Windows Server Backup Retention Policy - Can It Be Specified?
How do I specify Windows Server backup retention period?
"Hi Folks, I've been testing Windows Server Backup recently and got asked a question today about retention policy which got me thinking. ie. can you limit the number of backups, for example I wish to keep a rolling 60 day backup window. The literature I've gone through so far basically says it will start deleting old ones when it starts running out of space. As far as I'm concerned this is not a good thing as your HDD will just fill up with old unrequired data. Is it possible to set this via command prompt or in the registry somewhere?"
As you said, Windows Server Backup only deletes old backup versions when there is not enough space for a new backup, and you cannot specify the number of backup versions to keep or delete by time (i.e.: daily/weekly/monthly), etc. In this case, you can choose to delete old backup manually with Wbadmin command or use third-party backup software to customize Windows Server backup retention policy.
About Windows Server Backup retention policy
Windows Server Backup's retention policy is a built-in feature that helps manage disk usage by deleting old backup versions when there's not enough space for the current backup. Here's how it works:
Windows Server Backup will create a shadow copy of the backup volume after a new backup is complete and saves the backup versions in local volume shadow copies if there is enough space. If not, Windows Server Backup will first determine if shrinking the diff area can make the new backup happen and then shrink or not. Also, if the diff area is about 1/8 of the backup volume size, the backup will not be created.
How to delete old backup manually using Wbadmin command line
When Windows Server Backup fails to delete old backups due to automatic disk usage management limitations, you can use the `WBadmin delete backup` command to manually manage backup storage. This command allows you to delete specific backup versions, delete all backups except for specified versions, or delete the oldest backup.
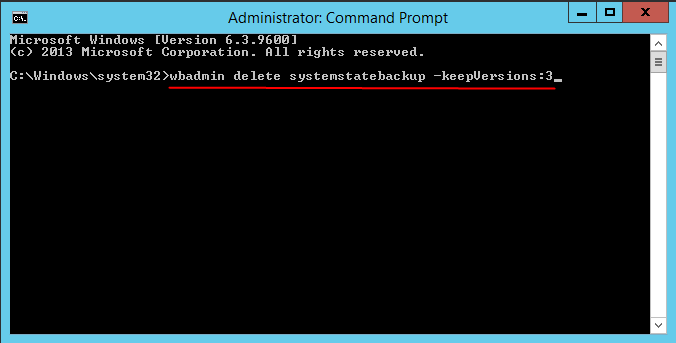
🧊 To delete system state backup, When Windows Server Backup fails to delete old backups due to automatic disk usage management limitations, you can use the `WBadmin delete systemstatebackup` command to manually manage backup storage. This command allows you to delete specific backup versions, delete all backups except for specified versions, or delete the oldest backup.
- wbadmin delete systemstatebackup -keepVersions:3
🧊 When Windows Server Backup fails to delete old backups due to automatic disk usage management limitations, you can use the `WBadmin delete backup` command to manually manage backup storage. This command allows you to delete specific backup versions, delete all backups except for specified versions, or delete the oldest backup.
- Wbadmin delete backup -version: 05/04/2015-18:25 -backupTarget: G: machine: Win-9814GD4FH95
✨ Notes:
-backupTarget: delete the system state backup stored on specific volume.
-machine: When backing up multiple computers to the same location using Windows Server Backup, it's essential to manage the storage effectively to avoid running out of space. One way to do this is by using the `WBadmin delete backup` command to delete old backups.
Flexible way to specify Windows Server backup retention policy (Best Practices)
To ensure efficient backup management and maintain optimal disk space usage, implementing a backup retention policy is crucial. Qiling Disk Master Server offers a comprehensive solution that combines backup and retention policy features, eliminating the need for manual deletion of old backups.
It allows you to customize the retention policy per your needs by providing 3 ways, namely, By quality, By time, By daily/weekly/monthly. Windows Server 2003, 2008, 2011, 2012, 2016, 2019, 2022 (including R2), SBS 2003, 2008, 2011, and Windows PC systems are supported.
- ★ In addition, there are useful backup features to make your task flexible and automatic:
- It allows you to backup system, files, partitions, and disks to any locations shown in File Explorer (including network location).
- It enables you to set daily/weekly/monthly scheduled backup.
- It provides you with 3 backup methods: full/incremental/differential backup. The last two methods are able to backup only changed data instead of everything.
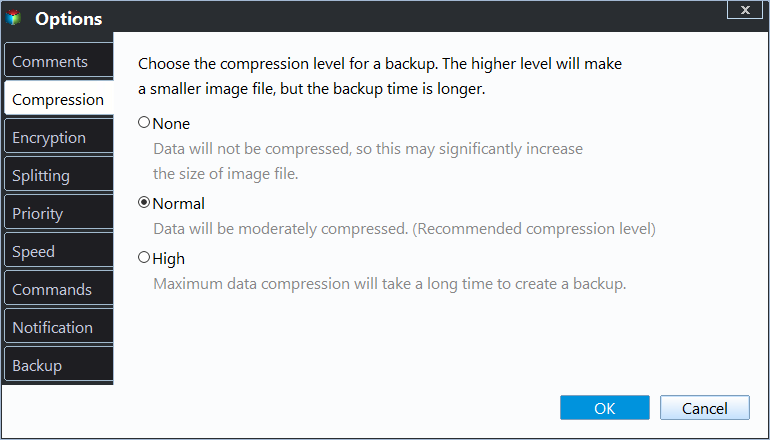
- Besides, you can set up an email notification to notify you whether the backup is complete or failed, compress backup image with normal or high compression level to save backup time and disk space, etc.
To explore the capabilities of Qiling Disk Master Server and experience the flexibility of customizing Windows Server backup retention periods, we invite you to download the 30-day free trial version. This trial period allows you to test the software without any commitment, giving you the freedom to evaluate its features and decide if it meets your needs.
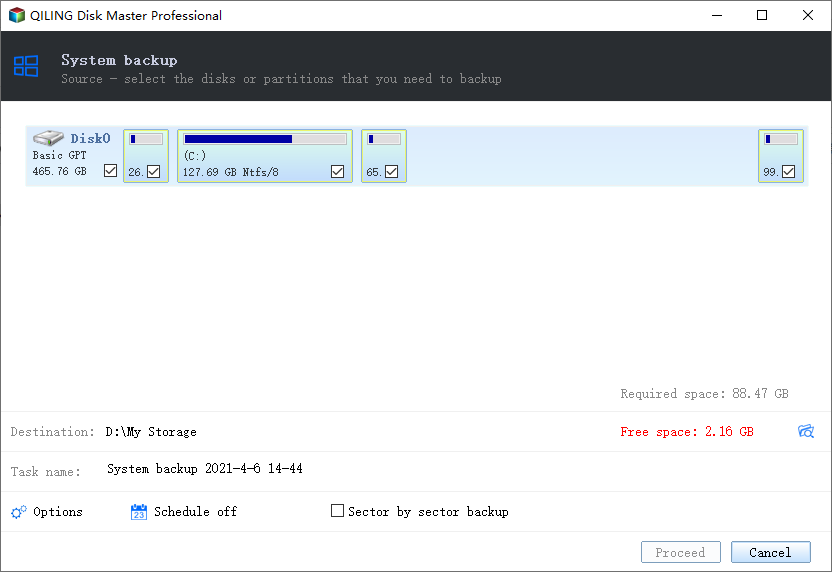
1. To experience the full capabilities of Qiling Disk Master, launch the server backup software and navigate to the Backup tab. Here, you'll discover four types of backup options, each designed to cater to specific needs. For this example, let's select System Backup.
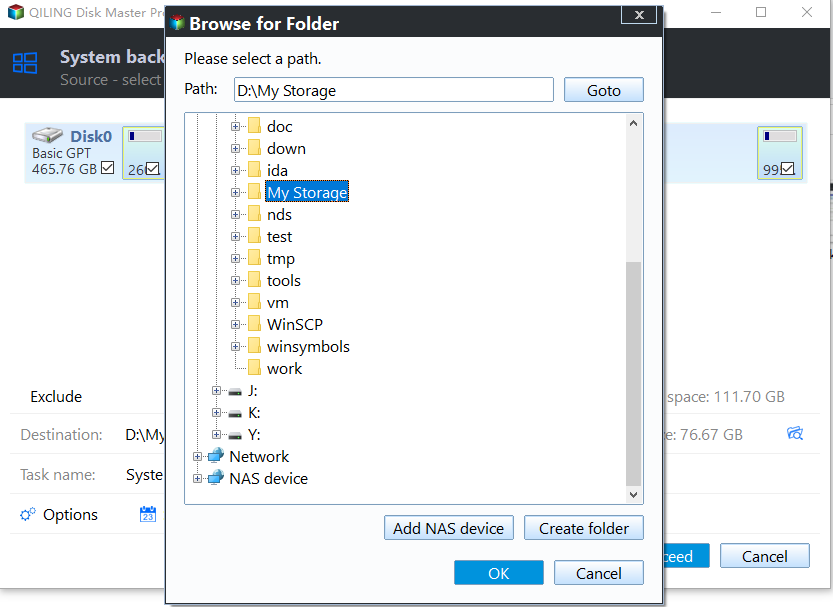
2. When using Qiling Disk Master to create system image backups, you'll need to select a location to store the backup files. This is a crucial step, as it determines where your backups will be saved.
3. To ensure that your backups run smoothly and efficiently, it's essential to configure the backup task properly. By doing so, you can avoid common issues like manual backup and insufficient disk space.
To ensure that your backups are comprehensive and secure, it's essential to configure the backup settings properly. By doing so, you can enhance the protection of your system and data.
To ensure that your backups are performed regularly and without manual intervention, it's essential to schedule them. By doing so, you can save time and effort, and also ensure that your backups are comprehensive and secure.
- Daily/Weekly/Monthly: Backing up your data is an essential task that ensures your important files and system configurations are safe in case of unexpected events, such as hardware failures, software crashes, or human errors. In Windows Server, you can automate this process by setting up a schedule backup, which will run continuously and automatically, safeguarding your data without requiring manual intervention.
- Event Triggers: To ensure that your data is protected at all times, you can configure Windows Server Backup to trigger backups based on specific events. This way, you can automate the backup process and ensure that your data is safe, even when you're not actively working on your system.
- Qiling Disk Master offers an intuitive and convenient way to back up your data using USB devices. Once you've plugged in the USB device, the software will automatically detect it and initiate the backup process. This seamless integration makes it easy to safeguard your important files and data.
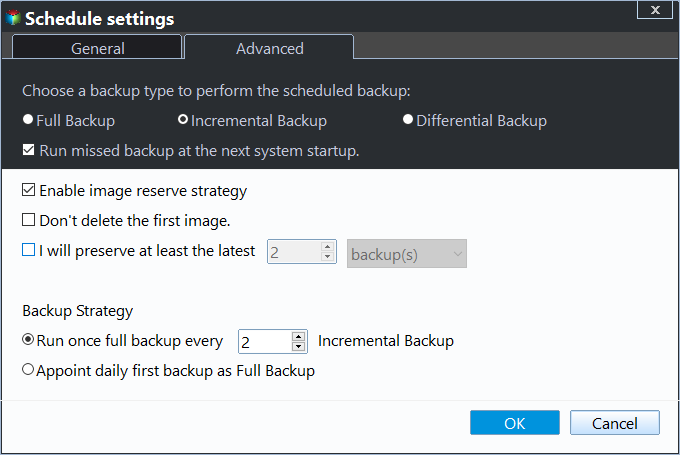
Then, click Scheme to set backup methods and backup retention policy. Select Incremental Backup or Differential Backup to backup only changed files under the Backup Methods. Next, turn on Enable Automatic Backup Cleanup and select the way to delete old backup image, By quality, By time, or By daily/weekly/monthly.
5. At last, click Proceed to make this backup and retention on schedule.
If your server is facing a serious situation, you can easily restore your server to an earlier state using Qiling Disk Master. This feature is particularly useful in case of a system failure or data corruption.
Conclusion
To configure a backup schedule and retention policy with Qiling Disk Master Server, follow these steps:
In addition to its backup and retention features, Qiling Disk Master Server can also be used as a file sync software to transfer files from one location to another. This can be useful for synchronizing files between different devices or locations, such as:
For organizations with a large number of PCs and servers, Qiling Disk Master Technician Plus is an ideal solution. This advanced version of Qiling Disk Master offers unlimited usage for all devices within the company, making it an excellent choice for protecting and managing IT infrastructure.
Related Articles
- [Solved] Windows Server 2008/2012/2016 Backup Disk Full
Why does Windows Server Backup disk full error occur and how to solve it? This article shows you how to free up backup disk space in Server 2008, 2012, 2016, etc. and offers a workaround to avoid the issue in the long term. - Windows Server Backup Schedule Less Than Once a Day
Learn the simple trick to use Windows Server Backup to schedule less than once a day backup job. Besides, an easier way to create multiple daily/weekly/monthly backup schedules is also included in this article. - Windows Server 2019/2016/2012 Hyper-V Backup Guide
You will learn how to create Windows Server incremental backup in Hyper -V virtual machines with WSB or a third-party tool, and then there will be no more data loss. - Windows Server Backup Not Deleting Old Backups - Fixed
Find Windows Server Backup not deleting old backups? Do not worry! You can find effective solutions to this problem in this article. You can also find another way to delete old backups automatically in Windows Server systems.