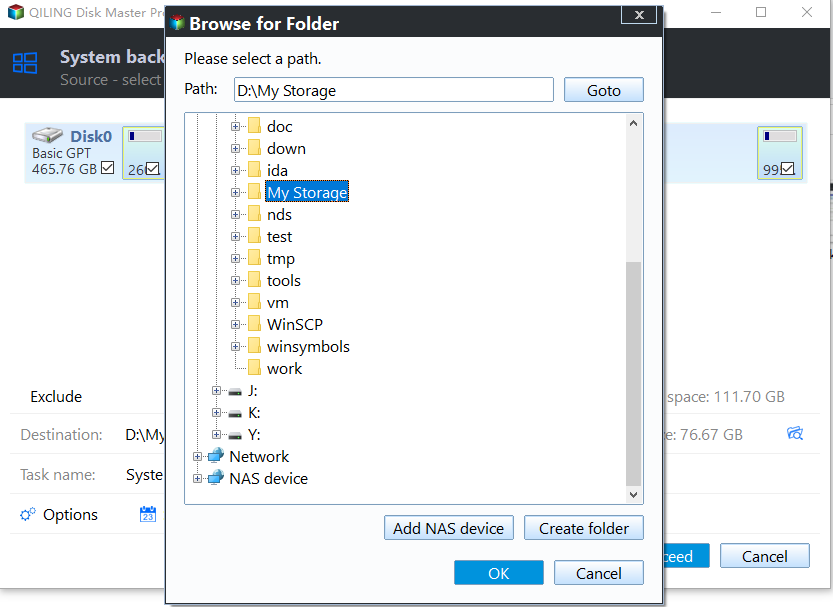
2. Click the folder icon to select a destination path for your scheduled backup.
"By default, this software will automatically select all necessary items for system restore. This is because there is a hidden boot-related partition on your computer, and if you ignore it, system restore may fail.
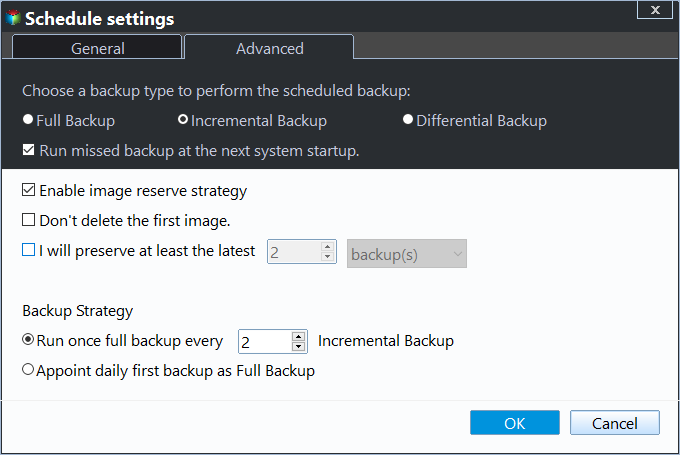
4. Click on the 'Schedule' option and choose your preferred settings from the 5 available options: Daily, Weekly, Monthly, Event triggers, and USN plug-in.
5. To set up your backup method, navigate to the 'Backup Scheme' tab and select either Incremental or Differential Backup. You can also choose to automatically clean up backup images by enabling the backup cleanup feature.
Step 6. After all settings are done, click "Proceed" to start the first backup.
How to manually free up space using wbadmin delete backup
In Windows Server 2012 and later operating systems, the 'wbadmin delete backup' command is used to delete non-system backups. If you're using one of these systems, you can learn the syntax and required parameters for this command-line utility.
wbadmin delete backup syntax:
wbadmin delete backup
{-keepVersions: | -version: | -deleteOldest}
[-backupTarget:]
[-machine:]
[-quiet]
One and only one of the following parameters must be specified: -keepVersions, -version, or -deleteOldest.
Parameters you may use in "wbadmin delete backup" command:
- -keepVersion: "The -keepVersions option specifies the number of the latest backups to keep. A positive integer value must be provided. If 0 is specified, all backups will be deleted.
- -version: Version identifier of the backup in MM/DD/YYYY-HH:MM format.
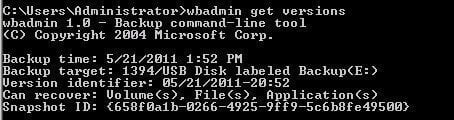
If you're unsure, you can use the command "wbadmin get versions" to verify which version can be deleted. Alternatively, use "wbadmin get times" to view the version type.
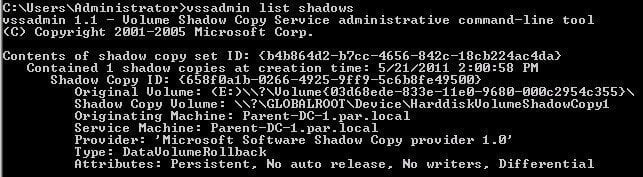
For added clarity, you can run the command `vssadmin list shadows` in an elevated command prompt. If you're still unsure, you can assign a drive letter to the shadow copies and then view their contents in File Explorer using the Diskshadow tool.
- -deleteOldest: delete the oldest system state backup.
- -backupTarget: "To locate backups not stored on the local computer, you can assign a drive letter, mount point, or GUID-based volume path to the shadow copies.
- -machine: "To specify the computer containing backups you want to delete, use the -computer parameter, typically when backing up multiple computers to the same location, and used in conjunction with the -backupTarget parameter.
Then, let's get more space by wbadmain delete backup:
1. Right-click on the Start icon and select Command Prompt (Admin) from the context menu.
2. specific the backup you want to delete by wbadmin delete backup syntax.
For example, you just want to keep the lastest 3 backups on the F: drive in the machine WIN-9814GD4FH95, you can type as follow.
wbadmin delete backup -keepVersions:3 -backupTarget:F: machine:WIN-9814GD4FH95
3. Type exit and press Enter to leave this window.
As mentioned earlier, wbadmin delete backup only works for non-system backup in Windows Server 2012 and later operating systems.
Thus, if you are using Windows Server 2008 or other previous systems, you can choose to delete its shadow copies by diskshadow. For details, please refer to wbadmin delete backup for Windows Server 2016/2012/2008.
Also, you may want to delete system state backup to gain more capacity. To make it you can use another command-line tool, it's wbadmin delete systemstate backup.
Once you're familiar with the syntax of the `wbadmin delete backup` command and its parameters, using `wbadmin delete systemstate backup` will be a breeze. The syntax and parameters are identical, and you'll simply need to replace `backup` with `systemstate backup`.
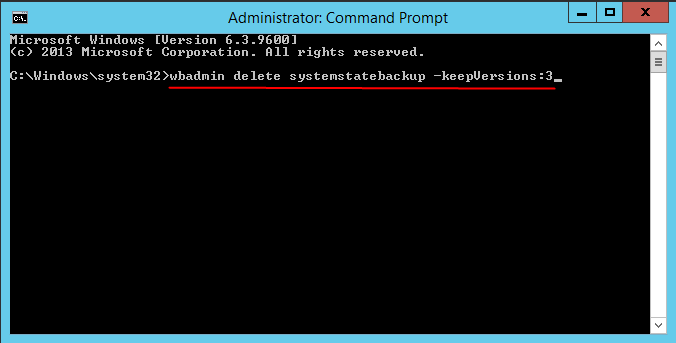
To delete all system state backups, except the most recent 3, run the following command in the Command Prompt window and press Enter to execute.
Type wbadmin delete systemstatebackup -keepVersions:3
Written in the end
While Windows Server Backup allows for multiple scheduled backups, it doesn't offer the flexibility to specify the number of copies to keep. This can sometimes lead to errors, such as "Windows Server Backup keeps only one copy". For a more straightforward solution, consider an alternative approach to keep multiple copies.
Qiling Disk Master Server offers a convenient solution for achieving multiple backup copies. With its flexible scheduling options and various backup methods, you can easily protect your server computer using one or more of its features. Furthermore, you can specify the desired number of backup copies to keep in advance, ensuring that your backup scheme meets your needs.
For businesses within a single organization, Qiling Disk Master Technician Plus is a suitable option. This software can be used on an unlimited number of servers and computers, making it ideal for creating automatic backups on all devices, deploying system images to multiple computers simultaneously, and creating bootable media on a removable device.
Related Articles
- Windows Server Backup: Differential & Incremental Backup
Understand how Windows Server Backup differential backup works (although Microsoft calls it incremental backup) and get the methods to take differential or incremental backup in Server 2008, 2012, 2016, etc. - How to Let Windows Server Backup Overwrite Old Backups
You can perform Windows Server backup overwrite old backups manually with 3 methods in simple steps, to make it flexible and automatic, try professional backup and restore software. - How to Create Multiple Schedules in Windows Server Backup
Read this guide to get three practical ways to create multiple schedules in Windows Server Backup. Applied to Windows Server 2003, 2008, 2012, 2016, etc. - Top 3 Best Download Free Backup Tools Work with A Restore Tool
Backup tools work with a restore tool is a term that Windows users search a lot. Check the backup tools list and examples in the article and select a suitable backup and restore tool according to your needs.