Let Windows Server Backup Overwrite Old Backups Now
- Windows Server Backup Not Overwriting Old Backups
- Why Is Windows Server Backup Disk Space Management Not Working
- How to Make Windows Server Backup Overwrite Old Backups Manually
- Way 1. Change Snapshot Storage
- Way 2. Use Vssadmin Delete Shadows
- Way 3. Use Wbadmin Delete Systemstate Backup
- How to Backup Windows Server and Delete old Backups Automatically
- Conclusion
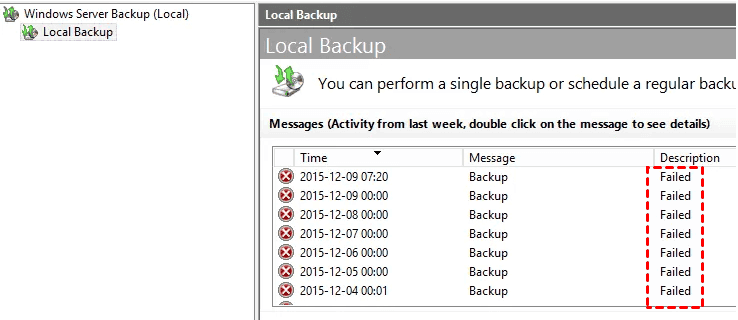
Windows Server Backup (WSB) is a built-in backup utility in Windows Server, allowing you to backup various components, including folders, volumes, system state, entire disks, and even perform bare metal backups and recoveries. However, you may encounter an issue where WSB fails to run due to a backup disk being full.
If you're experiencing issues with Windows Server Backup (WSB) failing to delete old backups, don't worry. This article will help you understand the reasons behind this issue and provide a step-by-step guide on how to let Windows Server delete old backups.
Windows Server Backup Not Overwriting Old Backups
I set a schedule full backup to a volume in Windows server 2008. It running smoothly until today, now my full backup failed due to the disk full and contains 2 old backups.
I thought the old backups will be deleted automatically to keep the newest backup after several backups; I don’t have any other options to modify. How can I keep the most recent versions of the backup and overwrite the oldest backup to spare space on my hard disk?
Why Is Windows Server Backup Disk Space Management Not Working
When you perform a backup using Windows Server Backup, especially incremental backups to a network share, the process creates a virtual hard disk (VHD) file for the source volume. This VHD file is a critical component of the backup process, and it plays a key role in the overall backup and restore process.
When the target storage location for Windows Server Backup is full, the auto-delete feature kicks in to free up space for the current backup. This feature is designed to automatically manage the storage space allocated for snapshots, ensuring that there's always enough room for new backups.
However,
Windows Server Backup will not shrink the storage space of shadow copies to 1/8 below the target volume size. That's why your backup failed and Windows Server Backup not deleting old backups.
One common misconception about Windows Server Backup is that there's a limit to the number of backup copies that can be stored. However, this is not the case.
How to Make Windows Server Backup Overwrite Old Backups Manually
You have three ways to make Windows Server Backup remove older backups: Change snapshot storage, use vssadmin delete shadows, or wbadmin delete systemstatebackup.
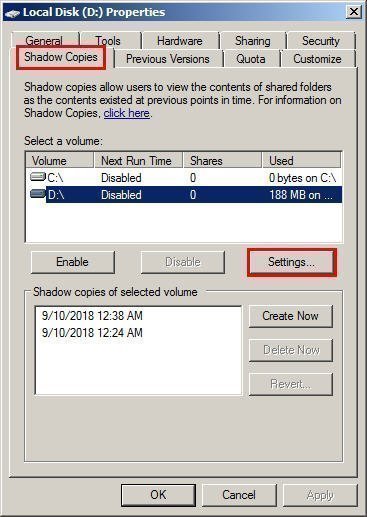
Way 1. Change Snapshot Storage
1. Double click the Computer, right click the volume containing shadow copies (snapshot), and choose Properities.
2. In Shadow Copies section, press Settings to change the path.
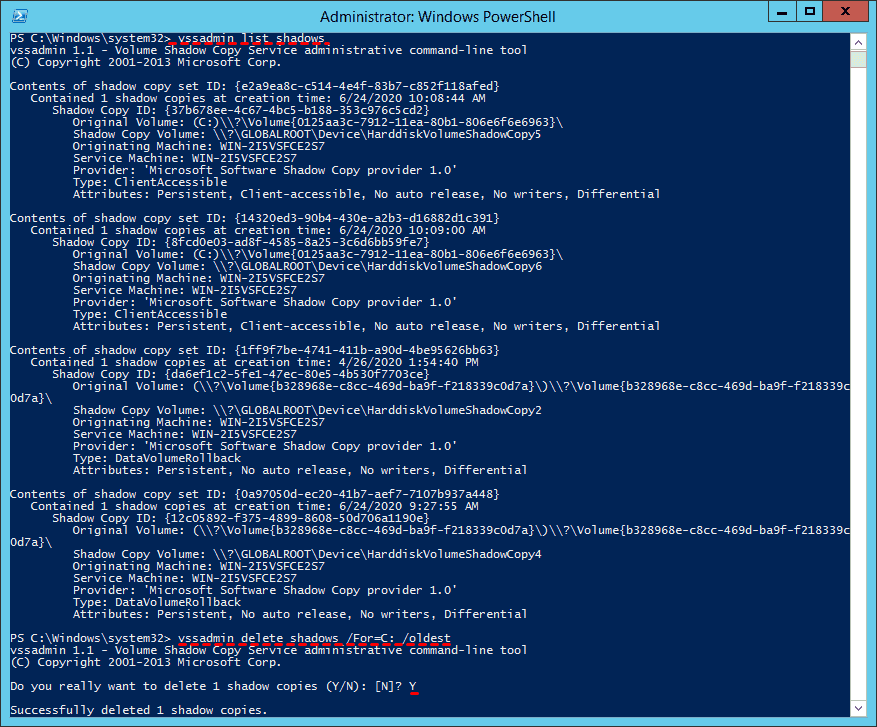
Way 2. Use Vssadmin Delete Shadows
1. Click Start, and input cmd in search box, run as administrator.
2. First of all, run the following command to track Windows Server backup multiple copies, like Shadow copy ID, creation time, shadow copy volume, etc.
vssadmin list shadows
3. To delete shadow copies on Windows Server, you can use the following command in the Command Prompt (cmd):
vssadmin delete shadows /For=C: /oldest To delete shadow copies on Windows Server, you can use the following command in the Command Prompt (cmd), replacing `C:` with the correct volume letter that contains the shadow copy you want to delete:
To delete shadow copies on Windows Server, you can run the following command in the Command Prompt (cmd):
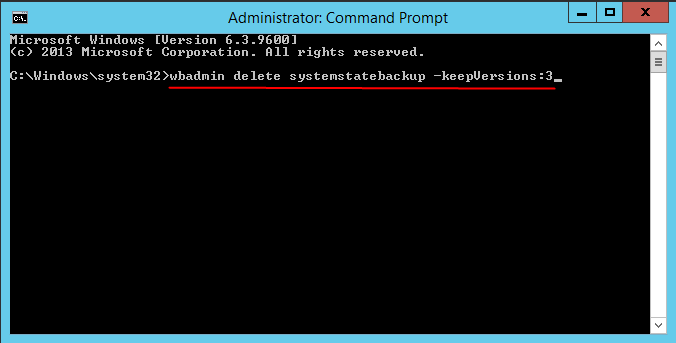
Way 3. Use Wbadmin Delete Systemstate Backup
1. Right click Start menu and select Command Prompt (Admin).
2. Type the following command and press Enter to delete all system state backups, except the most three copies.
wbadmin delete systemstatebackup -keepversions:3
However, it's not guaranteed to get free space, and sometimes you may find Windows Server Backup keeps only one copy. Thus, it's wise to get a professional third-party backup software to backup Windows Server and manage backup versions effortlessly.
How to Backup Windows Server and Delete old Backups Automatically
In addition to Windows Server Backup, you can use a professional backup and recovery software, such as Qiling Disk Master Server, to back up your system, entire disk, individual partitions, files, and folders to a variety of destinations.
Qiling Disk Master Server offers a range of backup options, including the ability to schedule backups with full backup, incremental backup, and differential backup. This feature allows you to create a backup plan that meets your specific needs, ensuring that your data is protected in the way that works best for you.
- By quantity: it's the easiest and simplest cleanup method, you just need to type the number of backup sets you want to keep, and then the old backups will be deleted afterward. One backup set consists of 1full plus 6 incremental backups.
- By time: it only keeps the latest 7 days of backups by default and you can choose to set days more than 7 or use weeks or months as the basis to delete backup images regularly.
- By daily/weekly/monthly: it's a hierarchical deletion method, and it will delete incremental backup at first and then full backups until the last full backup for every month is deleted.
Qiling Disk Master Server offers a range of backup options, including the ability to create a cloud backup. This feature allows you to store your backups in the cloud, ensuring that your data is protected and accessible from anywhere.
Please download the free trial and follow the tutorial below to have a try! This program applied to all Windows Server and PC editions (32-bit and 64-bit), like Windows Server 2003, 2008, 2012, 2016, 2019, 2022 (including R2), SBS 2003, 2008, 2011 and Windows 11, 10, 8.1, 8, 7, Vista, XP.
To ensure seamless backup and efficient disk space management for your Windows Server, we recommend using Qiling Disk Master Technician or TechPlus edition. These advanced tools are designed specifically for businesses, providing a comprehensive solution for managing backups and disk space.
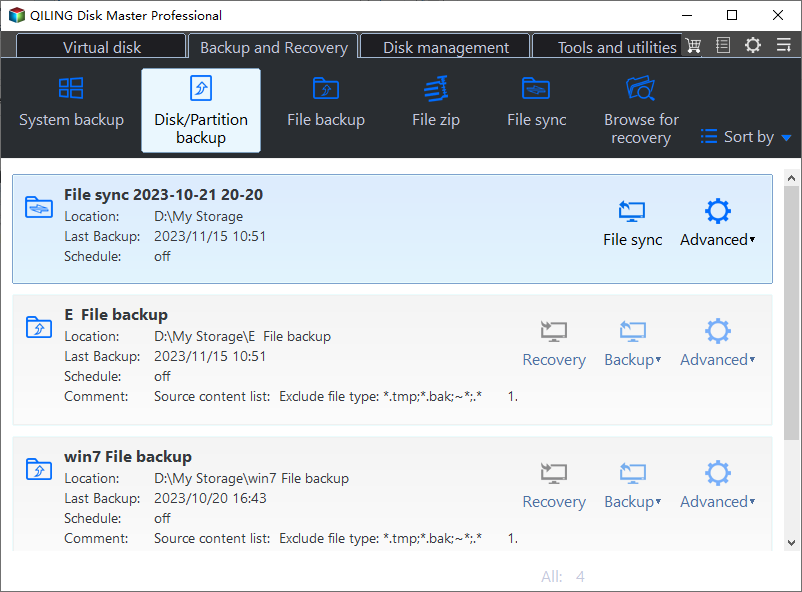
1. Open Qiling Disk Master Server, choose Backup, and then click Disk Backup.
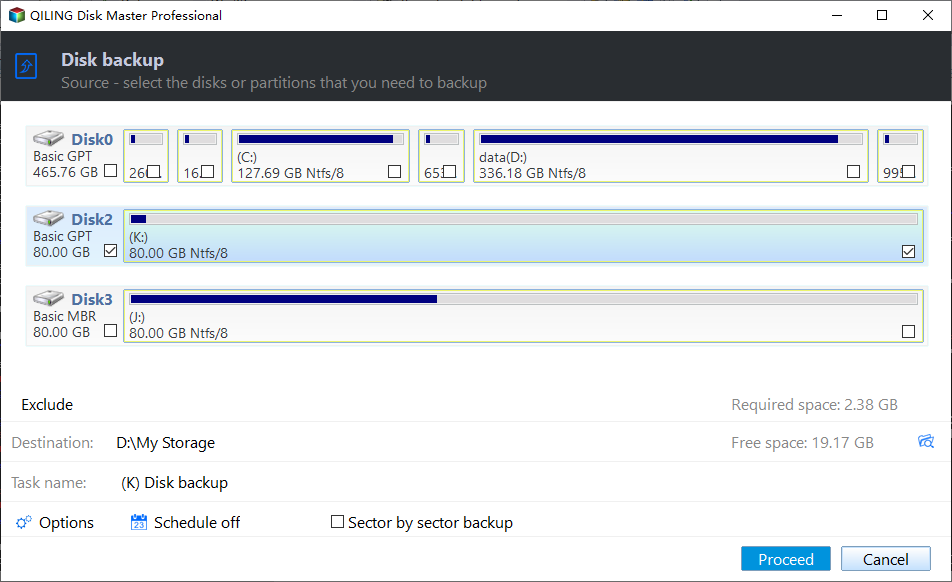
2. Input a proper Task Name. Click Disks to choose the system hard disk and then destination path below to save backup image.
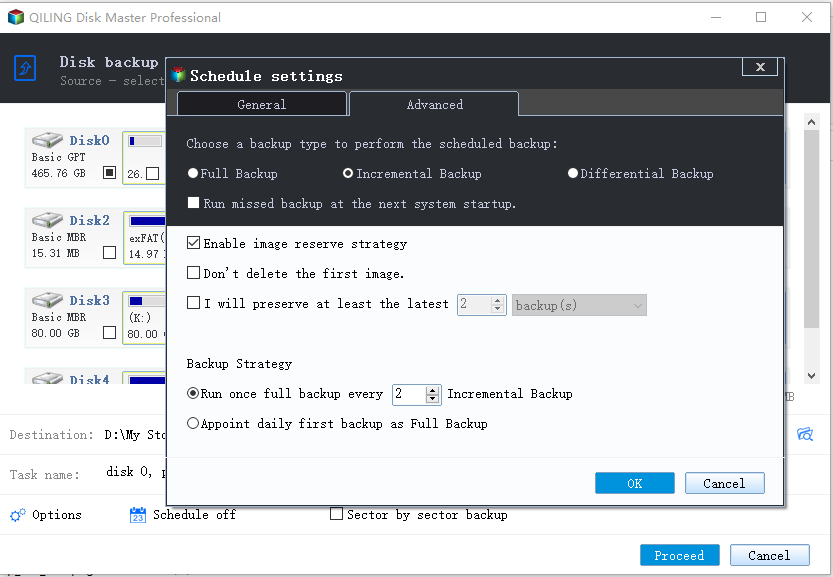
3. Click Schedule Backup and select Daily, Weekly, Monthly, Event triggers, USB plug in afterward under the Enable Schedule Backup tab. By default, it will enable Incremental Backup feature to backup only changed files.
4. Switch to Backup Scheme, you can change backup method if you prefer the differential backup method and then select backup cleanup by toggling on Enable Automatic Backup Cleanup, and choosing by quantity, by time, or by daily/weekly/monthly from the dropdown menu.
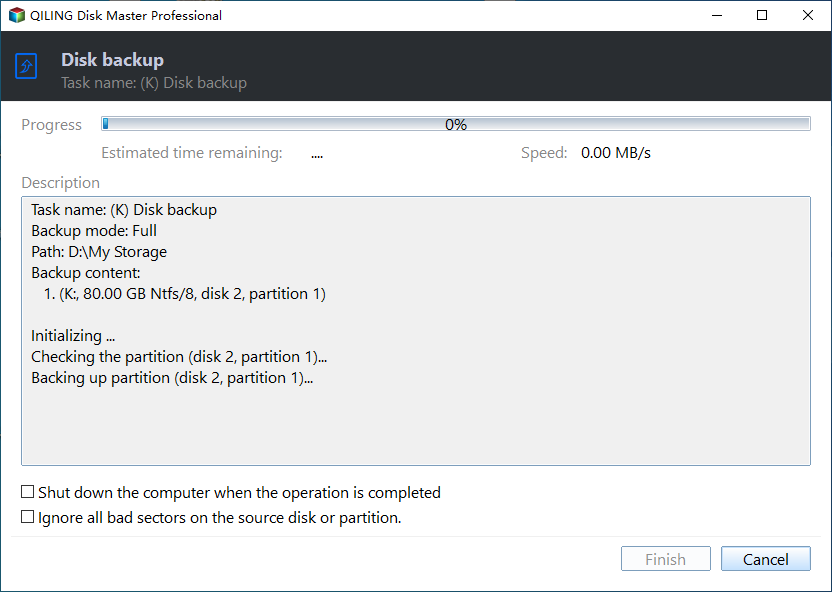
5. Confirm the backup task and press Proceed to create system image backup for Windows Server and it will delete old backups automatically based on the selected cleanup methods.
The Event Triggers backup include User logon, User logoff, System startup, System shutdown.
The USB plug in is a plug-and-pull backup method, so it will backup disk automatically when USB drive connected
You can also click Options to comment, compress, split, encrypt the backup image, and more.
Conclusion
If you are experiencing Windows Server Backup overwrite old backups, you can choose to make it delete the backup manually or try professional backup and restore software with automatic backup cleanup methods. Qiling Disk Master Server is a great choice and it provides you with more flexible choices.
As you plan for the future, it's essential to consider the possibility of needing to restore disk backups due to computer or hard disk failure. While restoring to a new hard drive is often the most straightforward option, you may also need to restore to a dissimilar hardware computer in the future. To prepare for this scenario, consider the following:
Related Articles
- Wbadmin Delete Backup for Windows Server 2016/2012/2008
Learn how to use "wbadmin delete backup" command to remove backups created by Windows Server Backup in Windows Server 2016/2012/2008 so as to save backup disk space. - The Solution to Windows Server Backup Disk Full - Qiling Disk Master
Why does Windows Server Backup disk full error occur and how to solve it? This article shows you how to free up backup disk space in Server 2008, 2012, 2016, etc. and offers a workaround to avoid the issue in the long term. - Windows 7 Backup and Restore Automatically Delete Old Backups
Annoyed about too many backups on your Windows 7 PC? This tutorial will introduce you how Qiling Disk Master work on Windows 7 backup and restore automatically delete old backups. - How to Delete Old Backups using Seagate Dashboard?
You can use Seagate Dashboard to delete old backups easily to free up more space for new backups. Or a professional way.